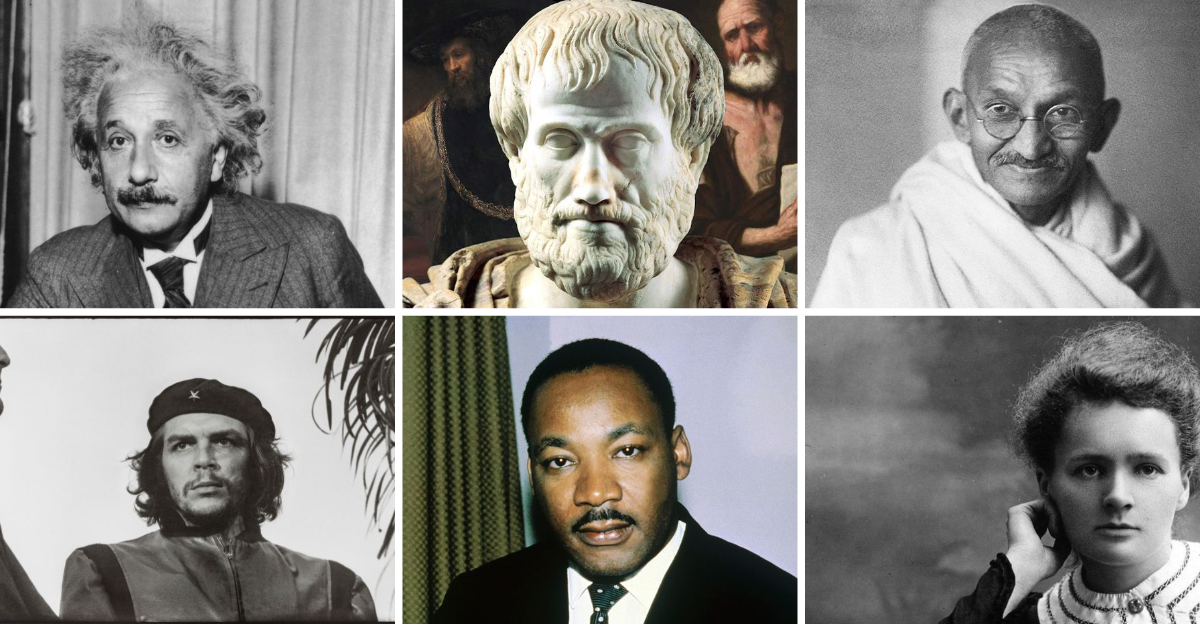
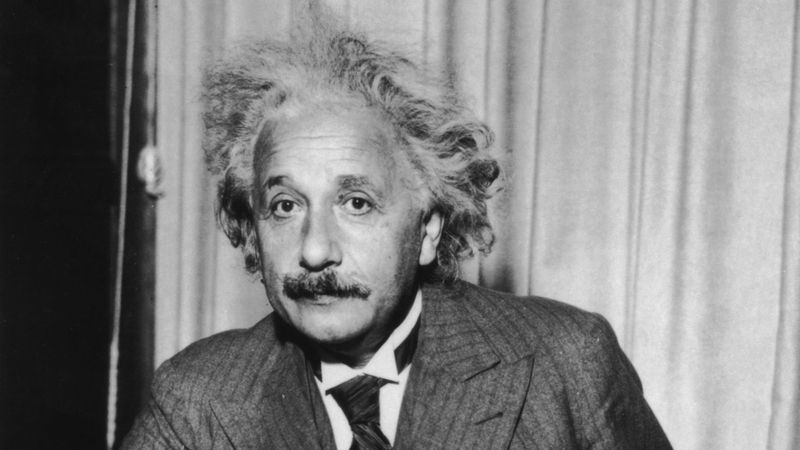Throughout history, certain individuals have left indelible marks on the world.
These influential figures have shaped societies, advanced knowledge, and changed the course of human events.
Here are 25 of the most influential people who have made significant contributions across various fields.
1. Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein revolutionized physics with his theory of relativity. His groundbreaking work in the early 20th century altered our understanding of time, space, and energy.
Einstein’s famous equation, E=mc^2, demonstrated the interconversion of mass and energy, impacting both scientific thought and technological advancement. His intellectual curiosity and innovative spirit made him a leading figure in theoretical physics.
Beyond his scientific achievements, Einstein was a vocal advocate for civil rights and pacifism. His legacy persists, influencing modern science and embodying the power of imagination in uncovering the universe’s mysteries.
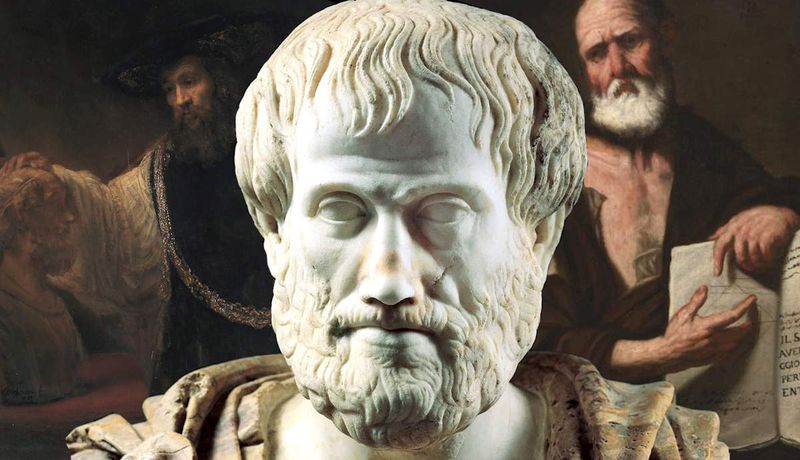
2. Aristotle
Aristotle, a towering figure in ancient philosophy, established foundational concepts in numerous disciplines. Born in Greece, he studied under Plato and later tutored Alexander the Great.
