Explore the fascinating yet alarming world of products that, despite their inherent dangers, remained on store shelves for years. These items, from household products to children’s toys, present a historical journey through consumer safety challenges.
1. Lead-Based Paint
Lead-based paint was a common household item that brought vibrant colors to many homes. However, beneath its sheen lay a silent danger. Lead is known for its neurotoxic effects, especially in children, leading to developmental issues.
Despite its risks, the paint was widely used until a ban in 1978, when awareness grew about its harmful impact. Before this, homes, schools, and toys were coated with it, unaware of the long-term consequences.
Its legacy remains in older buildings, posing a threat whenever renovations disturb the layers. Bright colors with a hidden, dangerous secret.
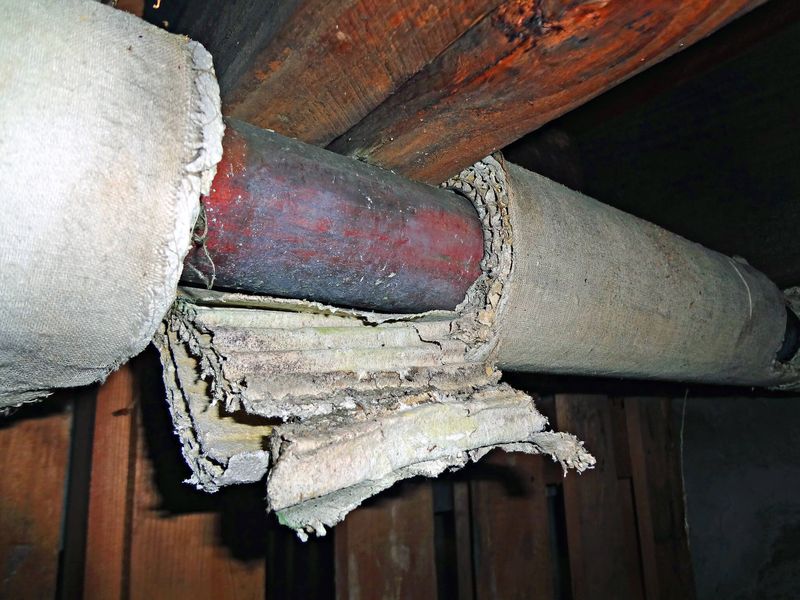
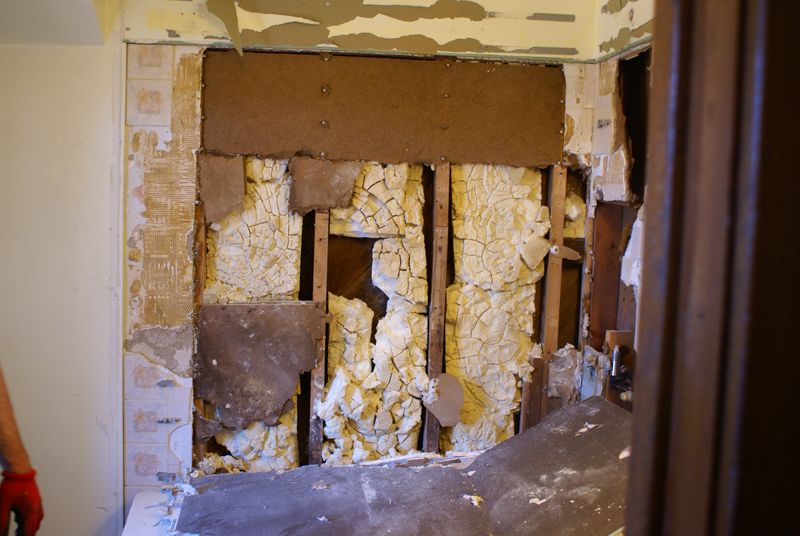
2. Asbestos Insulation & Products
For decades, asbestos was the go-to material for insulation and fireproofing. Its fibrous nature allowed it to withstand heat, making it a staple in construction. However, it came with a dire cost.
Asbestos fibers, when inhaled, can lead to severe respiratory diseases such as lung cancer and mesothelioma. Despite these dangers, it persisted in use until the late 1980s.
The material is now infamous, known more for its health risks than its insulating properties. Once a hero of construction, now a symbol of caution and regret.
