Exploring the often hidden and controversial world of religions banned around the globe, this blog post delves into the complex social, political, and cultural reasons behind these prohibitions. From spiritual practices to organized faiths, discover the ten religions that face legal restrictions and persecution in various countries. This post aims to shed light on these forbidden beliefs, offering a glimpse into the challenges faced by their followers.
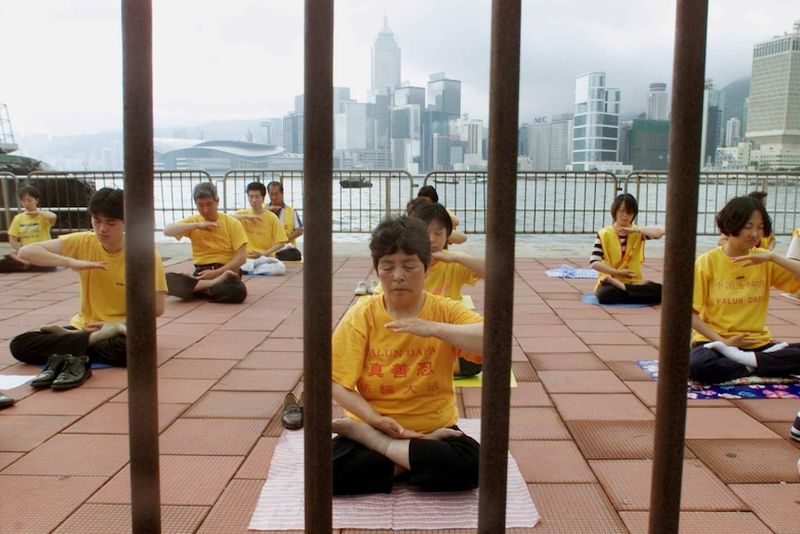
1. Falun Gong (China) ☯️🚫
In the late 1990s, China’s bustling cities witnessed tranquil Falun Gong gatherings in parks. Practitioners, dressed in yellow, performed slow, meditative exercises. However, in 1999, the Chinese government declared Falun Gong an illegal sect, launching a severe crackdown. The state media portrayed it as a threat to social stability. Accusations of forced organ harvesting from detained followers emerged, creating international outrage. Despite harsh measures, adherents continue their practice in secrecy, often facing imprisonment. It’s a tale of resilience and suffering, reflecting the lengths to which governments might go to suppress perceived threats.
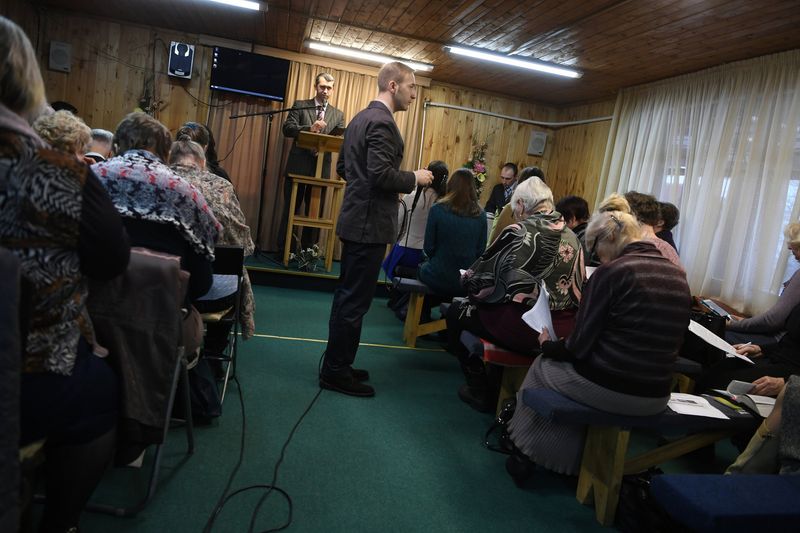
2. Jehovah’s Witnesses (Russia) 🕊️🇷🇺
Russia’s serene countryside holds a secret: Jehovah’s Witnesses quietly worshiping under the shadow of law. In 2017, Russia branded them as extremists, equating their peaceful worship with terrorism. This decision led to raids on homes, arrests, and confiscation of religious materials. Members faced harsh legal penalties, stigmatizing them in society. Despite these challenges, the community’s resolve remains unbroken, continuing their faith-driven activities discreetly. This situation questions the balance between state security and religious freedom, highlighting the complexities of modern governance. Jehovah’s Witnesses find their resilience tested in Russia’s legal landscape.
