The 1980s brought us more than just big hair and neon colors. This decade revolutionized medicine with groundbreaking innovations that continue saving lives today. From life-saving vaccines to revolutionary diagnostic tools, these medical milestones transformed healthcare forever.
1. MRI Scans Transform Medical Imaging
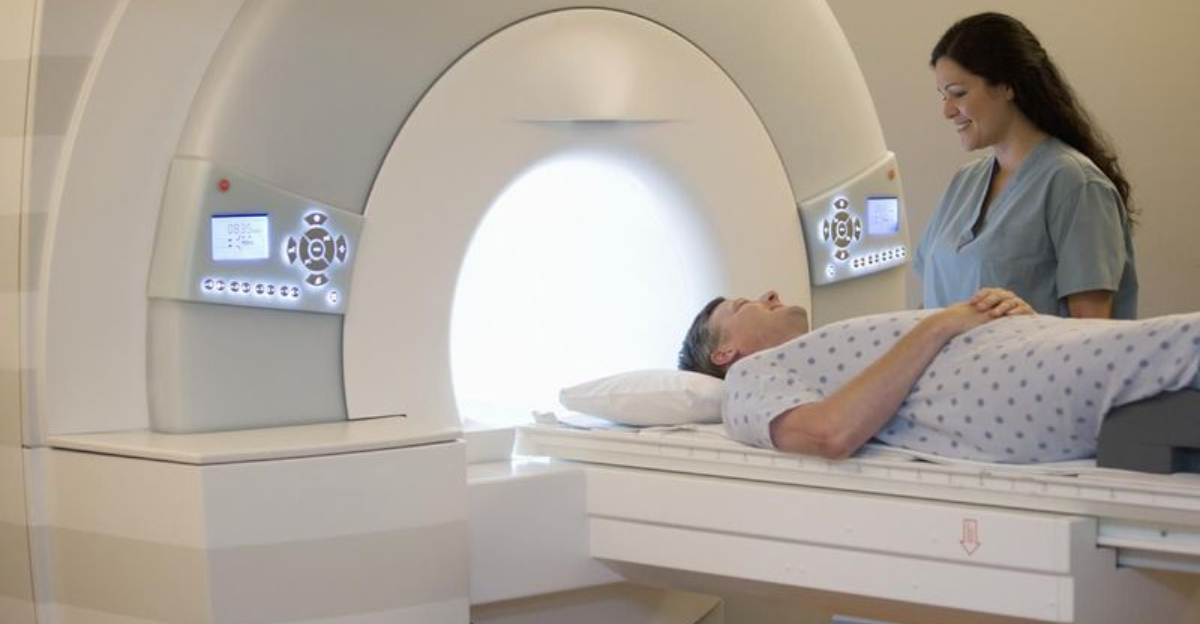
Picture doctors seeing inside your body without a single cut or harmful radiation. Magnetic Resonance Imaging made this possible in 1980, changing medicine forever.
MRI machines use powerful magnets and radio waves to create incredibly detailed pictures of soft tissues, organs, and bones. Doctors can spot brain tumors, torn muscles, and spinal problems with amazing clarity.
Before MRIs, many conditions required risky exploratory surgery just to diagnose. Now millions of patients get accurate diagnoses quickly and safely. From detecting strokes to finding hidden injuries, MRI technology has become essential in hospitals worldwide, helping doctors make better treatment decisions.