3. DDT Pesticide
DDT, a powerful insecticide, revolutionized pest control in agriculture and homes. Its effectiveness seemed unmatched, eradicating pests with ease. However, this chemical had a dark side.
Persisting in the environment, DDT accumulates in wildlife and humans, leading to reproductive and developmental issues. By 1972, its environmental impact was undeniable, prompting a U.S. ban.
Its story is one of initial triumph, followed by ecological tragedy. Once hailed as a savior for farmers, it became a cautionary tale of unintended consequences.
4. Thalidomide
Thalidomide was once a beacon of hope for expectant mothers suffering from morning sickness. Its promise of relief was enticing, yet its effects were devastating.
Prescribed widely in the late 1950s, it led to severe birth defects, affecting thousands of children globally. The drug was withdrawn in 1961, its damage irreparable.
This event reshaped pharmaceutical regulations, highlighting the need for rigorous testing. From hope to heartache, its legacy is one of caution and reform in drug safety.
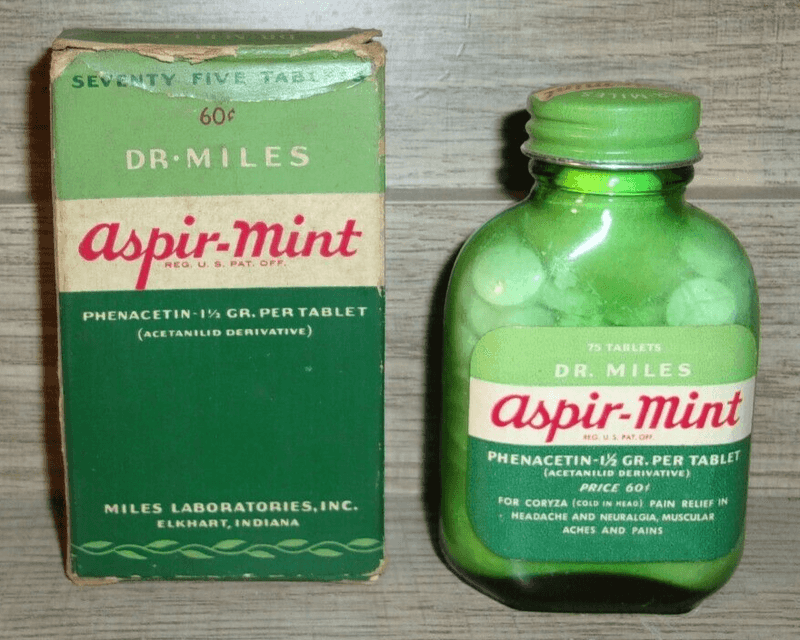
5. Phenacetin Analgesic
Phenacetin was a trusted name in pain relief for nearly a century. Introduced in 1887, it was a staple in households, known for alleviating headaches and fevers. However, its safety was an illusion.
Over time, associations with kidney damage and carcinogenicity emerged, leading to a U.S. ban in 1983. Many who sought relief unknowingly risked their health.
Its story is a reminder of the evolving understanding of drug safety. Once a household name, now a chapter in medical cautionary tales.
6. Hexachlorophene
Hexachlorophene, once hailed as an antibacterial marvel, was a common ingredient in soaps and powders. Its presence promised cleanliness and safety. However, this confidence was misplaced.
In 1972, links to infant neurotoxicity led to restrictions on its use. Parents unknowingly exposed their children to risks while seeking hygiene.
Though effective in its purpose, its legacy is marred by the dangers it posed. From cleanliness to caution, it serves as a reminder of the need for safety in hygiene products.
7. Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs)
PCBs, the industrial workhorse, were once integral to electrical appliances, paint, and sealants. Their stability and non-flammability made them indispensable. However, they harbored hidden dangers.
Toxic and persistent in the environment, PCBs bioaccumulate, posing risks to health and wildlife. By 1979, their use was banned due to these concerns.
Their story reflects industrial progress overshadowed by environmental harm. From innovation to infamy, PCBs highlight the complex balance between utility and health.
