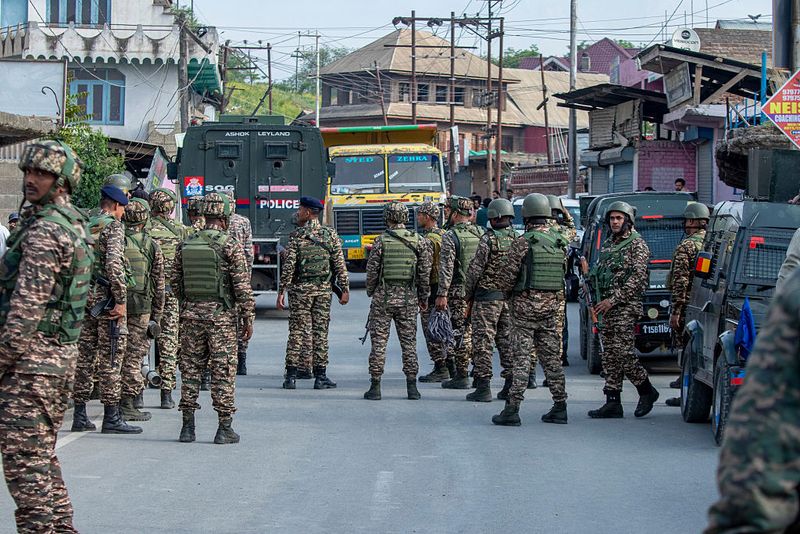Throughout history, humanity has witnessed fierce rivalries that have shaped civilizations, cultures, and borders. These rivalries, ranging from ancient times to the modern era, have been characterized by prolonged conflicts, ideological battles, and power struggles. Let’s delve into some of the most notable and intense rivalries in history.
1. Rome vs. Carthage (264–146 BCE)
The animosity between Rome and Carthage gave birth to the Punic Wars, three colossal conflicts over Mediterranean supremacy. Beginning in 264 BCE, these wars were fueled by each state’s desire for dominance.
The wars saw epic battles, including the legendary clash at Cannae. Hannibal’s strategic prowess and Rome’s resilience highlighted the hostilities. The conflict finally culminated in 146 BCE with Rome’s decisive victory and Carthage’s devastating destruction.
This rivalry left an indelible mark on history, showcasing the epic struggle between two of the ancient world’s superpowers.
2. England vs. France (1066–1815)
The rivalry between England and France spanned centuries, originating in 1066 with the Norman conquest. This long-standing enmity encompassed the Hundred Years’ War, a series of dynastic conflicts.
Battles such as Agincourt and Orleans became legendary, with iconic figures like Joan of Arc emerging. The Napoleonic Wars marked the rivalry’s climax, with Waterloo as a definitive turning point.
With the Congress of Vienna in 1815, peace was finally achieved, ushering in a new era of European geopolitics and ending one of history’s longest rivalries.
3. Ottomans vs. Habsburgs (1526–1791)
The Ottomans and Habsburgs clashed for Central European control, a rivalry ignited by territorial ambitions. The siege of Vienna in 1683 became a pivotal moment, symbolizing the high stakes of this struggle.
Both empires sought dominance, leading to numerous battles across the European continent. The Treaty of Sistova in 1791 marked the rivalry’s end, resulting in shifting power dynamics.
This enduring conflict highlighted the contrasting cultures and religious ideologies that shaped European history for centuries.
4. Persia vs. Greece (499–449 BCE & Beyond)
The Greco-Persian Wars were rooted in Persia’s expansion into Greek territories. Iconic battles like Marathon and Thermopylae showcased the fierce resistance of the Greek city-states.
This clash of civilizations continued beyond the wars, influencing Rome’s later conflicts with Persia’s successors, the Parthians and Sassanids. The cultural and military legacies of these wars were profound.
Greece’s triumphs against Persia became legendary, symbolizing the triumph of freedom over tyranny and forming a significant part of Western historical narratives.
5. Byzantine Empire vs. Abbasid Caliphate (7th–11th Centuries)
The Byzantine-Abbasid rivalry was a religious and territorial struggle, reflecting the broader Christian-Muslim conflict. The sieges of Constantinople epitomized this epic clash of empires.
Both powers sought to expand their influence, leading to centuries of warfare and cultural exchanges. The rivalry defined the medieval geopolitics of the Near East.
Despite eventual decline, it left a legacy of art, science, and diplomacy that influenced subsequent civilizations.
6. China vs. Nomadic Steppe Empires (3rd Century BCE–18th Century CE)
China’s confrontations with nomadic empires like the Xiongnu and Mongols were pivotal in shaping its history. These conflicts spurred the construction of the Great Wall as a defense against invasions.