Aristotle’s works spanned ethics, politics, metaphysics, and logic, forming the basis of Western thought. His methodical approach to scientific inquiry paved the way for future exploration and discovery.
His philosophical doctrines emphasized empirical observation and rational analysis, fostering intellectual growth for centuries. Today, Aristotle’s influence is evident in educational systems and philosophical discourse, highlighting the enduring relevance of his ideas in understanding the world.
3. Mahatma Gandhi
Mahatma Gandhi, a leader of peace and non-violence, spearheaded India’s struggle for independence from British rule. Known for his philosophy of ahimsa, or non-violence, Gandhi mobilized millions through peaceful civil disobedience.
His commitment to truth and justice inspired global movements for civil rights and freedom. Gandhi’s iconic Salt March exemplified his belief in the power of non-violent resistance to effect change.
Despite facing imprisonment and opposition, his unwavering dedication to non-violence left a profound impact on the world. Today, Gandhi is celebrated as a symbol of peace, inspiring generations to pursue justice through non-violent means.
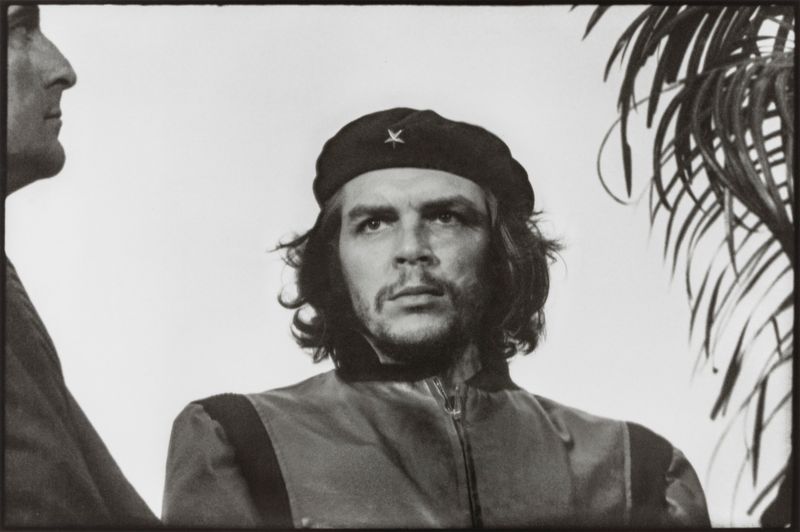
4. Che Guevara
Che Guevara, a prominent Marxist revolutionary, played a key role in the Cuban Revolution. Born in Argentina, Guevara’s early travels ignited a passion for social justice.
As a guerrilla leader, he fought against oppressive regimes. His iconic image, captured with a resolute expression, became synonymous with rebellion and change. Guevara’s writings on guerrilla warfare continue to inspire movements worldwide.
Despite his controversial methods, his commitment to challenging inequality left a lasting impact on Latin America. Today, Guevara remains a symbol of resistance and the fight for freedom, embodying ideals that transcend borders.
5. Martin Luther King Jr.
Martin Luther King Jr., a prominent leader in the American civil rights movement, advocated for equality and justice. His eloquent speeches and non-violent protests challenged racial segregation and discrimination.
King’s leadership during events like the Montgomery Bus Boycott and the March on Washington brought national attention to civil rights issues. His famous ‘I Have a Dream’ speech envisions a future of racial harmony.
He was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for his efforts to combat racial injustice through non-violent means. King’s legacy continues to inspire the fight for civil rights and social justice worldwide.
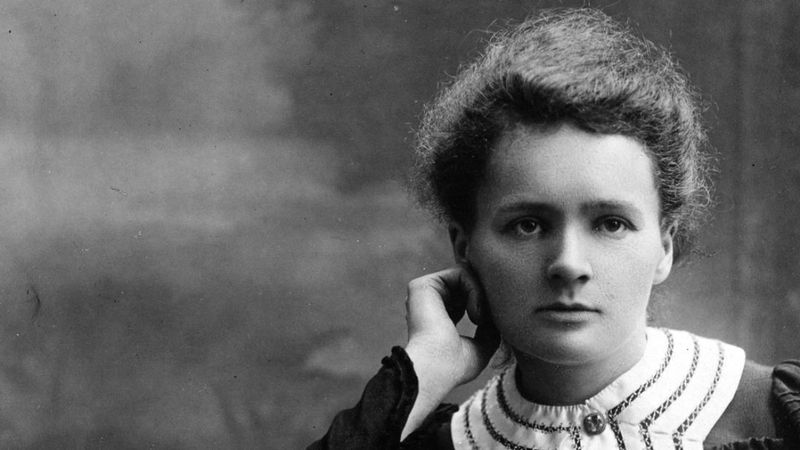
6. Marie Curie
Marie Curie, a pioneering scientist, made groundbreaking contributions to radioactivity research. Born in Poland, she became the first woman to win a Nobel Prize, and the only person to win in two different sciences.
Her discovery of radioactivity and elements like radium and polonium advanced medical treatments and scientific understanding. Curie’s dedication to research broke gender barriers in science.
Despite facing personal and professional challenges, her resilience and commitment to science left an indelible mark. Curie’s legacy endures, inspiring future generations of scientists to pursue knowledge and innovation beyond traditional boundaries.
