The Enola Gay, a Boeing B-29 Superfortress bomber, remains one of the most iconic aircraft in history. Known for its pivotal role during World War II, this aircraft symbolizes a momentous shift in warfare. This blog post explores 19 captivating aspects of the Enola Gay, from its design and missions to its ongoing legacy. We delve into the stories behind the aircraft, its crew, and the broader implications of its missions. Join us as we uncover the fascinating history and legacy of this legendary bomber.
1. First Flight
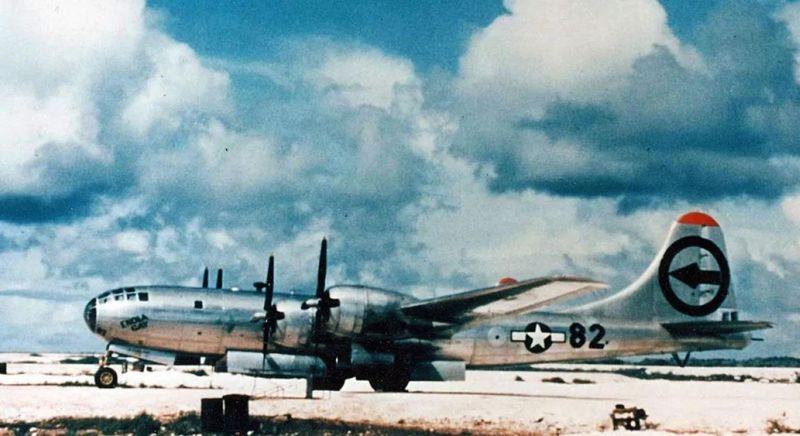
The Enola Gay’s maiden flight was on September 21, 1944, from the airfield located at the Boeing plant in Renton, Washington. The sleek aircraft, with its iconic silver exterior, made its way into the skies, marking the beginning of a journey that would etch its name into the annals of history. The aircraft’s revolutionary design, featuring pressurized cabins and remote-controlled guns, was a marvel of engineering at the time. This first flight set the stage for its future missions, and the excitement and anticipation surrounding it were palpable.
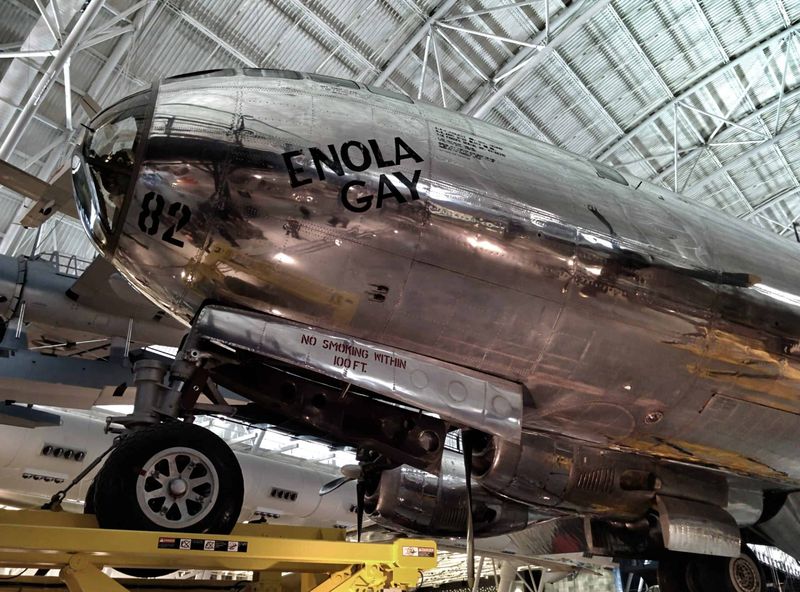
2. Naming the Enola Gay
Colonel Paul Tibbets, the pilot chosen for the historic mission, named the aircraft after his mother, Enola Gay Tibbets. This act of naming served not only as a personal tribute but also as a humanizing touch to a machine that would participate in a world-altering event. The name has since become synonymous with the mission it undertook. Tibbets’ choice reflects the intimate connections pilots often had with their aircraft, which transcended mere machinery. His decision was rooted in a desire to honor his family amid the harsh realities of war.
