The Vietnam War was not just a military conflict but a profound societal event that reshaped American culture and politics.
From transforming media reportage to influencing music and art, its effects have permeated every layer of society.
This blog post explores 15 significant ways in which the Vietnam War has left an indelible mark on the United States.
1. Eroded Trust in Government
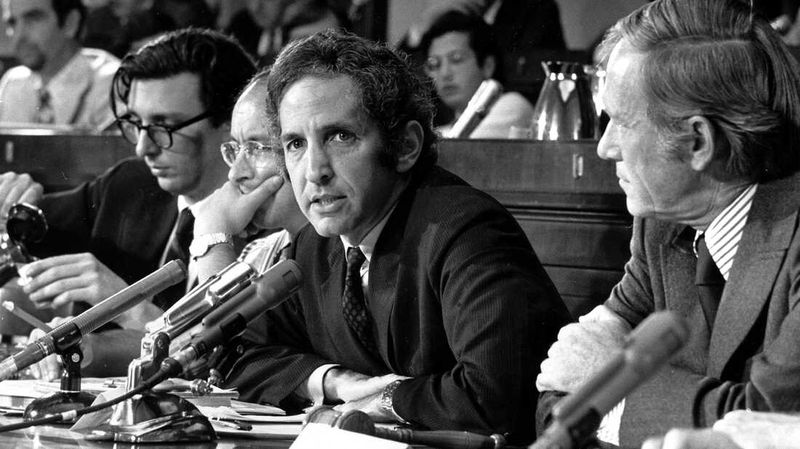
The Vietnam War era was a time of revelations that shook the faith of the American public. The release of the Pentagon Papers exposed a web of government deception, revealing the stark contrast between official statements and reality.
In living rooms across the nation, trust in political leadership crumbled, creating a sense of skepticism that persists today. This erosion of trust ignited a demand for transparency and accountability in government practices.
With each unfolding story, the public’s perception of governance was permanently altered, fostering a culture of questioning and vigilance.
2. Rise of the Anti-War Movement
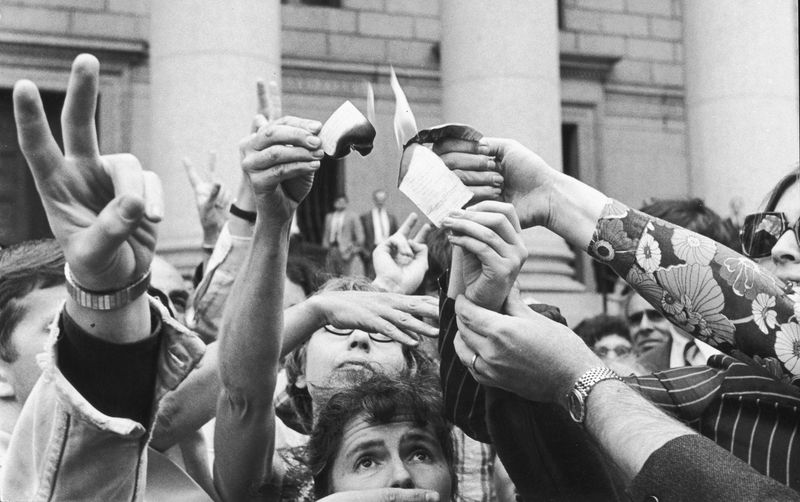
A vibrant force for change, the anti-war movement was a tapestry of voices united against the Vietnam War. Massive protests, like the Moratorium to End the War in Vietnam, became iconic symbols of citizen engagement.
Marches filled with passionate chants and signs calling for peace highlighted the power of collective activism. This movement redefined how Americans could influence policy and express dissent.
Lessons learned in these protests continue to shape strategies for social activism, demonstrating the enduring impact of peaceful resistance.