7. Nelson Mandela
Nelson Mandela, an emblem of resilience and reconciliation, led South Africa’s transition from apartheid to democracy. Imprisoned for 27 years, Mandela emerged as a symbol of hope and unity.
His presidency marked the end of racial segregation, as he championed equality and human rights. Mandela’s commitment to forgiveness and nation-building earned him global admiration and the Nobel Peace Prize.
Through his leadership and vision, Mandela transformed societal structures and inspired a commitment to justice. His legacy of courage and compassion continues to influence advocates for equality and peace worldwide.
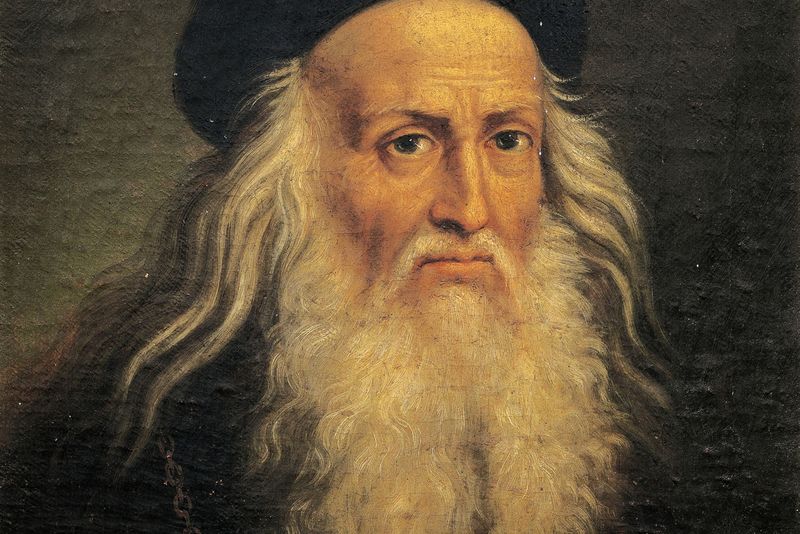
8. Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo da Vinci, a Renaissance genius, excelled as an artist, inventor, and thinker. His works, like the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper, showcase his mastery of art and human emotion.
Da Vinci’s curiosity extended to science and engineering, where he designed innovative machines and studied anatomy. His notebooks reveal an insatiable quest for understanding the natural world.
As a polymath, da Vinci embodied the spirit of the Renaissance, inspiring countless individuals to explore diverse fields. His multidisciplinary approach and creative brilliance continue to captivate and educate people worldwide.
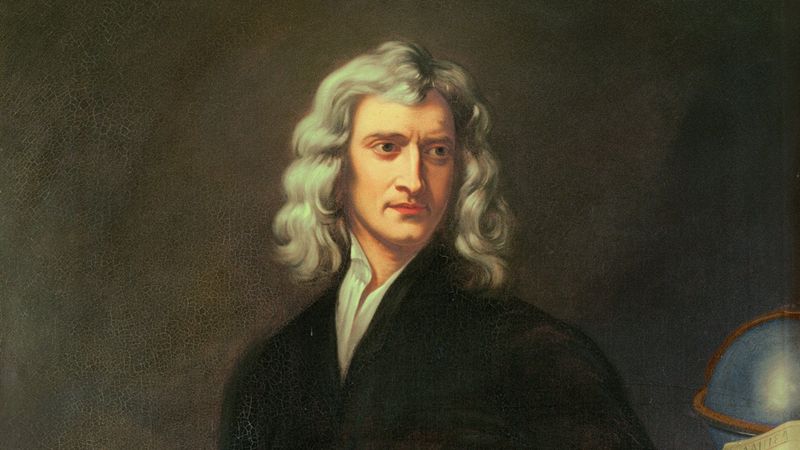
9. Isaac Newton
Isaac Newton, a luminary in mathematics and physics, laid the foundation for classical mechanics. His laws of motion and universal gravitation revolutionized scientific thought.
Newton’s work in optics and calculus furthered our understanding of the physical world. His Principia Mathematica remains a cornerstone in the history of science.
Newton’s analytical rigor and innovative methods influenced generations of scientists and mathematicians. His contributions continue to underpin modern scientific inquiry, illustrating the enduring impact of his intellectual legacy.
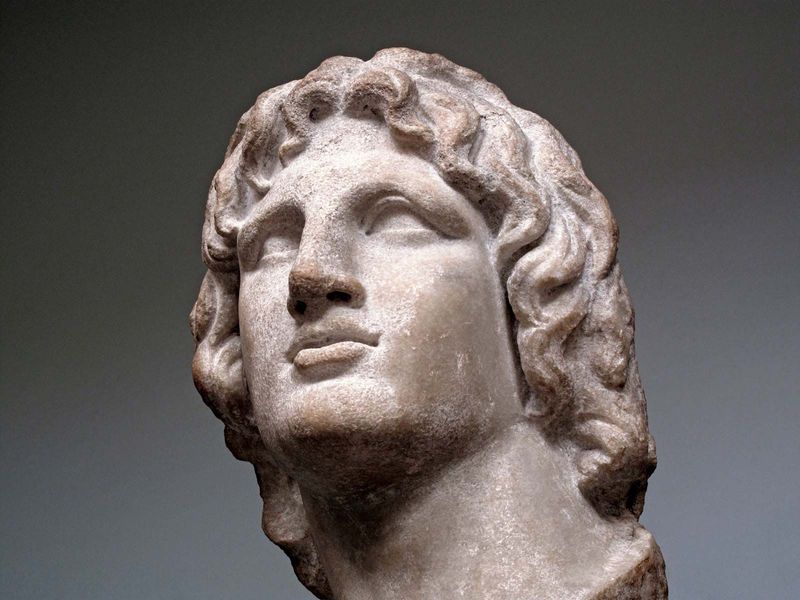
10. Alexander the Great
Alexander the Great, a military strategist and conqueror, expanded the Macedonian Empire to unprecedented extents. His campaigns across Asia and Egypt spread Greek culture and influence.