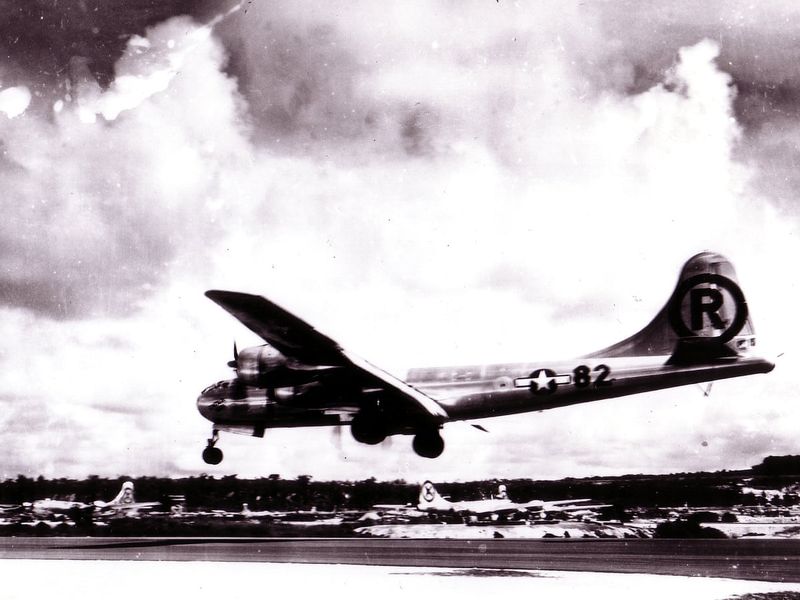
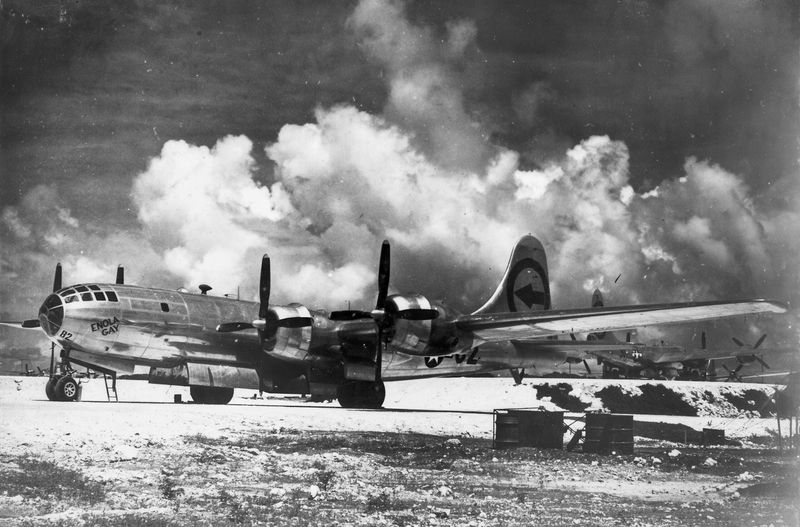
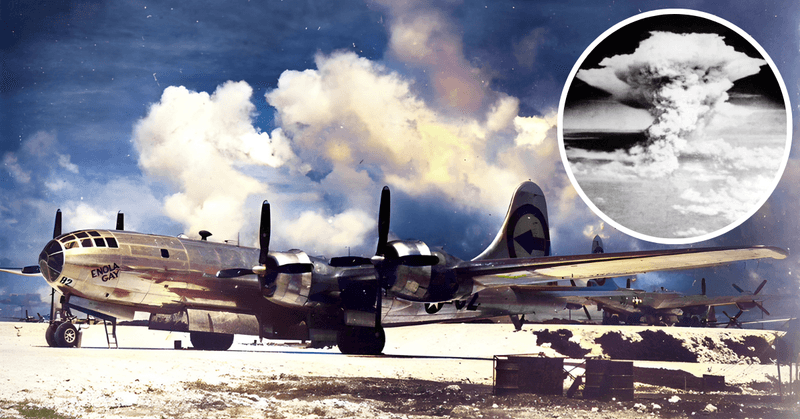
3. Key Mission at Hiroshima
On August 6, 1945, the Enola Gay carried out its most infamous mission: dropping the atomic bomb on Hiroshima, Japan. This mission was a turning point in World War II, leading to Japan’s eventual surrender and the end of the conflict. The operation was marked by precision and careful planning, with the crew trained extensively to ensure success. The moment of release was both somber and monumental, forever changing the landscape of warfare and international relations. The mission’s impact is still debated and studied to this day.