3. Transformation of Media Reporting
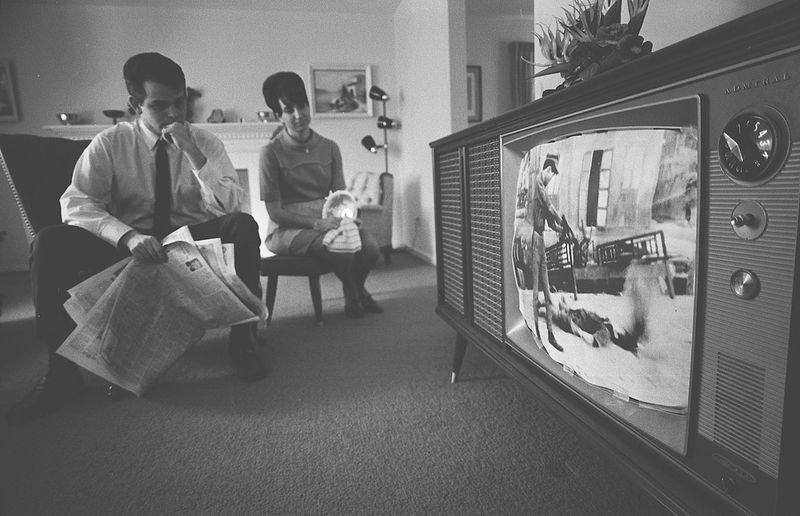
The Vietnam War marked a turning point in how conflicts were reported. For the first time, live television broadcasts brought the war’s brutal realities into American homes, changing public perceptions.
Families watched as scenes of battle unfolded, fostering a more informed and often critical view of war. This era of journalism encouraged a deeper understanding of the human cost of conflict.
As viewers witnessed the horrors firsthand, media reporting evolved, paving the way for more transparent coverage in future wars.
4. Impact on the Draft and Volunteerism
The Vietnam War era saw rising opposition to the draft, a symbol of disenfranchisement for many young Americans. Refusing to comply with the Selective Service System, individuals burned draft cards as an act of defiance.
This widespread resistance highlighted the need for change, eventually leading to the establishment of an all-volunteer military force. The shift reflected a growing belief in personal choice over compulsory service.
This transformation in military recruitment practices forever altered the relationship between citizens and military service.
5. Altered Foreign Policy Doctrine (“Vietnam Syndrome”)
The high human and political costs of the Vietnam War left a lasting caution in U.S. foreign policy, often referred to as the “Vietnam Syndrome.” This reluctance to engage militarily abroad emerged as a protective stance against repeating past mistakes.
Policy decisions became more measured, considering the long-term implications and public opinion. This doctrine influenced American involvement in international conflicts for decades.
The lessons learned emphasized the importance of strategic deliberation, underscoring a shift towards diplomacy and restraint.
6. Catalyst for Political Realignment
The Vietnam War intensified political polarization, redefining party platforms and voter alliances. The 1968 election became a pivotal moment, revealing deep societal divisions and sparking shifts in political strategies.
As parties reassessed their positions, new alliances formed, reshaping the American political map. This realignment fostered a more dynamic political discourse.
The war’s influence is evident in today’s political landscape, where echoes of these shifts continue to resonate in modern electoral strategies.
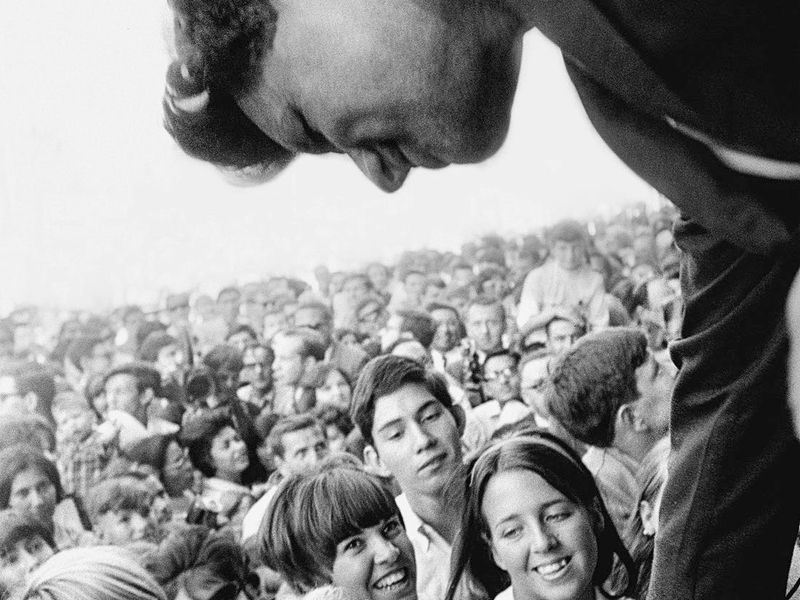
7. Empowerment of the Counterculture
The Vietnam War era saw the rise of a counterculture that challenged traditional values and norms. Young people, driven by anti-war sentiment, embraced lifestyles and ideologies that promoted peace and freedom.