Under his leadership, cities were founded, and cultural exchanges flourished, leaving a lasting legacy on the regions he conquered. Alexander’s tactics and charisma made him a legendary figure in history.
Despite his young age, his relentless ambition and military prowess shaped the ancient world. Alexander’s influence persists in the fusion of cultures and spread of Hellenistic civilization, exemplifying the reach of his historical impact.
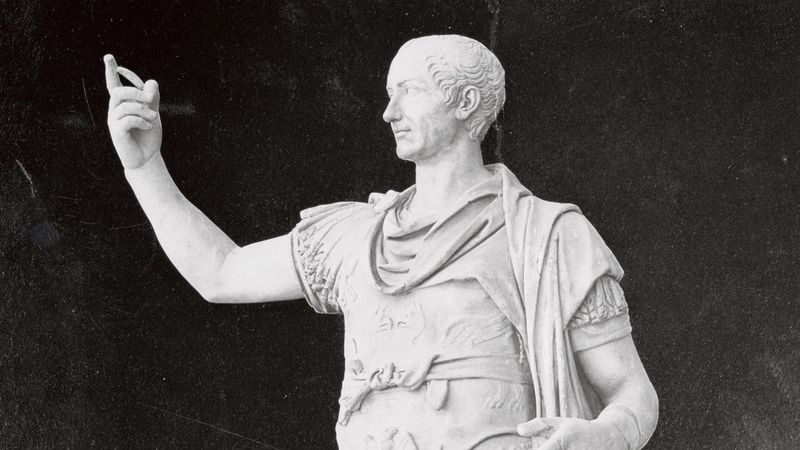
11. Julius Caesar
Julius Caesar, a pivotal figure in Roman history, transformed the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. His military conquests expanded Rome’s territories, solidifying his power.
Caesar’s political reforms and centralization efforts laid the groundwork for the imperial structure. Despite his controversial rule, he was a skilled orator and leader.
His assassination marked a turning point, leading to the rise of the Roman Empire. Caesar’s legacy endures in the political and military strategies that shaped ancient Rome and influenced Western civilization.
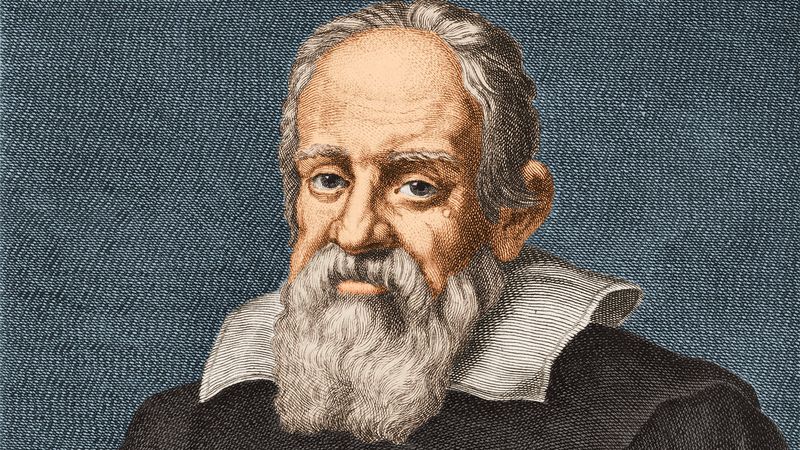
12. Galileo Galilei
Galileo Galilei, a pioneering astronomer, challenged the established views of the cosmos. His use of the telescope led to discoveries like Jupiter’s moons and Venus’s phases.
Galileo’s support for heliocentrism placed him at odds with religious authorities, highlighting the tension between science and tradition. His advocacy for empirical observation transformed astronomical study.
Despite facing persecution, Galileo’s work laid the foundation for modern astrophysics. His legacy lives on, inspiring the pursuit of scientific truth and the spirit of inquiry.
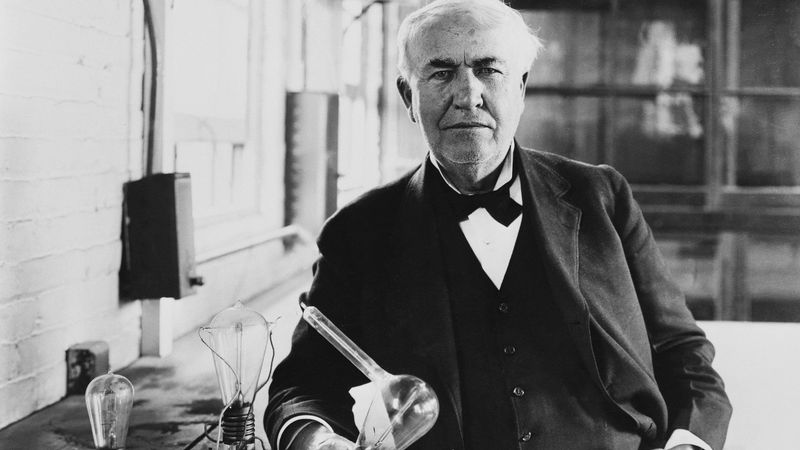
13. Thomas Edison
Thomas Edison, an inventive genius, revolutionized technology with his numerous inventions. Known for the electric light bulb and phonograph, his work illuminated the path to modern industrialization.