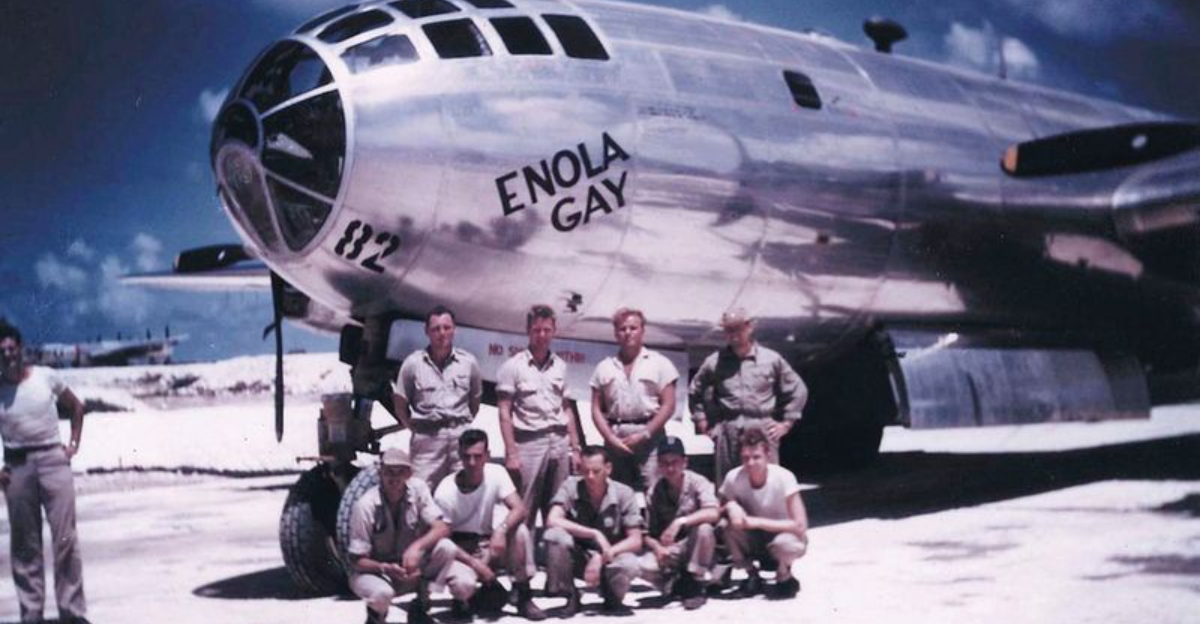
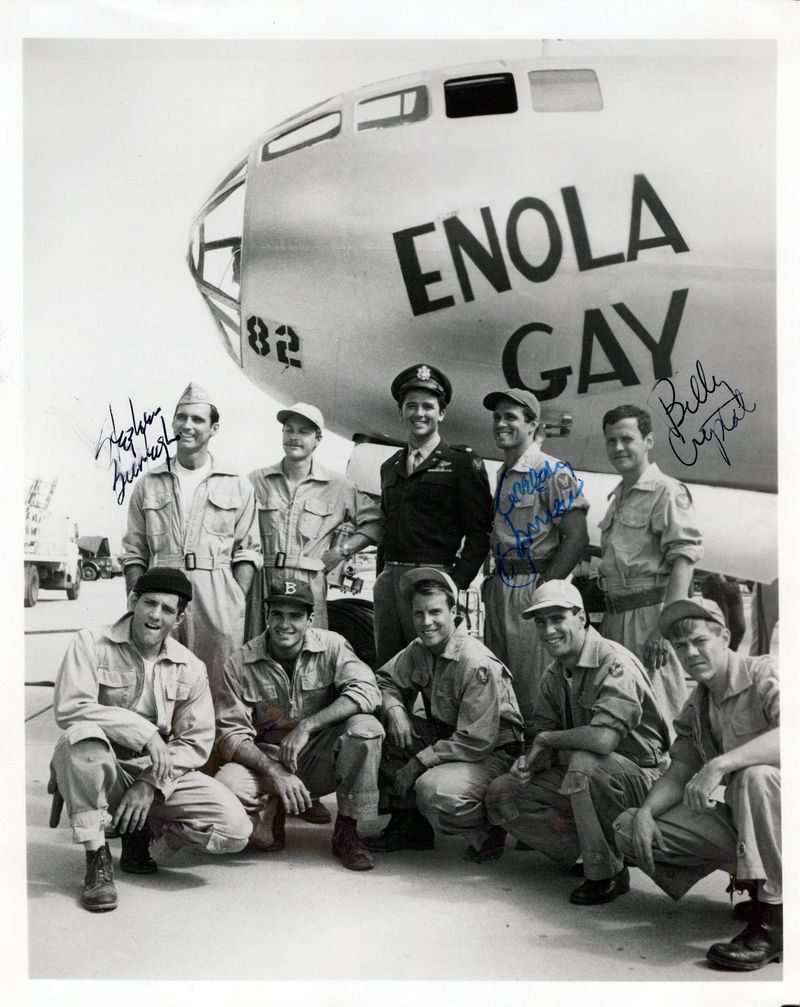
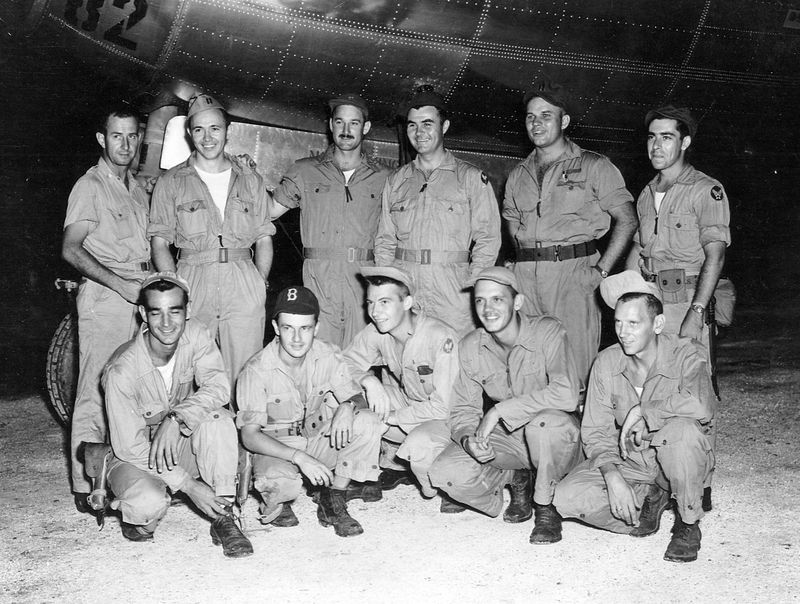
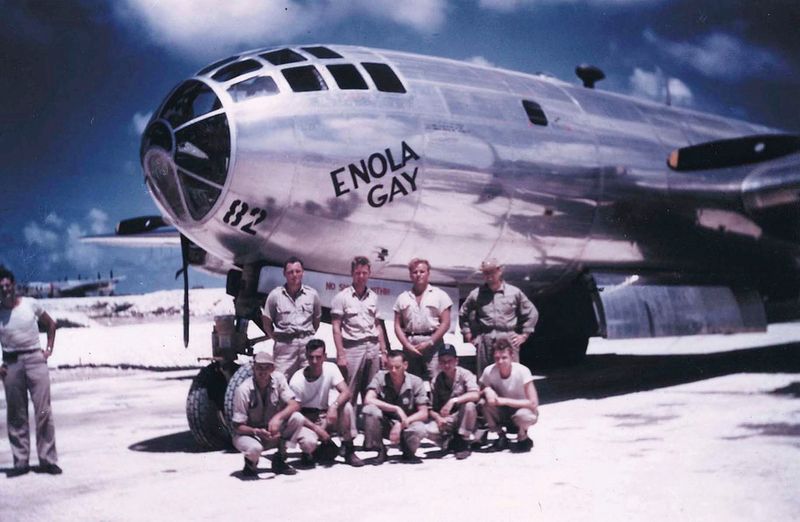
4. Crew’s Unique Role
The crew of the Enola Gay consisted of 12 men, each playing a vital role in the mission’s success. From the pilot, Colonel Tibbets, to the navigator, bombardier, and radio operators, each member was meticulously chosen for their expertise and composure under pressure. The camaraderie among the crew was palpable, built on trust and shared responsibility. Their training was rigorous, focusing on precision, teamwork, and resilience. This crew became a part of history, their names remembered alongside the aircraft they operated with unwavering dedication.
5. The Manhattan Project Connection
The Enola Gay’s mission was the culmination of the top-secret Manhattan Project, which developed the atomic bomb. This project brought together the world’s leading scientists, engineers, and military strategists in a race against time. The aircraft’s role was pivotal, serving as the delivery mechanism for the devastating new weapon. The connection between the bomber and the project highlights the intersection of science and warfare. It underscores the profound ethical and moral questions raised by the development and use of atomic energy in conflict.