2. Statins Revolutionize Heart Health
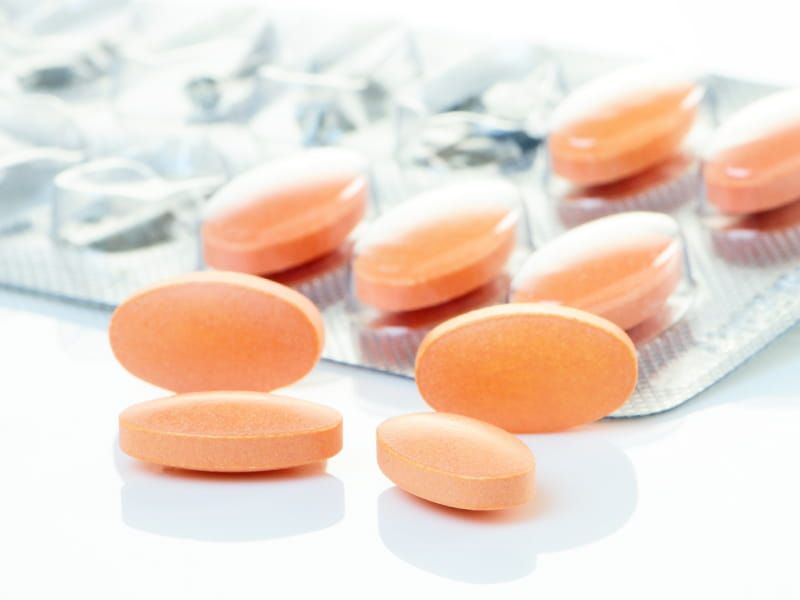
High cholesterol used to be a death sentence for many people. Then came statins in 1987, small pills that pack a powerful punch against heart disease.
Lovastatin became the first widely available statin drug, helping millions lower their cholesterol levels naturally. These medications block an enzyme that produces cholesterol in the liver, dramatically reducing heart attack risks.
Studies showed statins could cut heart disease deaths by up to 40%. Today, over 200 million people worldwide take these life-saving medications. What started as a breakthrough in the ’80s continues protecting hearts everywhere, proving that sometimes the smallest innovations make the biggest difference.
3. Laser Cataract Surgery Restores Vision
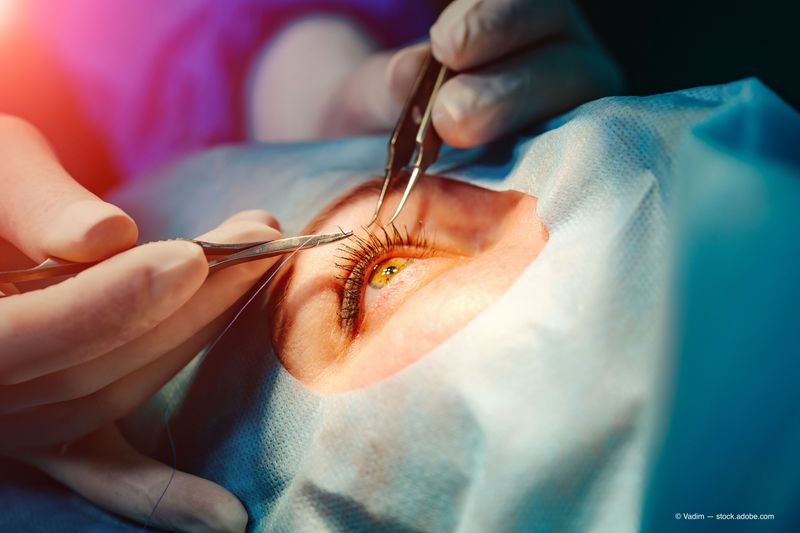
Imagine losing your sight slowly, then getting it back in minutes. Laser cataract surgery made this miracle routine by 1988.
Traditional cataract surgery required large incisions and long recovery times. Laser technology changed everything, using precise light beams to remove cloudy lenses with incredible accuracy. The procedure became faster, safer, and more effective.
Millions of elderly patients regained clear vision thanks to this innovation. Recovery time dropped from weeks to days, and complications became rare. Today’s cataract surgery traces back to these ’80s laser pioneers who refused to accept that aging meant losing sight forever.
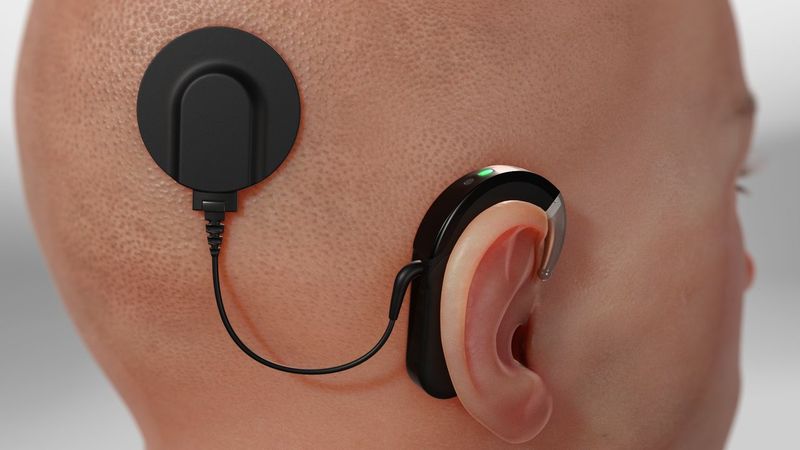
4. Cochlear Implants Give Sound to Silence
For deaf individuals, the world existed in complete silence until cochlear implants arrived in the early 1980s. These remarkable devices bypass damaged hearing parts entirely.