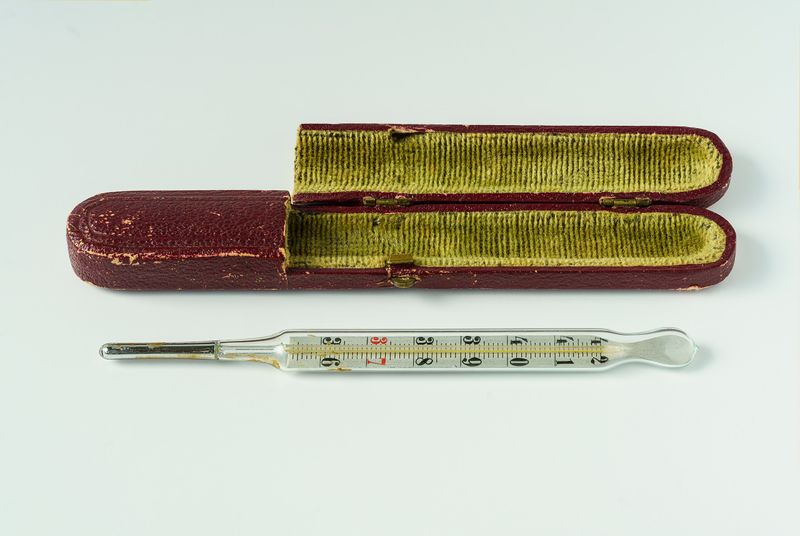
8. Mercury Thermometers
Mercury thermometers were once the pinnacle of medical accuracy, their slender glass bodies a staple in homes and hospitals. However, beneath their precision lay danger.
Mercury, a potent neurotoxin, posed significant health risks if thermometers broke. Despite this, they remained in use until phased out in the 2000s.
Their gradual replacement with digital alternatives marked the end of an era in temperature measurement, trading tradition for safety. A story of precision overshadowed by hazard.
9. PBDE Flame Retardants
PBDEs were the invisible guardians against fire in homes and electronics, embedded within furniture foam and casings. Their presence went unnoticed, yet they silently safeguarded lives.
However, concerns about endocrine disruption and developmental harm emerged, leading to a phase-out by 2004. Their silent protection came with unintended consequences.
Reflecting a time when safety trumped health concerns, PBDEs serve as a reminder of the intricate dance between protection and risk.
10. Trans Fats
Trans fats, once the darling of the food industry, promised longer shelf life and enhanced flavor. Found in margarine and processed foods, they were a pantry staple.
Yet, beneath their culinary appeal lay a health crisis. Linked to heart disease, the FDA finally banned them in 2018. This marked a turning point in nutritional awareness.
From ubiquity to caution, trans fats highlight the evolving understanding of diet and health. A culinary journey from convenience to caution.
11. BPA in Plastics
BPA was the unsung hero of plastics, providing resilience and clarity to products like baby bottles and can linings. However, beneath its utility lay risks.
Concerns over endocrine disruption, particularly in infants, led to bans in infant products by 2011-12. Parents unknowingly exposed their children to hormonal imbalances.
The tale of BPA is one of utility overshadowed by caution, highlighting the growing understanding of chemical safety in daily life.
12. PFOA in Teflon Cookware
PFOA, essential in creating Teflon’s nonstick magic, revolutionized cooking in the 20th century. Its convenience was unmatched, making cleanup a breeze.
However, links to cancer and immune effects led to its phase-out by 2013-15. The nonstick ease came at a hidden cost to health.
PFOA’s story is a lesson in balancing innovation with safety, where the kitchen’s magic turned into a cautionary tale.
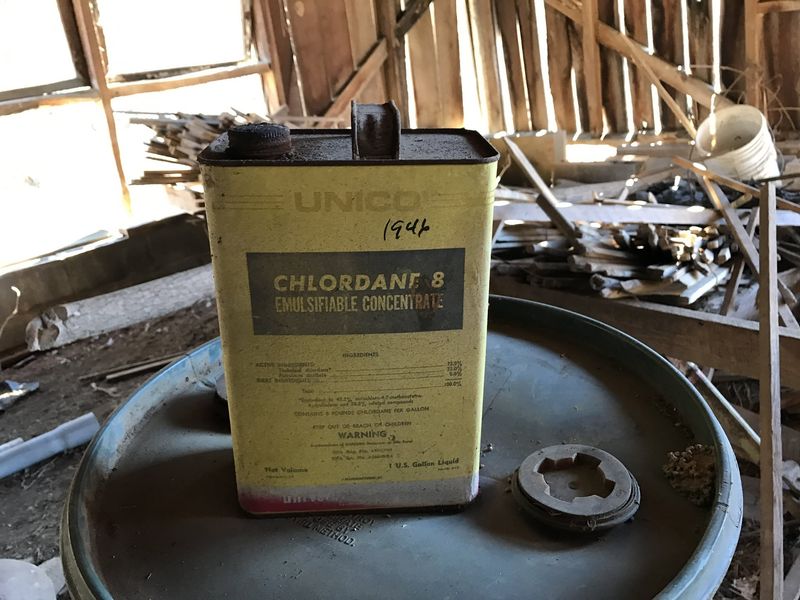
13. Chlordane
Chlordane was the unsung hero in termite defense, widely used in homes and gardens. Its persistence promised long-lasting protection, but this attribute became its downfall.