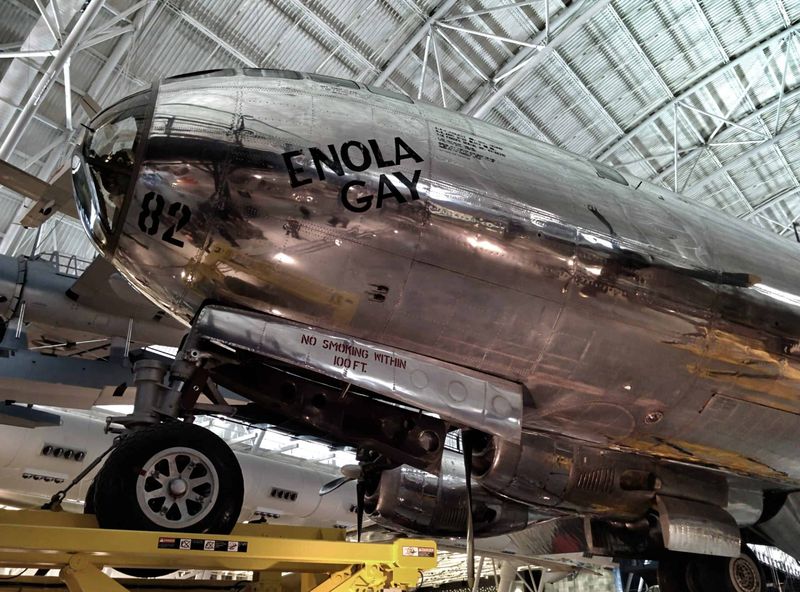
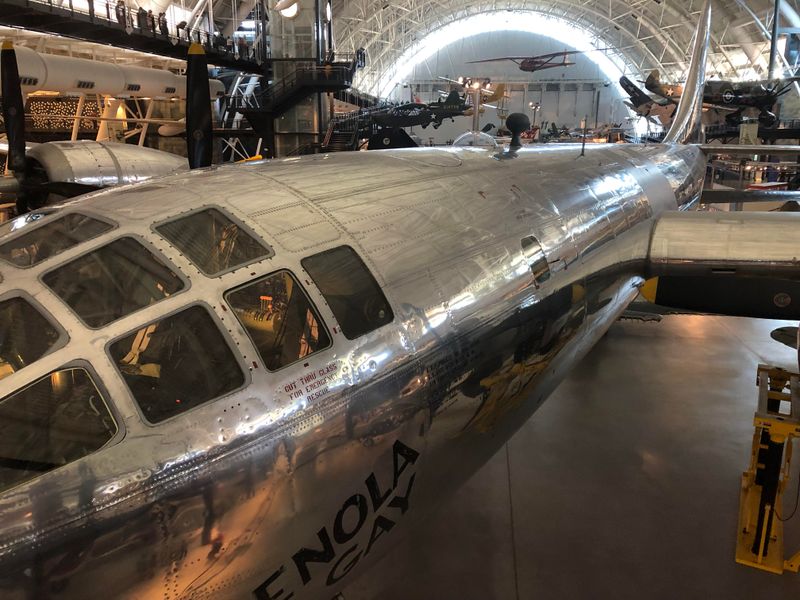
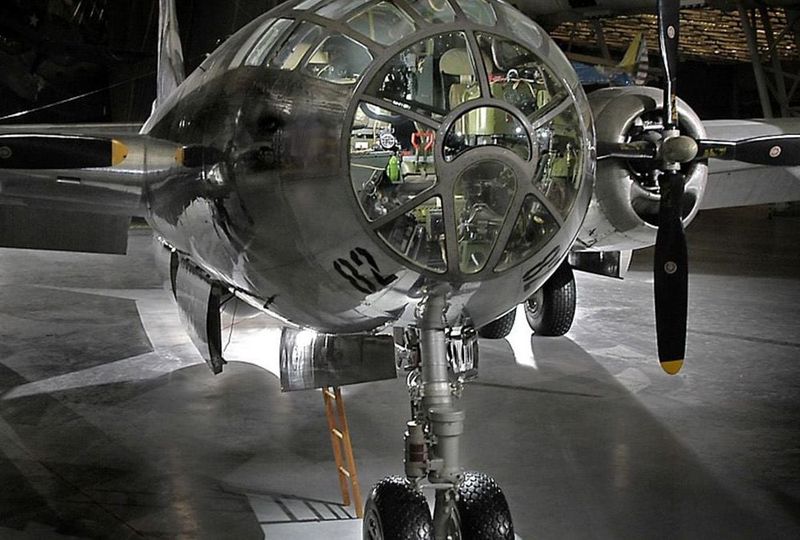
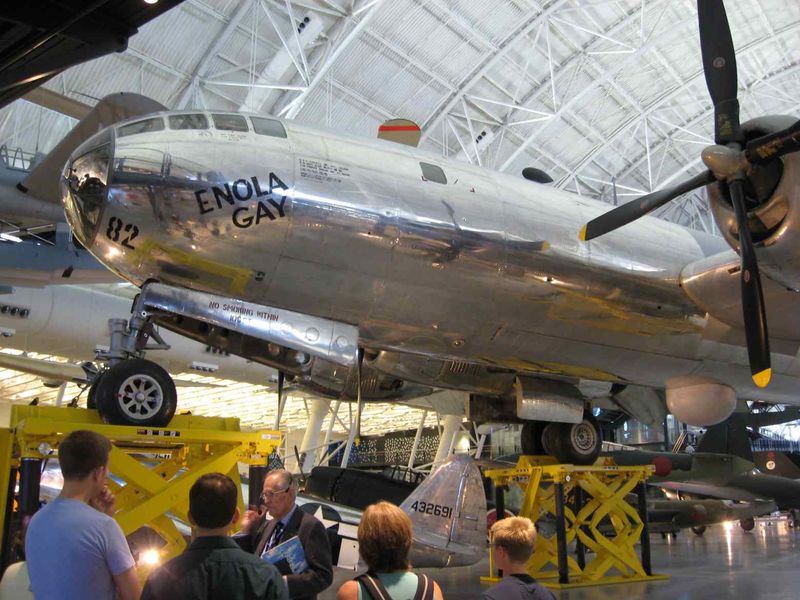
6. Preservation and Display
After its retirement, the Enola Gay was meticulously restored and is now displayed at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Virginia. This preservation allows visitors to connect with a tangible piece of history. The exhibit provides context and insight into the aircraft’s missions and the broader implications of its use. The restoration process was detailed and respectful, ensuring the aircraft remains a testament to its historical significance. Visitors often leave with a deeper understanding of the complexities of war and the legacy of this iconic bomber.
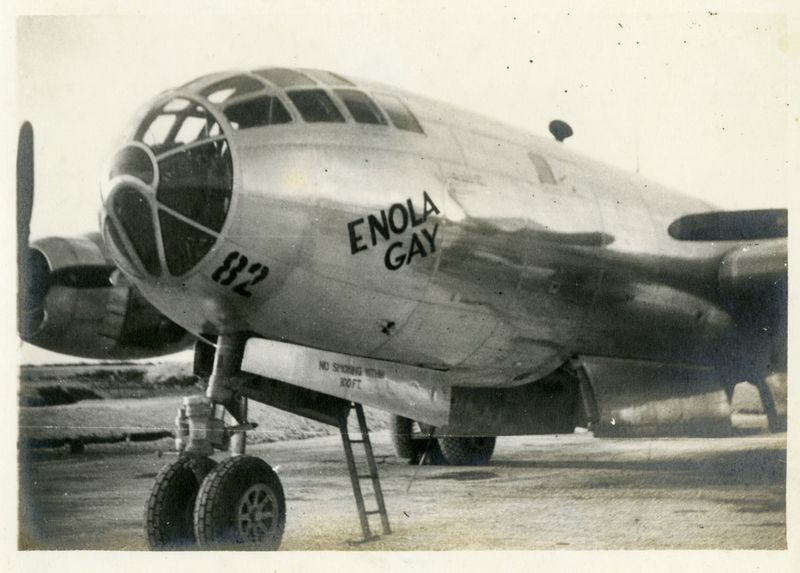
7. Technological Marvel
The Enola Gay was a technological marvel of its time, featuring advanced engineering that set it apart from other aircraft. Its design included pressurized cabins, remote-controlled gun turrets, and a sophisticated bombing system. These innovations allowed for higher altitude flights and increased accuracy in targeting. The aircraft’s capabilities were a testament to American engineering prowess during World War II. These technological advancements played a crucial role in the mission’s execution, showcasing the intersection of innovation and military strategy.
8. Training and Preparation
The crew underwent extensive training to prepare for the Enola Gay’s missions. This included flight simulations, drills, and specialized courses on atomic bomb handling. The rigorous preparation ensured the crew was ready for any scenario, emphasizing precision and accuracy. Their training fostered a strong sense of confidence and camaraderie, essential for the high-stakes mission they would undertake. The dedication and discipline of the crew were evident as they committed to their roles. This preparation was crucial to the mission’s overall success and the crew’s safety.
9. Controversial Legacy
The legacy of the Enola Gay is steeped in controversy, with debates surrounding the morality and necessity of its mission. Some view the atomic bombing as a necessary end to World War II, while others see it as a tragic event that led to immense civilian suffering. These discussions continue to evoke strong emotions and differing perspectives on war ethics. The aircraft symbolizes both technological triumph and human tragedy, embodying the duality of its historical impact. Its story prompts reflection on the consequences of warfare and the quest for peace.