Unlike hearing aids that amplify sound, cochlear implants directly stimulate the auditory nerve. A small computer processes sounds and sends electrical signals straight to the brain. The FDA approved the first devices in 1985.
Thousands of deaf children and adults experienced sound for the first time. Many learned to speak clearly and enjoy music, conversations, and everyday sounds. Modern cochlear implants evolved from these early ’80s models, continuing to connect people to the hearing world.
5. AZT Provides First AIDS Treatment Hope
When AIDS appeared in the early ’80s, patients faced certain death. Everything changed in 1987 when AZT became the first approved HIV treatment.
Azidothymidine works by blocking HIV from copying itself inside cells. While not a cure, AZT significantly slowed disease progression and extended lives. Clinical trials showed remarkable improvements in patient survival rates.
AZT gave hope to millions facing this devastating disease. It paved the way for modern HIV treatments that now allow people to live normal lifespans. From a death sentence to a manageable condition, AZT started the medical revolution that continues saving lives today.
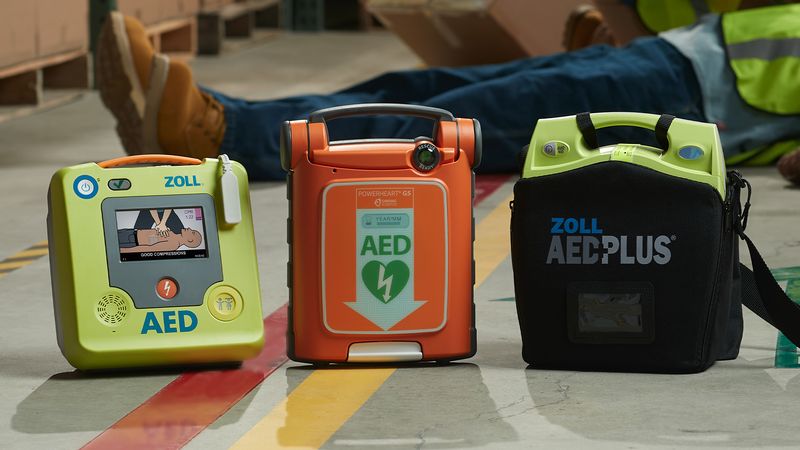
6. Automated External Defibrillators Save Hearts
Cardiac arrest strikes without warning, and minutes matter. Automated External Defibrillators, introduced in 1985, put life-saving power in everyone’s hands.
AEDs analyze heart rhythms automatically and deliver electric shocks when needed. Simple voice commands guide users through the process, making it possible for anyone to help. No medical training required.
Studies showed 70% survival rates when AEDs were used within minutes of cardiac arrest. These portable devices now hang in schools, offices, and public spaces worldwide. What once required paramedics became something a teenager could do, multiplying the chances of survival dramatically.
7. Hepatitis B Vaccine Prevents Liver Disease
Hepatitis B infected millions worldwide, causing liver cancer and cirrhosis. The breakthrough vaccine developed between 1981-1986 changed everything.
Scientists created the first genetically engineered vaccine using advanced biotechnology. Unlike traditional vaccines, this one used synthetic materials to trigger immunity safely. The innovation marked a new era in vaccine development.
Vaccination programs dramatically reduced hepatitis B infections globally. Countries that implemented widespread vaccination saw liver cancer rates plummet. This vaccine saved countless lives and proved that genetic engineering could create safer, more effective medical treatments. The technology developed here laid groundwork for many modern vaccines.