The Han, Tang, and Ming dynasties each faced formidable threats from the steppe. The Mongol dominance, under Genghis Khan, profoundly impacted China’s political landscape.
Despite periods of peace, these rivalries emphasized the perpetual tension between settled societies and nomadic invaders.
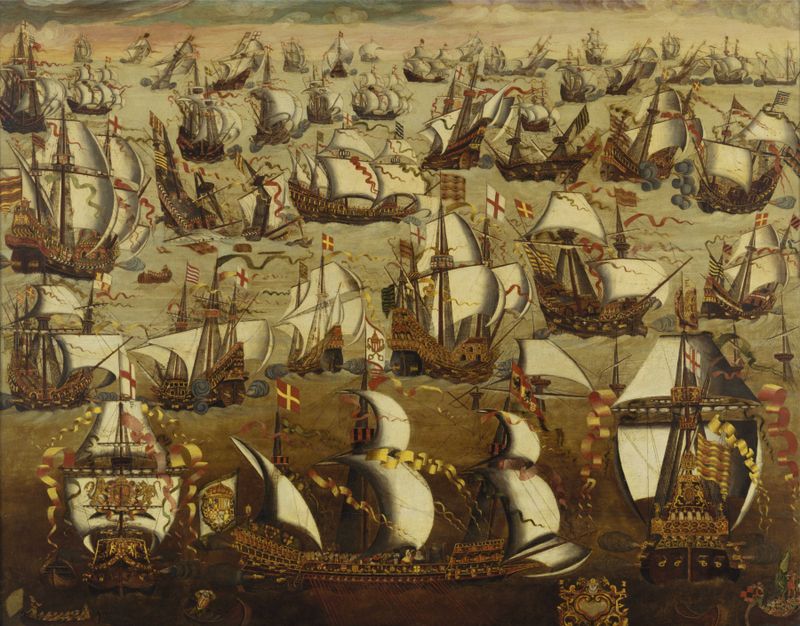
7. Spain vs. England (16th–18th Centuries)
The rivalry between Spain and England was rooted in religious and colonial ambitions. The Protestant Reformation intensified tensions, culminating in the defeat of the Spanish Armada in 1588.
The two powers clashed in the New World and Europe, competing for dominance. The War of Spanish Succession added further complexity to their relationship.
This rivalry reshaped global trade and politics, leaving a lasting legacy on the colonial landscapes.
8. Venice vs. Genoa (13th–15th Centuries)
Venice and Genoa, two maritime powerhouses, vied for control over Mediterranean trade. Their competitive spirit led to four major wars, each seeking to establish dominance.
The War of Chioggia, a defining conflict, ended with Venice’s victory, securing its place as a dominant maritime force. Despite fierce battles, mutual cultural exchanges thrived.
This rivalry exemplified the intense commercial competition of the era, shaping the economic history of Renaissance Italy.
9. France vs. Habsburgs (1494–1756)
The rivalry between France and the Habsburgs spanned numerous wars, including the Italian Wars and the Thirty Years’ War. Both powers sought European hegemony through strategic alliances and battles.
The War of the Spanish Succession marked a turning point, with France emerging as a dominant force. The Diplomatic Revolution of 1756 eventually ended hostilities.
This long-standing conflict was instrumental in shaping the political and military landscape of Europe.
10. Russia vs. Poland-Lithuania (16th–18th Centuries)
The fierce rivalry between Russia and Poland-Lithuania was marked by relentless battles over territorial control. The struggle for Eastern European dominance defined their relationship.
Numerous wars and shifting alliances characterized the period, culminating in the partitions of Poland in the late 18th century. This event dramatically altered the region’s political landscape.
The rivalry left a legacy of cultural and historical influences, sparking continued interest in the region’s complex past.