10. Restoration Efforts
The meticulous restoration of the Enola Gay was a lengthy process, undertaken to preserve its historical integrity. Experts worked diligently to restore the aircraft to its original condition, ensuring every detail was authentic. This restoration included repairing its structure, preserving original components, and applying fresh paint while maintaining historical accuracy. The process was a labor of love, driven by a desire to honor history and educate future generations. Through these efforts, the aircraft continues to serve as a powerful reminder of its storied past.
11. Cultural Impact
The Enola Gay’s mission had a profound cultural impact, influencing art, literature, and media. The aircraft and its story have been depicted in films, books, and documentaries, sparking conversations about the ethical implications of nuclear warfare. Its narrative has become a symbol of both the horror and heroism of war, inspiring countless interpretations. The cultural resonance of the Enola Gay extends beyond its mission, reflecting broader themes of conflict, morality, and the human condition. Its story continues to captivate and provoke thoughtful discussion.
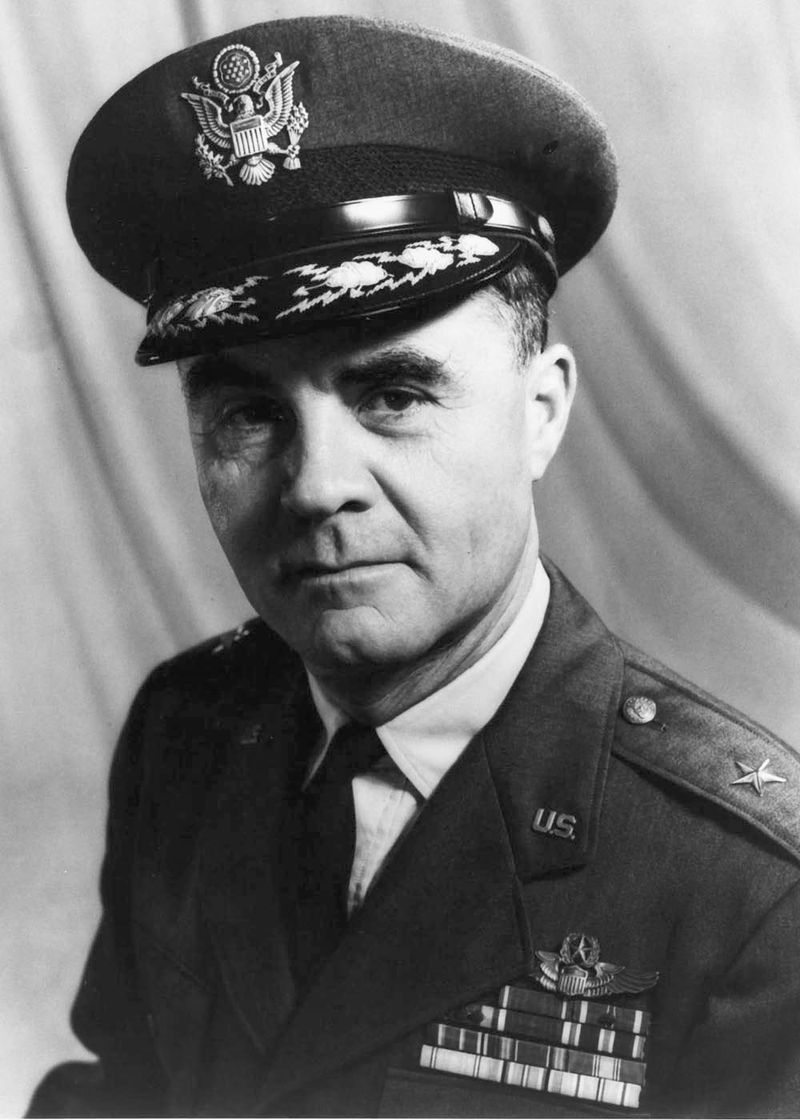
12. Paul Tibbets’ Legacy
Colonel Paul Tibbets, the pilot of the Enola Gay, left a complex legacy marked by his role in the atomic bombing of Hiroshima. Tibbets’ leadership and decision-making were critical to the mission’s execution. Throughout his life, he defended his actions, viewing them as necessary to end the war swiftly. His legacy is both celebrated and critiqued, reflecting the nuanced perspectives on his contributions. Tibbets’ story is intertwined with that of the Enola Gay, embodying the moral and ethical complexities faced by military leaders.
13. Public Reaction
The public reaction to the Enola Gay’s mission was mixed, with initial celebrations of victory overshadowed by the sobering reality of atomic warfare. News of the bombing spread rapidly, eliciting varied responses from joy to horror. For many, it marked the end of a devastating conflict, while others questioned the morality of using such a weapon. The mission sparked global debates, influencing public opinion on nuclear arms and international relations. These reactions underscore the complex emotions and ethical considerations surrounding the use of atomic bombs.