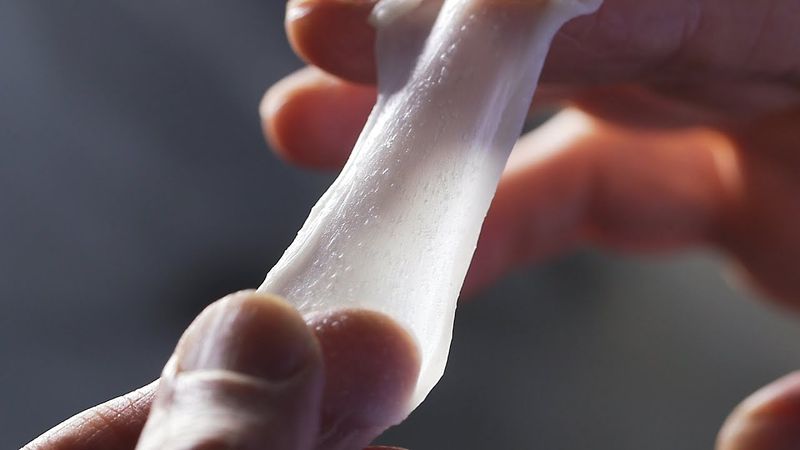
8. Artificial Skin Heals Burn Victims
Severe burns once meant certain death or permanent disfigurement. Artificial skin, developed in 1981, offered burn victims new hope for healing.
Scientists created living tissue using both synthetic materials and real cells. This artificial skin could be placed over burns, promoting natural healing while preventing deadly infections. The innovation revolutionized burn treatment worldwide.
Burn units reported dramatically improved survival rates and better healing outcomes. Patients who would have died from extensive burns began recovering completely. The technology also advanced reconstructive surgery, helping accident victims and wounded soldiers. From laboratory experiment to life-saving treatment, artificial skin proved that science could literally rebuild human bodies.
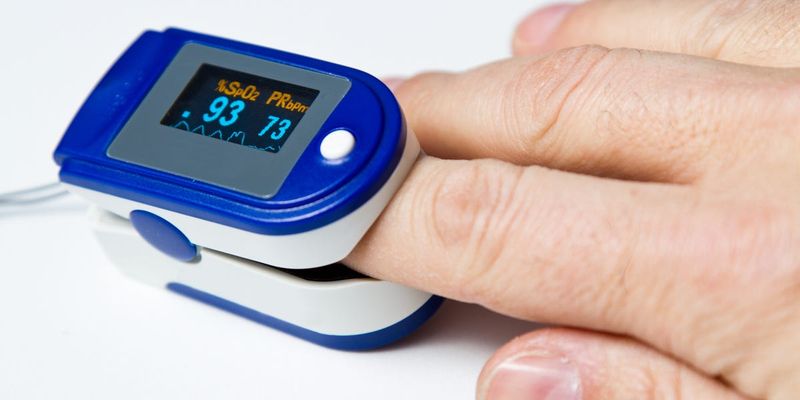
9. Pulse Oximeters Monitor Oxygen Levels
Before 1981, measuring blood oxygen required painful needle sticks and laboratory tests. Pulse oximeters changed monitoring forever with a simple clip-on device.
These small devices shine light through fingertips to measure oxygen levels instantly. Red and infrared light absorption reveals exactly how much oxygen blood carries. The technology became standard in every hospital room.
Doctors could now spot breathing problems immediately, preventing countless emergencies. Surgery became safer when anesthesiologists could monitor patients continuously. The simple finger clip saved lives by catching oxygen drops before they became dangerous. Modern medicine depends on this ’80s innovation every single day.