Edison’s relentless experimentation and entrepreneurial spirit fostered innovation in various fields. His invention of the phonograph greatly influenced the entertainment industry.
Despite facing failures, Edison’s perseverance and creativity made him a symbol of American ingenuity. His legacy in technological advancement continues to inspire inventors and innovators worldwide.
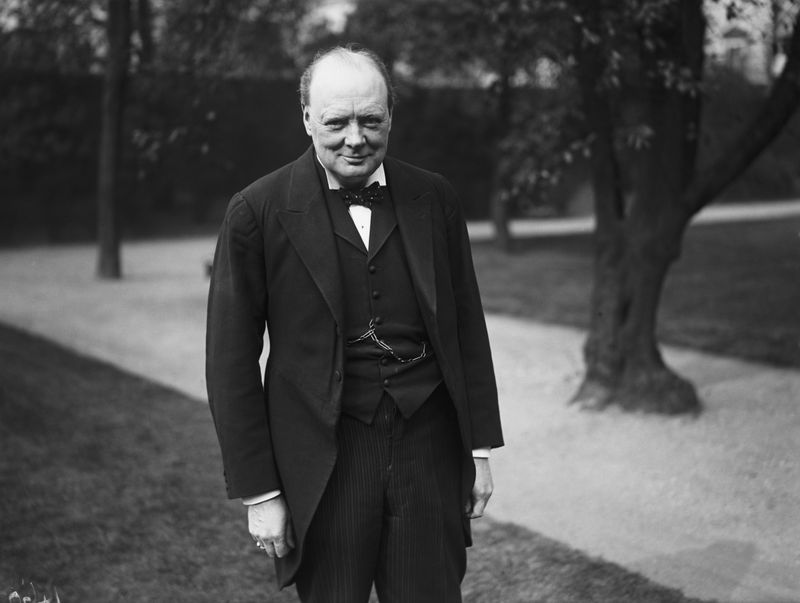
14. Winston Churchill
Winston Churchill, a stalwart leader, guided Britain through World War II with resilience and determination. Known for his stirring speeches, he inspired national unity against adversity.
Churchill’s leadership during pivotal moments, such as the Battle of Britain, solidified his place in history. His strategic vision and diplomatic efforts shaped post-war Europe.
Beyond his wartime role, Churchill was a prolific writer and statesman. His legacy of courage and leadership continues to resonate, exemplifying the power of tenacity in overcoming challenges.
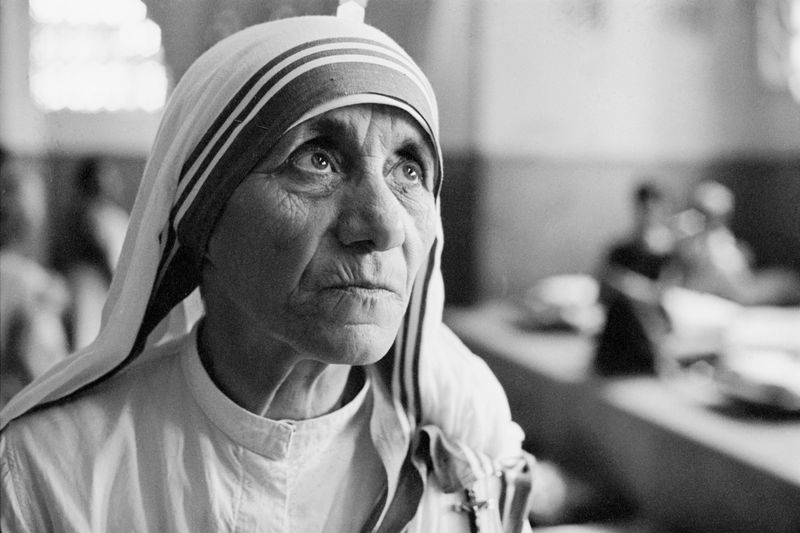
15. Mother Teresa
Mother Teresa, a beacon of compassion, dedicated her life to serving the poorest of the poor. Founding the Missionaries of Charity in India, she provided care and love to those in need.
Her selfless work garnered international respect, earning her the Nobel Peace Prize. Mother Teresa’s unwavering commitment to humanitarian service touched countless lives across the globe.
Through her simple acts of kindness, she highlighted the importance of empathy and charity. Her enduring legacy of love and service inspires others to give selflessly.