This movement fostered a spirit of rebellion, encouraging individuals to question authority and explore new ways of living. It was a time of artistic expression and social experimentation.
The counterculture’s legacy is evident in the continued celebration of diversity and self-expression in today’s society.
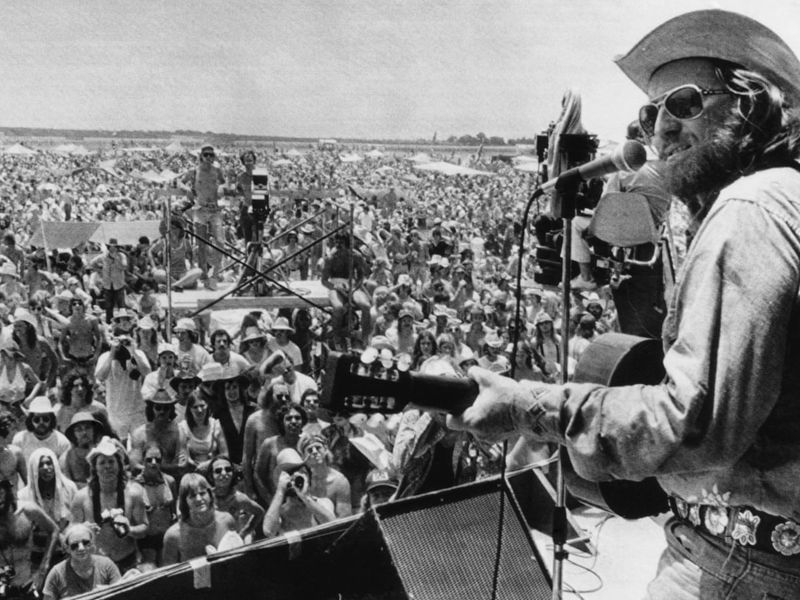
8. Influence on Music and the Arts
Music and the arts were profoundly shaped by the Vietnam War, serving as both a form of protest and a means of healing. Songs like “Fortunate Son” captured the era’s disillusionment, echoing the public’s frustration.
Art and music became powerful tools for expression, offering solace and solidarity to those opposed to the war. These creative outlets helped articulate the emotional landscape of the time.
The impact of this artistic movement is still felt, influencing how art addresses social and political issues today.
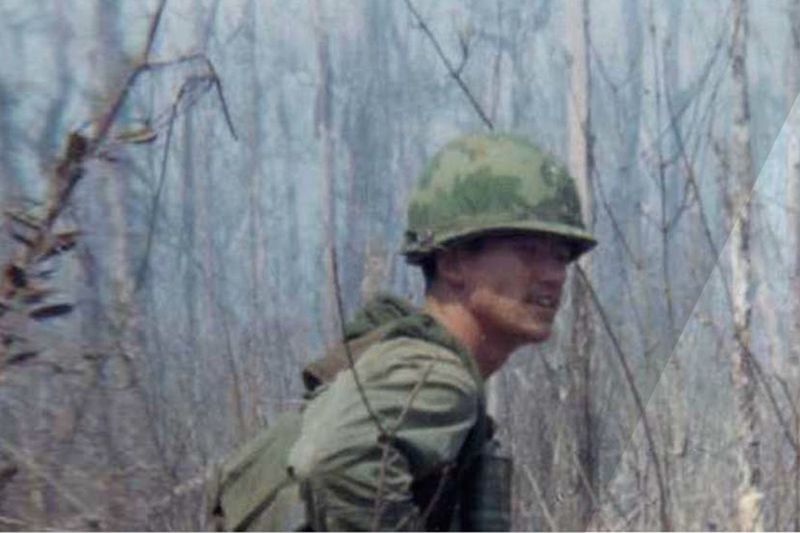
9. Veteran Advocacy and Mental Health Awareness
Returning from war, many Vietnam veterans faced challenges that highlighted the need for better mental health care. The struggles with PTSD and reintegration underscored the importance of addressing mental well-being.