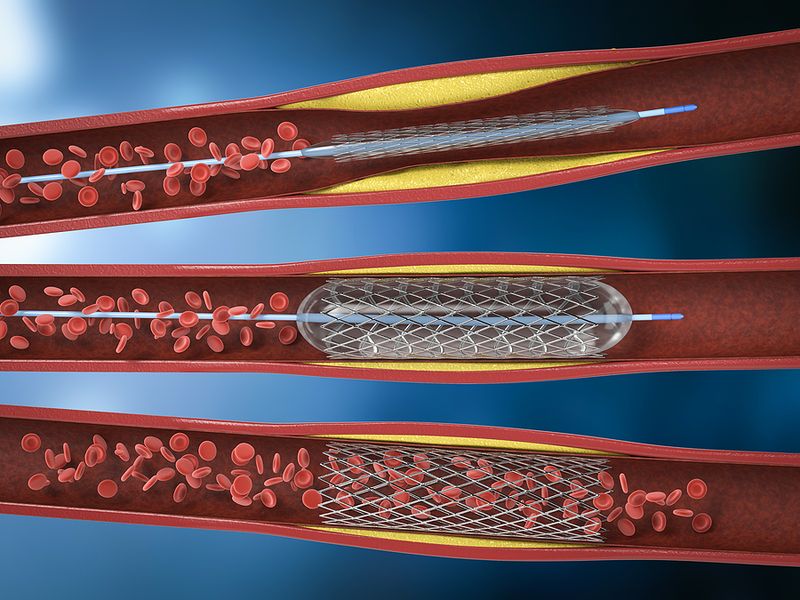
10. Angioplasty Balloon Catheters Open Blocked Arteries
Heart attacks from blocked arteries required major bypass surgery until balloon catheters arrived in the 1980s. Andreas Gruentzig pioneered this minimally invasive miracle.
Doctors thread tiny balloons through blood vessels to blocked arteries. Once positioned, the balloon inflates, crushing plaque against artery walls and restoring blood flow. The entire procedure takes hours, not days.
Patients avoided risky open-heart surgery and recovered quickly. Heart attack victims could get treated immediately, preventing permanent heart damage. Millions of people with heart disease got their lives back through this simple yet brilliant innovation. The balloon catheter proved that sometimes the best solutions are elegantly simple.
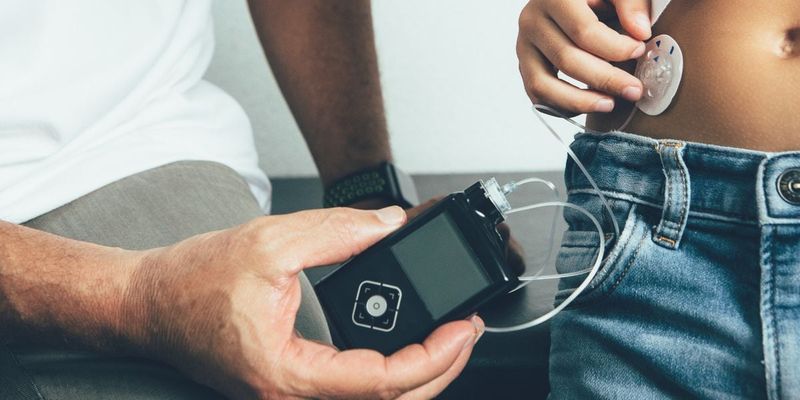
11. Insulin Pumps Control Diabetes Better
Diabetics once faced daily insulin injections and unpredictable blood sugar swings. Early insulin pumps in the 1980s offered continuous, precise control.
These small devices deliver insulin automatically throughout the day, mimicking how healthy pancreases work. Patients program pumps to match their eating and activity patterns. Blood sugar levels became much more stable.
Diabetic complications like kidney failure and blindness decreased significantly. Children with diabetes could live more normal lives without constant injections. The technology evolved from bulky early models to today’s smartphone-sized devices. What started as experimental treatment became essential care for millions of diabetics worldwide.