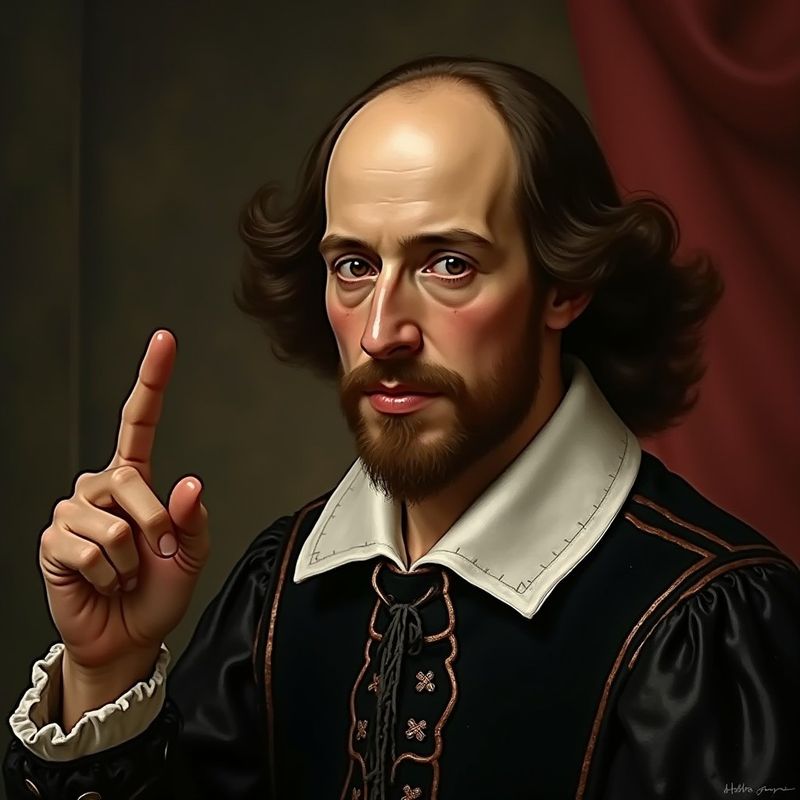
16. William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare, the Bard of Avon, transformed English literature with his timeless works. His plays and sonnets capture the human experience with unparalleled depth and imagination.
Shakespeare’s influence permeates modern language, culture, and storytelling. His exploration of themes like love, power, and ambition continues to resonate across generations.
Despite the passage of time, his plays remain a staple of theatrical performance and literary study. Shakespeare’s legacy endures, illustrating the enduring power of storytelling and poetic expression.
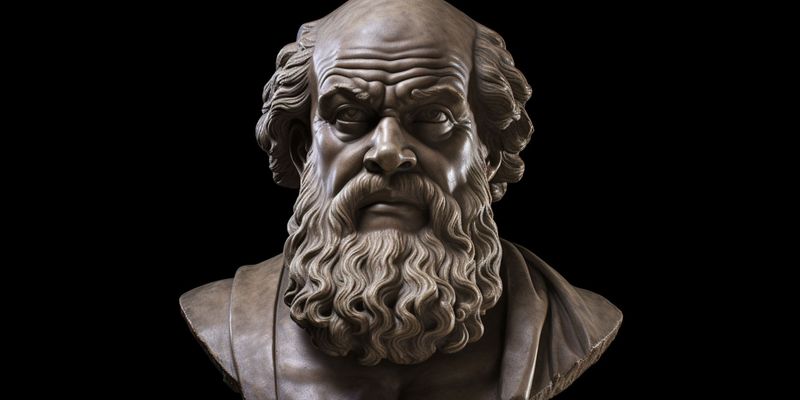
17. Socrates
Socrates, a classical philosopher, laid the groundwork for Western philosophical thought. Known for his dialectical method, he sought to understand ethics and human behavior through questioning.
Socrates’ teachings influenced his students, including Plato, shaping philosophical inquiry for centuries. His commitment to truth and knowledge often put him at odds with Athenian society.
Despite his trial and execution, Socrates’ legacy endures in the pursuit of wisdom and critical thinking. His philosophical ideals continue to inspire the exploration of ethical and existential questions.
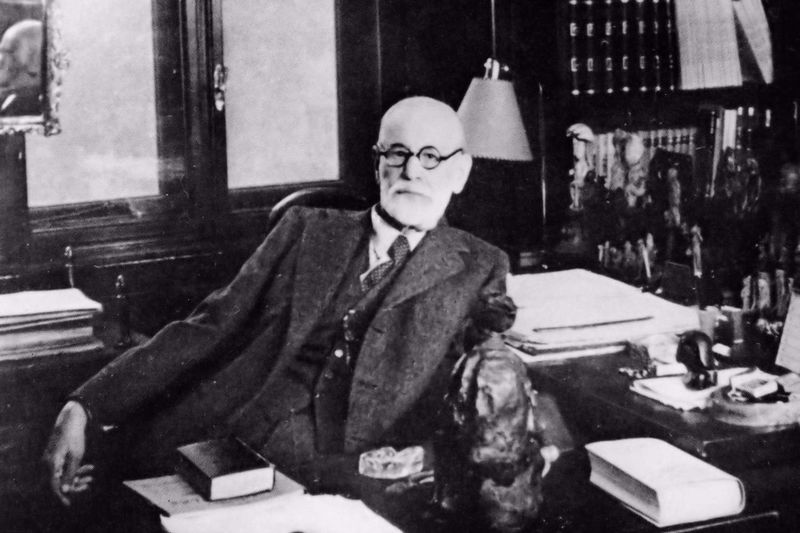
18. Sigmund Freud
Sigmund Freud, the father of psychoanalysis, revolutionized the understanding of the human mind. His theories on the unconscious, dreams, and childhood experiences shaped modern psychology.
Freud introduced concepts like the id, ego, and superego, exploring the complexities of human behavior. His pioneering work laid the foundation for therapeutic practices and mental health awareness.
Despite controversies surrounding his theories, Freud’s influence on psychology and culture remains significant. His legacy persists in the ongoing exploration of the mind and its intricate workings.