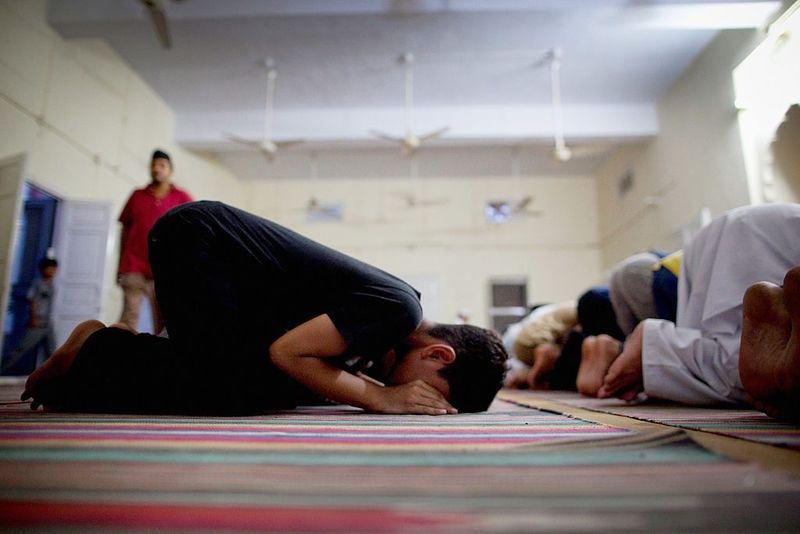
3. Ahmadiyya Islam (Pakistan) ☪️📛
In Pakistan, the Ahmadiyya community’s faith is both their strength and burden. Declared non-Muslims in the 1970s, Ahmadis face severe legal and social discrimination. Their mosques are often targeted, religious literature banned, and identification as Muslims is forbidden. Authorities mandate this exclusion, leading to widespread persecution. Despite these hardships, Ahmadis persist in their devotion, practicing under constant threat. Their resilience is a testament to unwavering faith amidst adversity. This situation underscores the clash between religious identity and state-imposed definitions, affecting millions of lives daily in Pakistan.
4. Baha’i Faith (Iran) 🌐❌
In Iran, the Baha’i community’s vibrant spirit is met with systematic suppression. Considered heretical by Iranian authorities, Baha’is face exclusion from education and employment. Their leaders are frequently imprisoned, and places of worship desecrated. Despite this, the Baha’i remain committed to their principles of unity and peace, conducting gatherings in secrecy. Their plight draws international attention, highlighting human rights concerns in Iran. The community’s story is one of perseverance against institutionalized oppression, showcasing their undying spirit and hope for eventual acceptance and freedom.
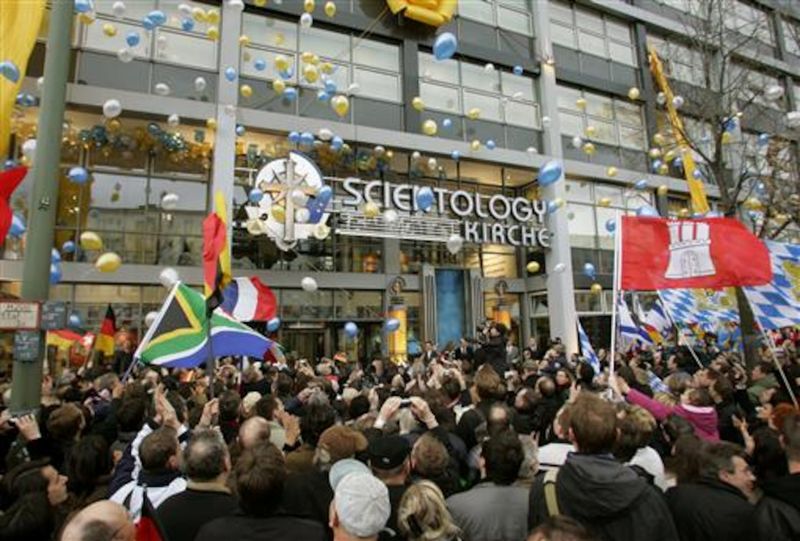
5. Scientology (Various Countries) ⚛️🕵️♂️
Scientology, with its enigmatic practices, faces scrutiny and restrictions worldwide. In countries like Germany, France, and Russia, it’s seen as a commercial enterprise rather than a faith. Governments impose regulations, citing concerns over financial exploitation and psychological manipulation. Followers encounter societal skepticism, and the church’s secrecy fuels debate. Despite legal challenges, Scientology’s adherents continue their quest for spiritual advancement. The religion’s journey is marked by controversy and determination, reflecting broader tensions between modern spirituality and state authority. Each country’s approach varies, but the core issues remain universally contentious.