By 1988, concerns over environmental persistence and cancer risk led to a ban. Homeowners sought safety but faced unintended exposure.
Chlordane’s legacy is one of enduring presence, highlighting the need for caution in seeking durable solutions. From protection to precaution, its story is a complex one.
14. Lindane
Lindane, once a trusted ally in battling lice, was a household staple. Its effectiveness made it a go-to remedy, but hidden dangers lurked.
Neurotoxicity and carcinogenicity concerns led to the cancellation of most uses by 2002-06. Parents unwittingly exposed children to risks while seeking relief.
From remedy to risk, Lindane’s tale underscores the evolving understanding of safety in personal care products. A balance between effectiveness and health.
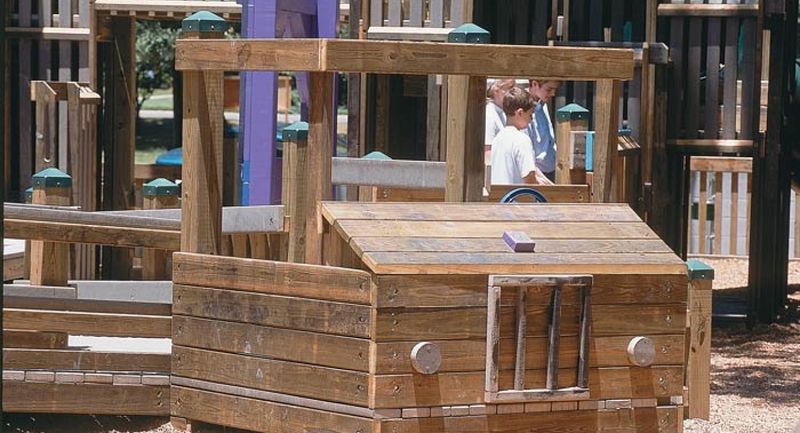
15. Arsenic-Treated Wood (CCA Lumber)
CCA lumber, widely used for decks and playground equipment, promised durability and resistance to decay. However, the arsenic in its treatment posed hidden risks.
Concerns about leaching and cancer led to its phase-out by late 2003. Families unknowingly exposed children to potential harm in play areas.
From durable to dangerous, CCA lumber’s story is a cautionary tale about the hidden costs of chemical treatments in everyday materials.
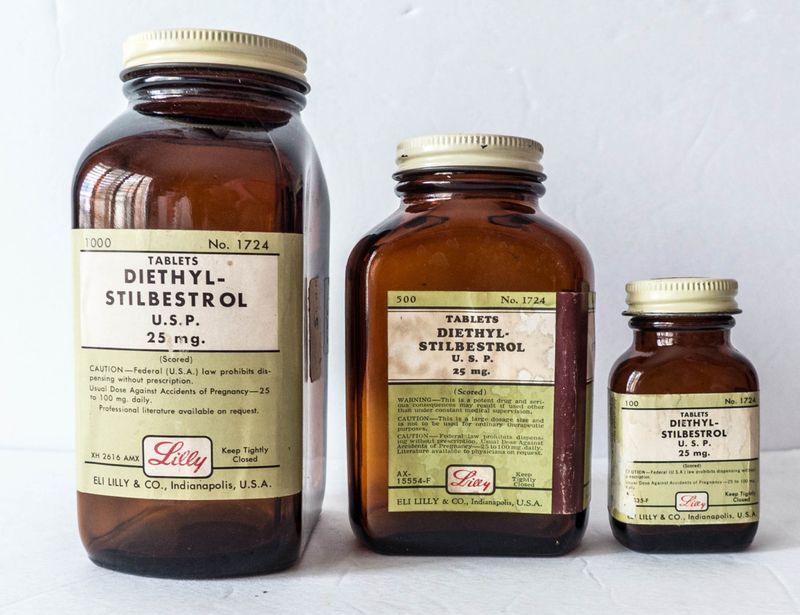
16. Diethylstilbestrol (DES)
DES, a synthetic estrogen, was once prescribed to prevent pregnancy complications. Its promise was alluring, but the consequences were severe.