Veteran advocacy groups emerged, pushing for reforms in how veterans were treated and supported. Public awareness campaigns helped shift perceptions, emphasizing compassion and understanding.
These efforts led to improvements in veteran care and sparked a broader dialogue about mental health, setting the stage for future advancements.
10. Advancement in Military Strategy and Technology
The Vietnam War forced a reevaluation of military strategies and technologies. The challenges faced prompted the development of new tactics, intelligence methods, and technological advancements.
This period of innovation laid the groundwork for future military operations, emphasizing the importance of adaptability and precision. Lessons learned influenced how wars were fought, leading to more strategic approaches.
The war’s impact is evident in today’s modern military practices, where technology and strategy continue to evolve.
11. Economic and Fiscal Impacts
The economic toll of the Vietnam War was felt across the nation. The enormous costs contributed to budget deficits and inflation, affecting families struggling to make ends meet.
As the government reallocated resources, domestic economic policies shifted to address these challenges. Welfare programs and public services were impacted, prompting debates about fiscal responsibility.
The war’s financial legacy influenced economic strategies and highlighted the need for balancing defense spending with domestic priorities.
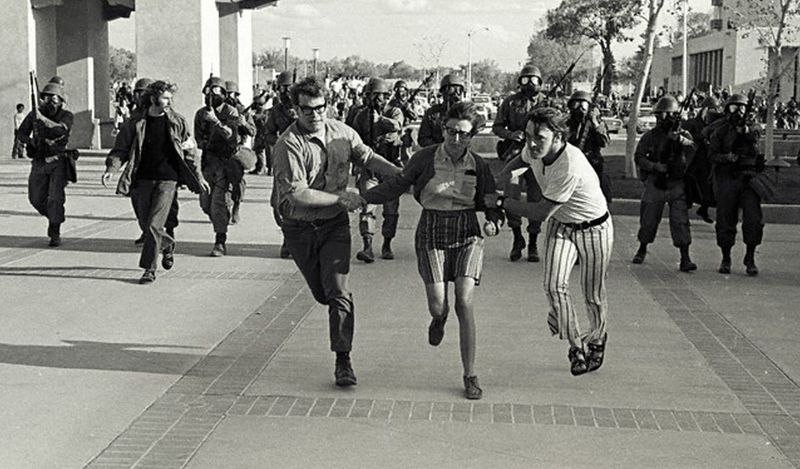
12. Expansion of University Campuses as Political Arenas
University campuses became hotbeds for political discourse during the Vietnam War. Students engaged in rallies and debates, transforming educational institutions into centers of activism.
This period of heightened political engagement fostered a culture of critical thinking and debate, encouraging young people to challenge the status quo. Academic environments evolved to accommodate this new dynamic.
The legacy of this era is seen in the continued role of universities as arenas for social and political action.
13. Intersection with the Civil Rights Movement
The Vietnam War intersected with the Civil Rights Movement, highlighting systemic inequalities. Disparities in draft selection and racial injustices became focal points for activists.
This convergence strengthened both movements, fostering solidarity and shared goals. The fight for civil rights was intertwined with the anti-war effort, amplifying voices for change.
These struggles paved the way for significant social reforms, leaving a lasting impact on the fabric of American society.