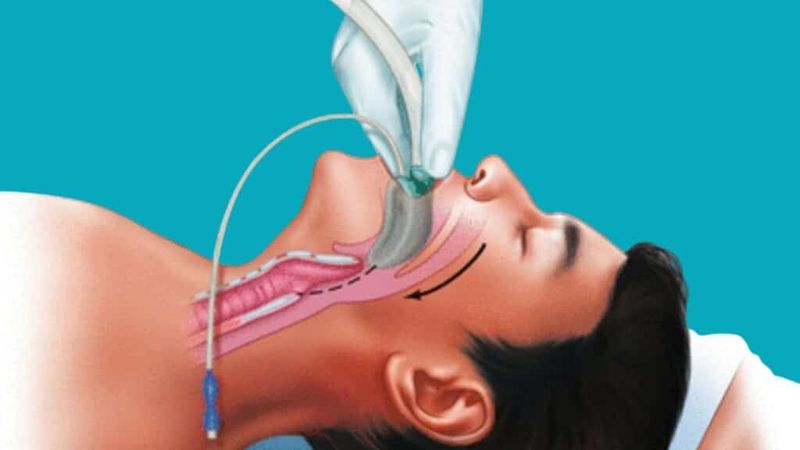
12. Laryngeal Mask Airway Improves Surgery Safety
Anesthesiologist Archie Brain noticed that breathing tubes during surgery sometimes caused serious throat injuries. His 1981 invention solved this dangerous problem.
The Laryngeal Mask Airway fits over the voice box instead of going down the throat. It provides secure breathing during operations while causing less trauma. Recovery became more comfortable for patients.
Surgical complications dropped dramatically when hospitals adopted LMAs. Patients experienced less throat pain and faster recovery times. Emergency responders also found LMAs easier to use than traditional breathing tubes. This simple design change made surgery safer for millions of patients worldwide, proving that small improvements can have huge impacts.
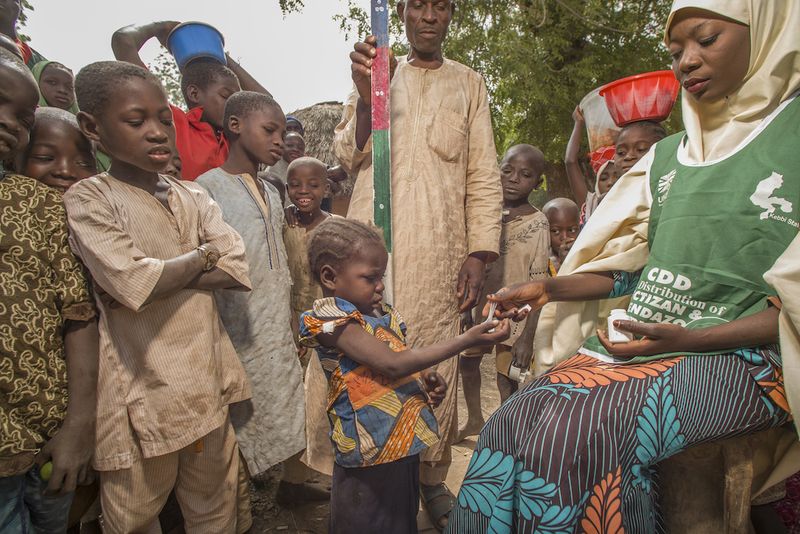
13. Mectizan Eliminates River Blindness
River blindness plagued millions in Africa, caused by parasitic worms spread by black flies. Mectizan, introduced in 1987, offered the first real hope for elimination.
Merck developed this medication and launched an unprecedented donation program, giving it away free to affected communities. Single annual doses kill the parasites effectively. Mass treatment programs began across Africa.
Entire regions saw river blindness nearly disappear within decades. Children grew up without fear of this devastating disease. The Mectizan Donation Program became a model for global health initiatives. From pharmaceutical laboratory to African villages, this medication proved that medical breakthroughs could reach the world’s poorest people.