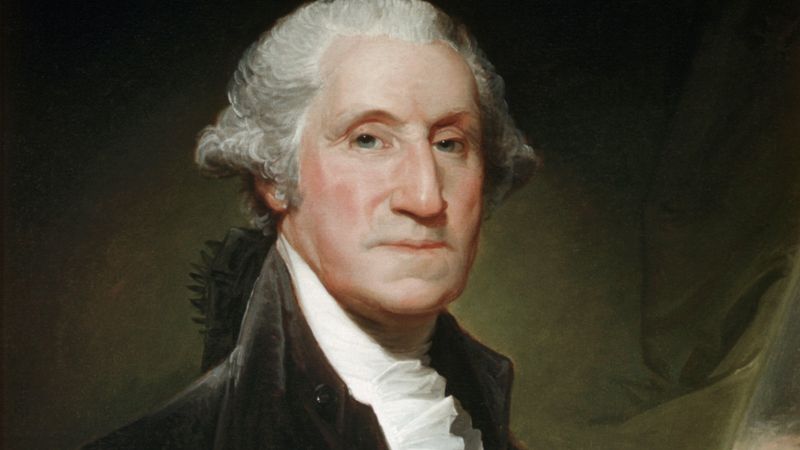
19. George Washington
George Washington, the first President of the United States, played a vital role in the American Revolutionary War. His leadership and integrity established the new nation’s democratic principles.
Washington’s presidency set precedents for future leaders, emphasizing unity and national identity. His farewell address warned against political divisiveness and foreign entanglements.
As a symbol of American independence and governance, Washington’s legacy is celebrated for its profound impact on the nation’s founding and development.
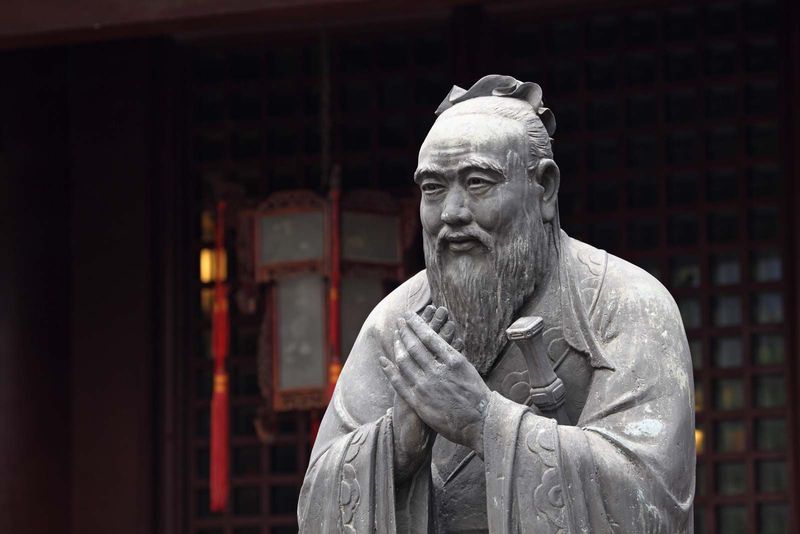
20. Confucius
Confucius, an esteemed Chinese philosopher, emphasized ethics, morality, and social harmony. His teachings, compiled in the Analects, promote virtues like filial piety, respect, and integrity.
Confucianism shaped Chinese culture, education, and governance, influencing societal norms for millennia. Confucius’ philosophy underscores the importance of familial and social relationships.
His enduring influence is evident in the values that guide personal and communal conduct. Confucius’ legacy continues to inspire individuals seeking wisdom and ethical living.
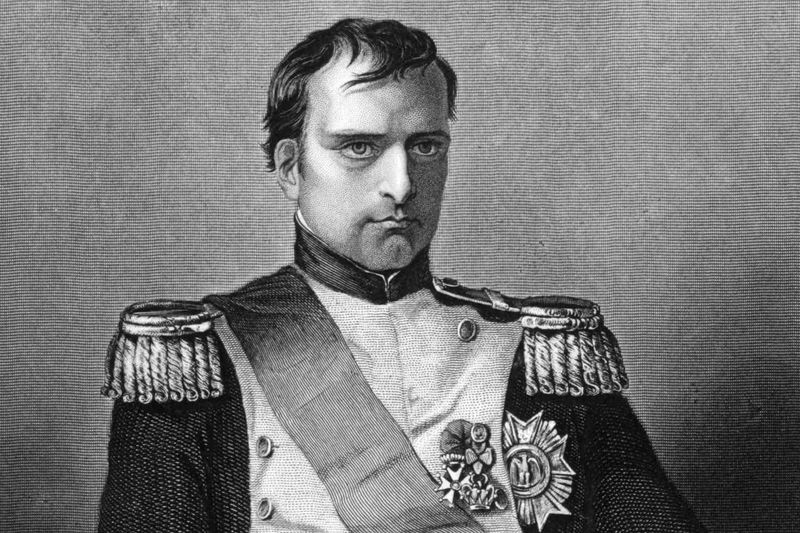
21. Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte, a military and political leader, rose to prominence during the French Revolution. His reforms in law and administration modernized France and influenced European systems.
Napoleon’s ambitions led to widespread conflict, but his contributions to civil law, embodied in the Napoleonic Code, remain significant. His leadership skills and strategic acumen are widely studied.
Despite his eventual downfall, Napoleon’s legacy endures in the realms of military strategy and governance. His complex character continues to intrigue historians and inspire leaders.