6. Church of Almighty God (China) 🌩️🈲
Known as “Eastern Lightning,” the Church of Almighty God faces dire persecution in China. Labeled a dangerous cult, its followers are subject to arrests and harsh treatment. The government views them as a threat to social harmony, leading to intense crackdowns. Despite the risks, members continue their faith-driven mission, meeting secretly and spreading their beliefs. Their resolve symbolizes a struggle for religious expression in an authoritarian regime. This situation highlights the tension between state power and individual freedom, with adherents caught in a perilous cycle of faith and survival.
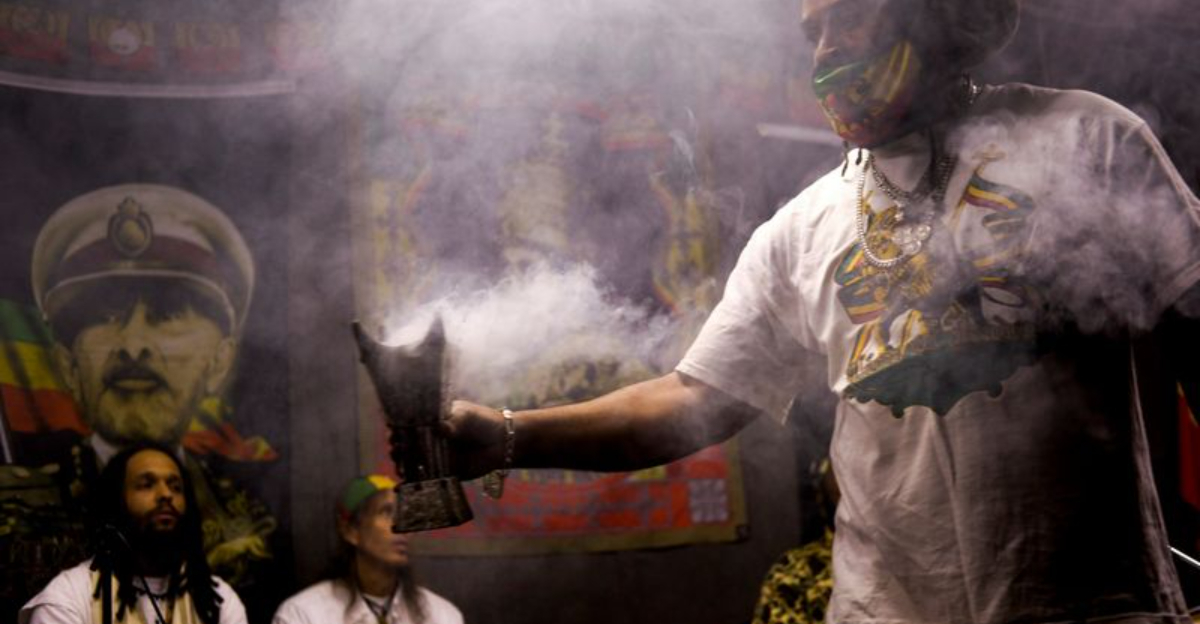
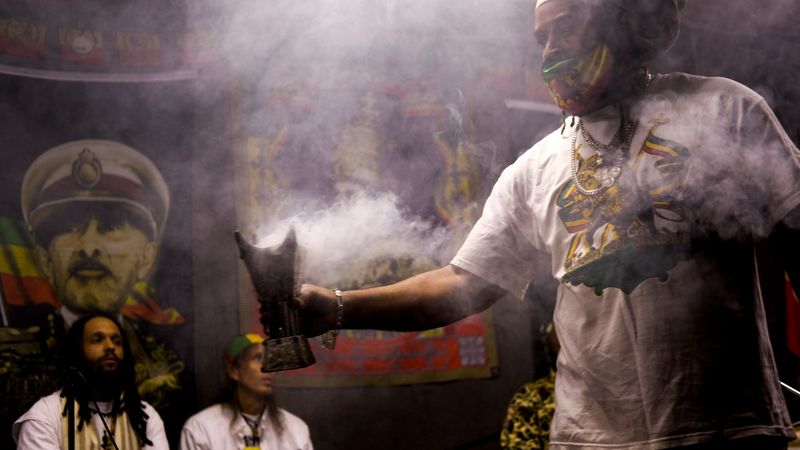
7. Rastafarianism (Various Countries) 🇯🇲✝️
Rastafarianism, with its roots in Jamaica, often faces legal hurdles due to ritual cannabis use. In many countries, laws criminalize this practice, clashing with Rastafari’s spiritual beliefs. Despite misconceptions and discrimination, Rastafarians maintain their cultural identity through music and art. Their community’s resilience is evident in their unwavering commitment to their faith and lifestyle. They navigate societal challenges with creativity and determination, advocating for understanding and acceptance. This narrative reflects broader themes of cultural diversity and the quest for religious tolerance in an often unyielding world.