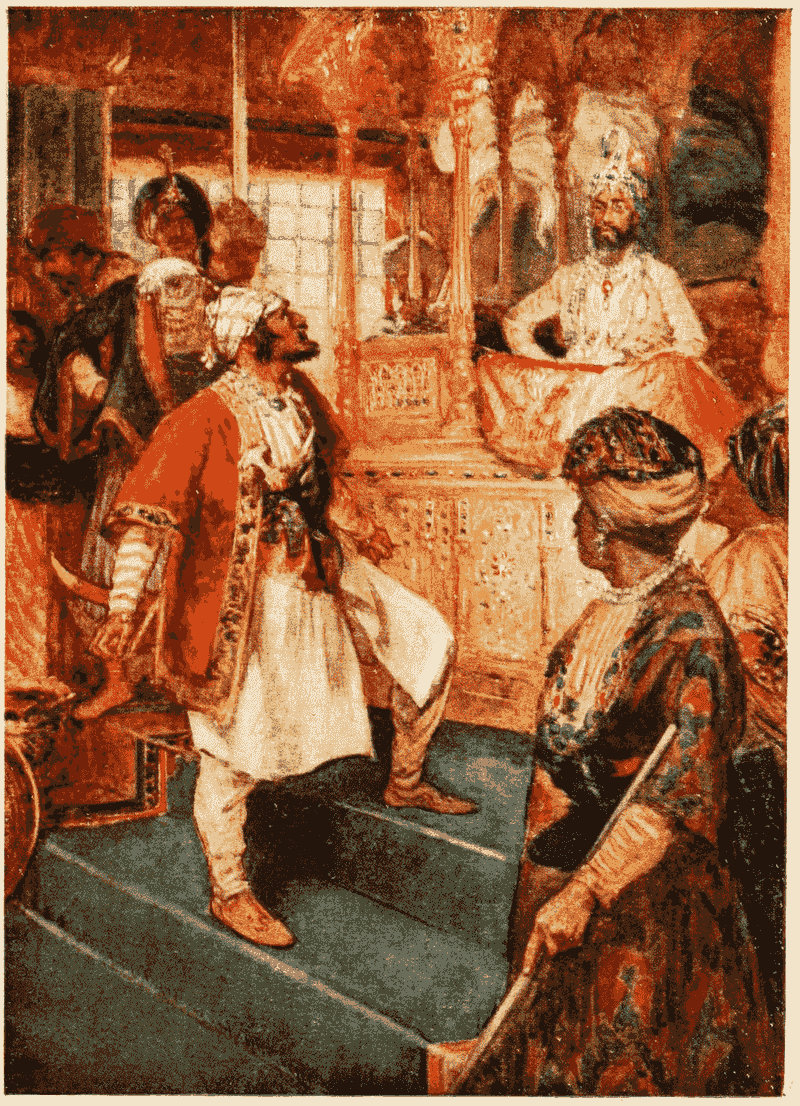
11. Mughals vs. Marathas (17th–18th Centuries)
The struggle for dominance in India saw the Mughals and Marathas engage in prolonged warfare. The Marathas’ resilience and guerrilla tactics challenged Mughal supremacy.
Battles across the Indian subcontinent tested both empires, leading to shifting power dynamics. The eventual decline of the Mughals paved the way for British colonization.
This intense rivalry played a crucial role in shaping India’s historical and cultural landscape.
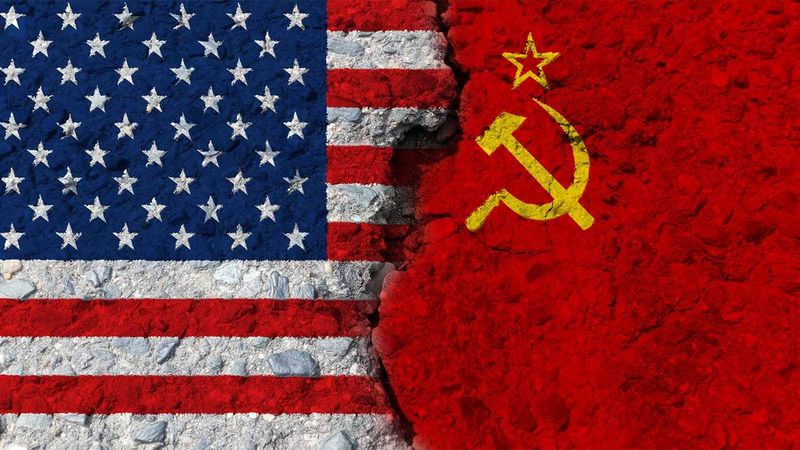
12. USA vs. USSR (1947–1991)
The Cold War between the USA and USSR was a global ideological and geopolitical rivalry. The arms race and space race marked this tense period, with the threat of nuclear conflict looming.
Proxy wars in Korea, Vietnam, and Afghanistan intensified the conflict. The Soviet Union’s collapse in 1991 symbolized the end of this era.
This rivalry reshaped global politics, leading to a world profoundly impacted by its legacy.
13. Shiites vs. Sunnis (632 CE–Present)
The schism between Shiites and Sunnis began over succession disputes following Prophet Muhammad’s death. This religious-political split continues to influence global conflicts.
The Iran-Iraq War and other regional disputes highlight the enduring nature of this rivalry. It reflects deeper theological differences and political power struggles.
Despite efforts for reconciliation, this division remains a driving force in Middle Eastern geopolitics.
14. India vs. Pakistan (1947–Present)
Born from the 1947 Partition, the India-Pakistan rivalry centers on Kashmir. Three major wars and numerous skirmishes have defined their turbulent relationship.
Nuclear capabilities and diplomatic tensions add complexity to their interactions. Efforts for peace remain ongoing, yet challenges persist.
This rivalry highlights broader regional dynamics, with global implications for security and diplomacy.