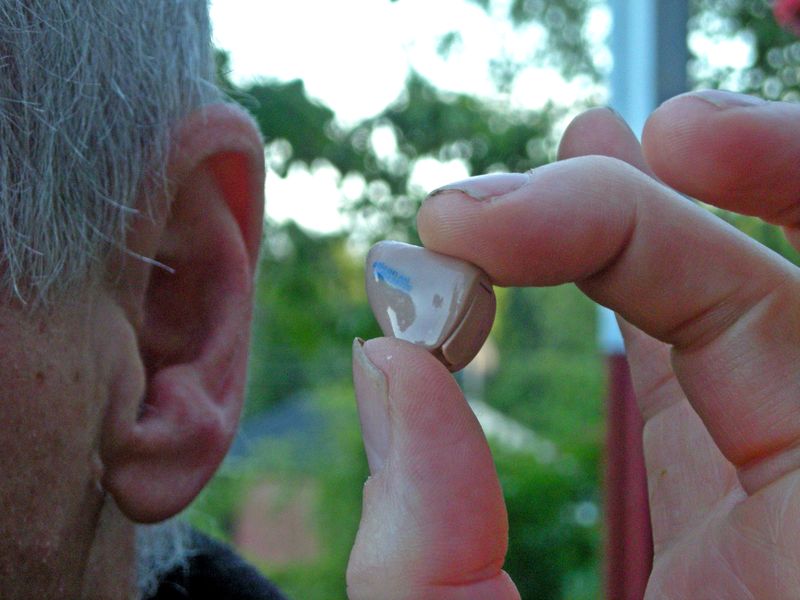
14. Digital Hearing Aids Enhance Sound Quality
Hearing aids once produced tinny, unclear sound that barely helped users. The Nicolet Phoenix, launched in 1987, brought digital clarity to hearing assistance.
Digital processors could separate speech from background noise, adjust volume automatically, and reduce feedback squealing. Sound quality improved dramatically compared to analog devices. Users could finally hear conversations clearly in noisy environments.
Millions of hearing-impaired people reconnected with their families and communities. The technology advanced rapidly, leading to today’s nearly invisible devices. What started as bulky experimental equipment became sophisticated computers for the ear. Digital hearing aids proved that better technology truly improves quality of life.
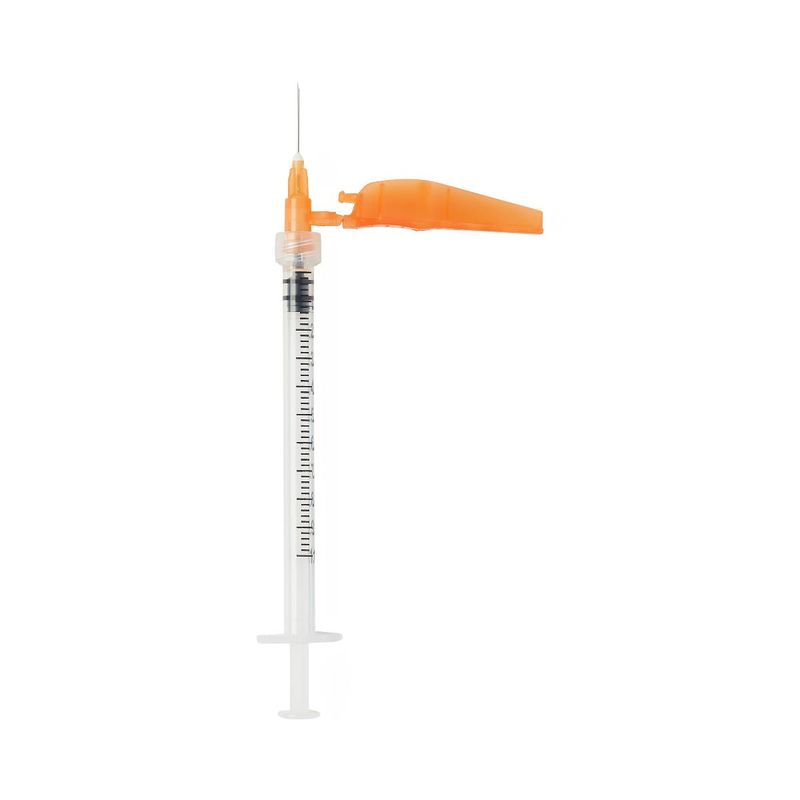
15. Safety Needles Protect Healthcare Workers
Needlestick injuries plagued healthcare workers, especially during the AIDS crisis. Becton Dickinson’s Safety-Lok syringe, introduced in 1988, provided crucial protection.
The innovative design automatically covers the needle after use, preventing accidental sticks. Healthcare workers no longer feared HIV and hepatitis exposure from used needles. Hospital infection rates dropped immediately.
Millions of doctors, nurses, and technicians stayed safer at work. The design became standard worldwide, protecting healthcare systems globally. During disease outbreaks, safety needles proved essential for maintaining medical care. This simple safety improvement saved countless healthcare careers and lives, showing that protecting medical workers ultimately protects everyone.