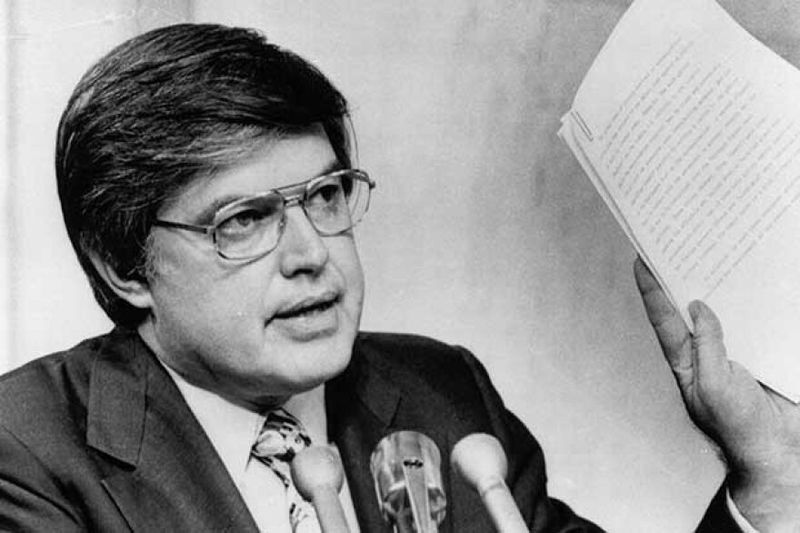
14. Rise in Government Oversight and Reform
Scandals and secretive practices during the Vietnam War era led to increased government oversight. Congressional investigations, like the Church Committee hearings, sought to uncover hidden activities.
These inquiries fostered greater transparency and accountability, leading to reforms in intelligence and military operations. Public demand for oversight grew, reflecting a desire for ethical governance.
The legacy of this scrutiny is evident in today’s political environment, where oversight remains a critical component of democracy.
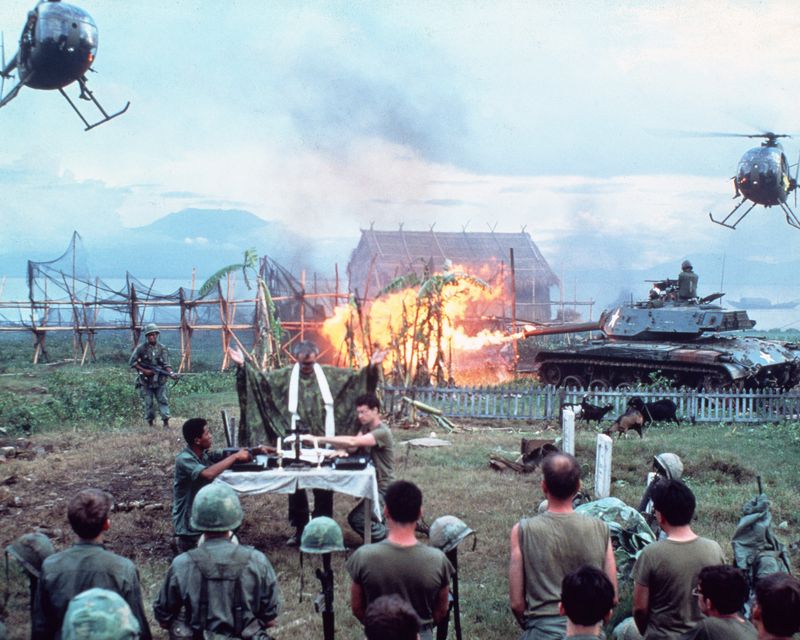
15. Evolution of American War Cinema
The Vietnam War profoundly influenced American cinema, inspiring a wave of films that explored its complexities and human cost. Movies like “Apocalypse Now” offered gritty depictions of war’s realities.
These films reshaped public narratives, prompting viewers to reflect on the impact of conflict. The portrayal of soldiers and their struggles brought a nuanced understanding to audiences.
This cinematic evolution continues to influence how war stories are told, enriching the cultural tapestry with powerful visual narratives.