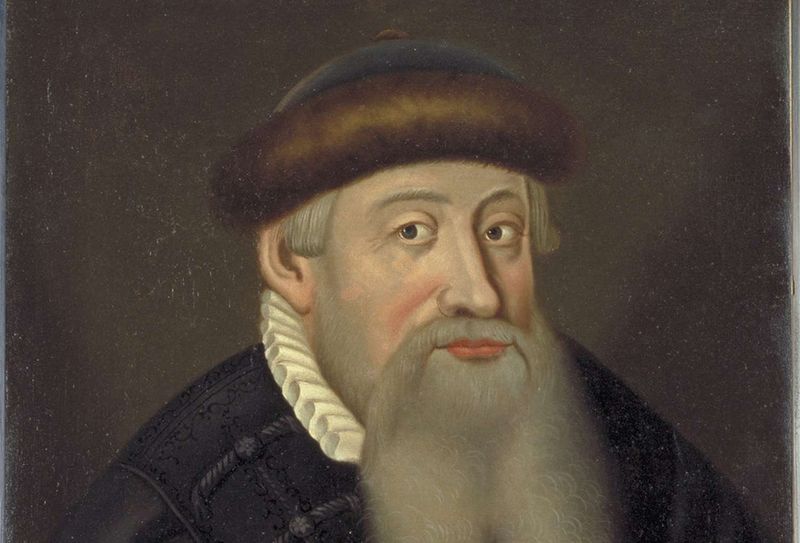
22. Johann Gutenberg
Johann Gutenberg, the inventor of the movable-type printing press, revolutionized information dissemination. His invention enabled the mass production of books, significantly impacting education and literacy.
Gutenberg’s press facilitated the spread of knowledge and ideas, contributing to the Renaissance and Reformation. His work democratized access to information, transforming society.
The legacy of Gutenberg’s invention is seen in the continued evolution of print media. His contributions highlight the enduring impact of technological innovation on culture and learning.
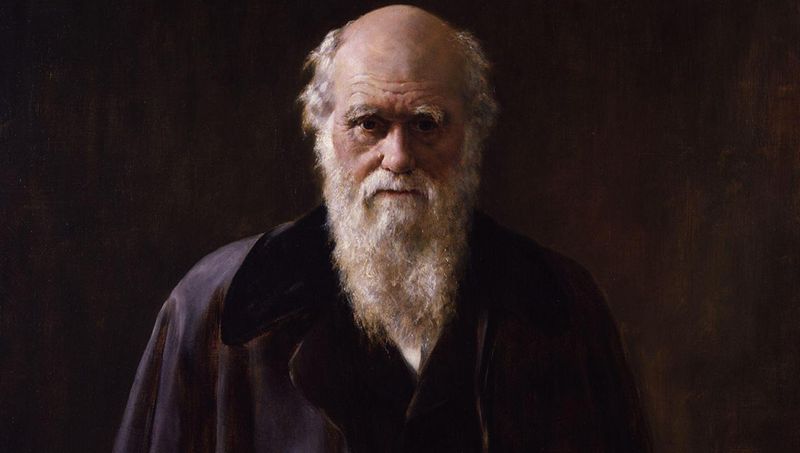
23. Charles Darwin
Charles Darwin, a pioneering naturalist, proposed the theory of evolution by natural selection. His observations during the voyage of the HMS Beagle led to groundbreaking insights.
Darwin’s ‘On the Origin of Species’ challenged prevailing views on creation, profoundly influencing biological sciences. His work sparked debates and further study in evolution.
Despite initial resistance, Darwin’s ideas are foundational to modern biology and ecology. His legacy is evident in the scientific exploration of life’s diversity and complexity.
24. Queen Elizabeth I
Queen Elizabeth I, the last Tudor monarch, presided over England’s Golden Age. Her reign was marked by cultural flourishing, political stability, and maritime expansion.
Elizabeth’s leadership fostered an era of exploration and the arts, exemplified by figures like Shakespeare. Her diplomatic acumen and strong governance solidified England’s position as a global power.
Despite personal and political challenges, Elizabeth’s legacy endures in the cultural and historical advancements of her time. Her rule exemplifies the impact of effective leadership on national prosperity.
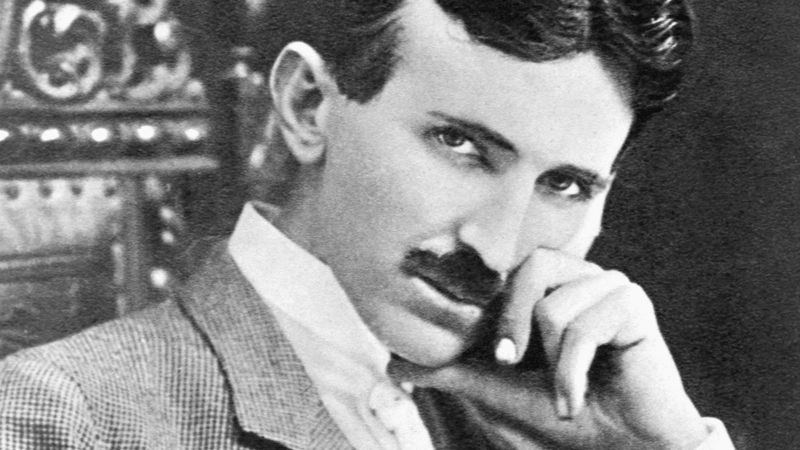
25. Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla was a Serbian-American inventor and engineer known for his groundbreaking work in electricity and electromagnetism. His innovations include the development of alternating current (AC) systems, which revolutionized the way electricity is delivered.
Tesla’s visionary ideas extended beyond his time, encompassing wireless transmission and renewable energy. Despite facing financial difficulties, his contributions have had a lasting impact on modern technology.
Today, Tesla is celebrated as a pioneer whose work laid the foundation for various electrical technologies, making him a key figure in scientific advancement.