8. Santería (Cuba) 🐓🔮
Santería, an Afro-Cuban religion, thrives amidst cultural vibrancy and official disapproval. Practiced underground, it blends African traditions with Catholicism. The Cuban government intermittently targets Santería, viewing it with suspicion. Despite this, practitioners uphold their rituals, preserving a rich cultural heritage. Their practices, often misunderstood, include animal sacrifices and divination, adding to the mystique. Santería’s story is one of cultural survival, where spirituality intersects with identity and resilience. The religion’s followers find solace and strength in their faith, navigating the complexities of modern Cuban society.
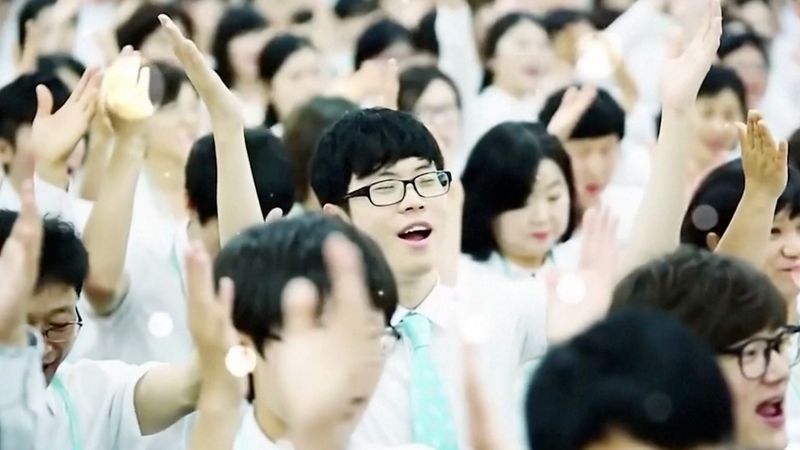
9. Shincheonji Church (South Korea) ✝️🇰🇷
The Shincheonji Church in South Korea, known for its secretive nature, faces periodic crackdowns. Allegations of public health violations, notably during the COVID-19 pandemic, intensified scrutiny. Critics accuse the church of deceptive practices, contributing to societal stigma. Despite this, followers remain dedicated, filling large congregations in pursuit of spiritual enlightenment. The church’s story highlights issues of transparency and societal trust in religious institutions. It reflects broader tensions between faith communities and public policy, challenging the delicate balance between freedom of religion and societal responsibility.
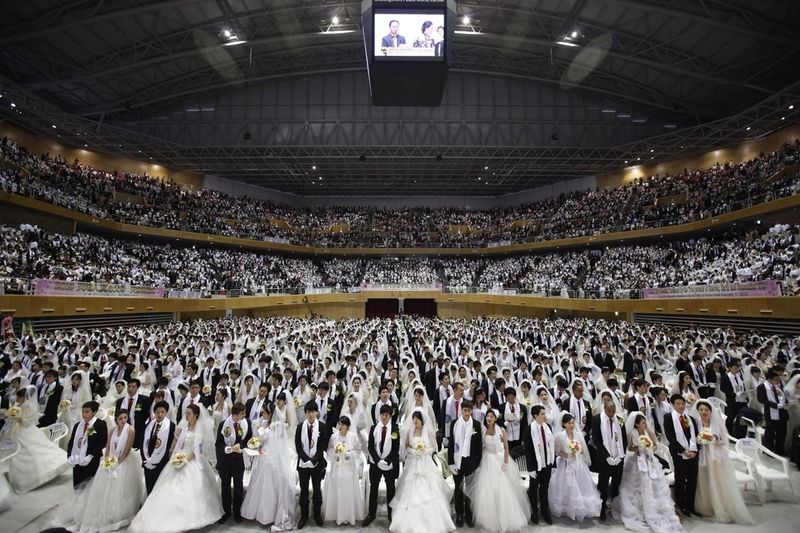
10. Unification Church (Various Countries) 🌍✝️
Known globally for its mass weddings, the Unification Church faces restrictions in several countries. Allegations of coercive recruitment and financial exploitation cast a shadow over its activities. Despite legal battles and societal skepticism, the church’s followers remain committed to their beliefs. Their practices, blending Christianity with unique teachings, continue to attract diverse adherents. The Unification Church’s narrative is one of persistence amidst controversy, illustrating the fine line between religious innovation and societal norms. Its journey reflects the challenges of maintaining ideological purity while navigating global perceptions.