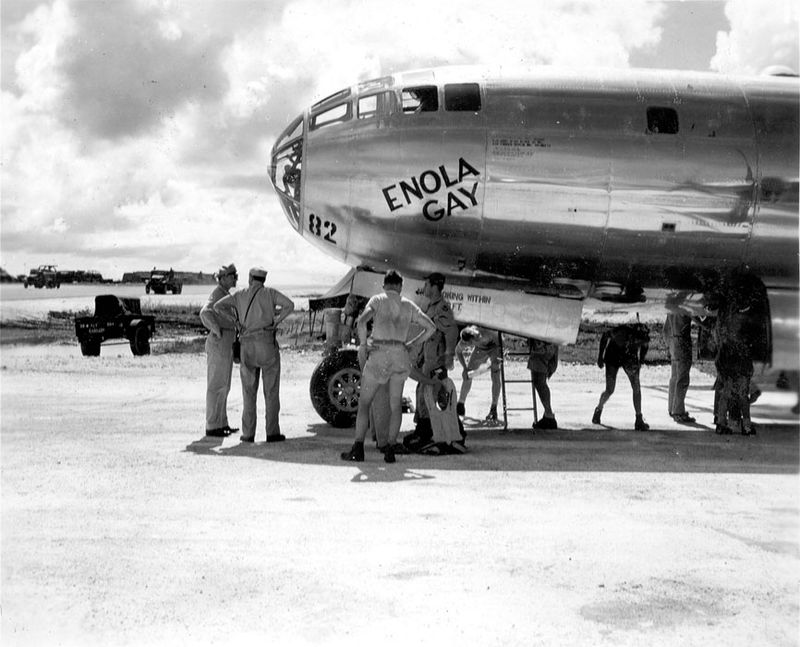
14. Operational Challenges
Flying the Enola Gay on its mission came with significant operational challenges. Navigating long distances, potential enemy threats, and unpredictable weather required careful planning and adaptation. The crew had to be prepared for any obstacle, maintaining focus and composure under pressure. The aircraft’s advanced technology helped mitigate some risks, but human skill was crucial in overcoming challenges. These operational hurdles highlight the expertise and determination of the crew, emphasizing their role in the mission’s successful completion despite potential adversities.
15. Historical Documents
The Enola Gay’s mission is well-documented through various historical records, including mission orders, flight logs, and personal accounts from the crew. These documents provide valuable insights into the planning and execution of the atomic bombing. They reveal the meticulous attention to detail and strategic considerations involved in the operation. Preserved in archives and museums, these records serve as a testament to the complex decision-making processes of wartime leaders. They offer a window into history, allowing future generations to learn from past events.
16. Impact on Aviation
The Enola Gay’s mission had a lasting impact on aviation, influencing both military and civilian aviation strategies. The aircraft’s advanced design and successful execution of its mission demonstrated the potential of long-range bombing capabilities. This led to developments in aircraft technology and strategic bombing techniques. The mission also prompted discussions on the ethical use of air power in conflicts. The legacy of the Enola Gay in aviation history is a reminder of the evolving nature of warfare and the continued pursuit of technological innovation.
17. International Relations
The Enola Gay’s mission played a pivotal role in shaping post-World War II international relations. The use of the atomic bomb prompted global discussions on nuclear disarmament and non-proliferation. The mission’s impact on Japan-U.S. relations was profound, influencing diplomatic efforts and reconciliation processes. It also accelerated the Cold War, as nations grappled with the implications of nuclear power. The Enola Gay’s legacy in international relations underscores the complexities of achieving peace and stability in a world transformed by atomic weaponry. These discussions continue to shape global policies today.
18. Education and Awareness
The history of the Enola Gay is an essential component of educational curricula, fostering awareness and understanding of World War II and its aftermath. Lessons about the aircraft and its mission prompt discussions on the ethical implications of warfare and the responsibilities of global citizenship. Educational programs, museum exhibits, and documentaries offer insights into the historical context and consequences of the atomic bombing. These efforts aim to educate future generations about the complexities of war, emphasizing the importance of peace and reconciliation.
19. Ethical Discussions
The Enola Gay’s mission has fueled ongoing ethical debates about the use of atomic weapons. Scholars, ethicists, and historians have long discussed the morality of the bombing, weighing the potential lives saved against the immense destruction caused. These discussions highlight the tension between military necessity and humanitarian concerns. The mission’s legacy prompts reflection on the ethical responsibilities of leaders and the impact of technological advancements on warfare. It serves as a catalyst for broader debates on peace, conflict resolution, and the future of international security.