Linked to rare cancers and reproductive harm, its use was discontinued in 1971. Generations felt its impact unknowingly.
DES serves as a reminder of the importance of thorough testing and awareness in pharmaceuticals. From promise to pain, its legacy reshaped medical perspectives.
17. Radium-Luminous Watches
Radium-luminous watches captivated the public with their glow-in-the-dark allure. Their innovation fascinated, yet they harbored a deadly secret.
Radium ingestion, primarily by workers, led to severe health issues, immortalizing the “Radium Girls” tragedy. These watches remained available through the 1960s.
Their story is one of fascination turning to horror, a reminder of the hazardous allure of unchecked innovation. From marvel to menace, their legacy is a cautionary tale.
18. Urea-Formaldehyde Foam Insulation (UFFI)
UFFI was the answer to energy crises in the 1970s, insulating homes with a promise of efficiency. However, its off-gassing posed significant health risks.
Respiratory issues and other health concerns led to its ban in 1982. Homeowners seeking warmth faced unintended consequences.
UFFI’s story highlights the balance between energy efficiency and health, serving as a lesson in cautious innovation. From insulation to inhalation risk.
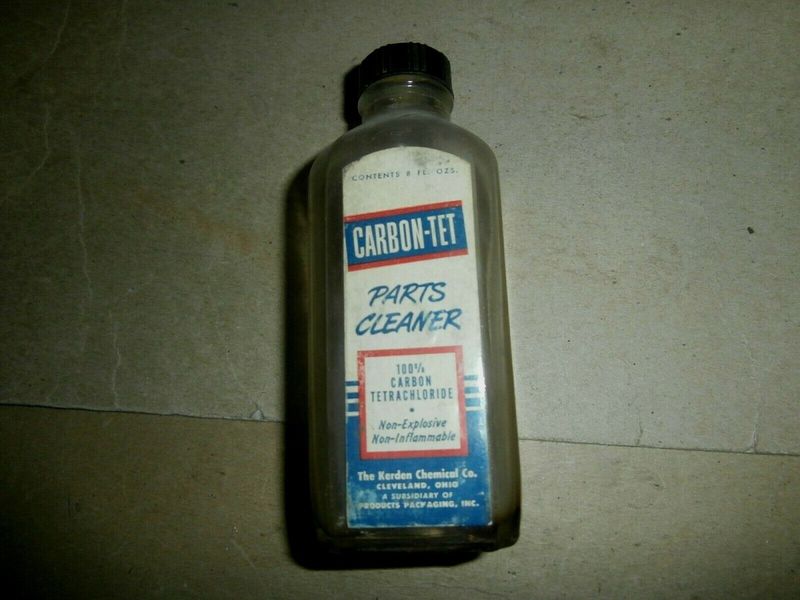
19. Carbon Tetrachloride
Carbon tetrachloride was once a household name, known for its cleaning prowess and fire suppression. Its utility seemed unmatched, yet lurking dangers awaited.
Concerns over liver toxicity and cancer risk led to a ban in 1970. Families unknowingly faced health risks amidst everyday cleaning tasks.
From commonality to caution, its story underscores the need for safety in household chemicals. A journey from everyday essential to cautionary tale.
20. Methylene Chloride
Methylene chloride was once the magic in paint strippers, dissolving layers with ease. Its effectiveness made it a DIY favorite, but its risks were severe.
Links to fatalities and cancer led to a 2019 consumer-use ban. Enthusiasts unknowingly exposed themselves to hazards while renovating.
From utility to risk, its story is a reminder of the balance needed in chemical use, where ease of use meets caution.