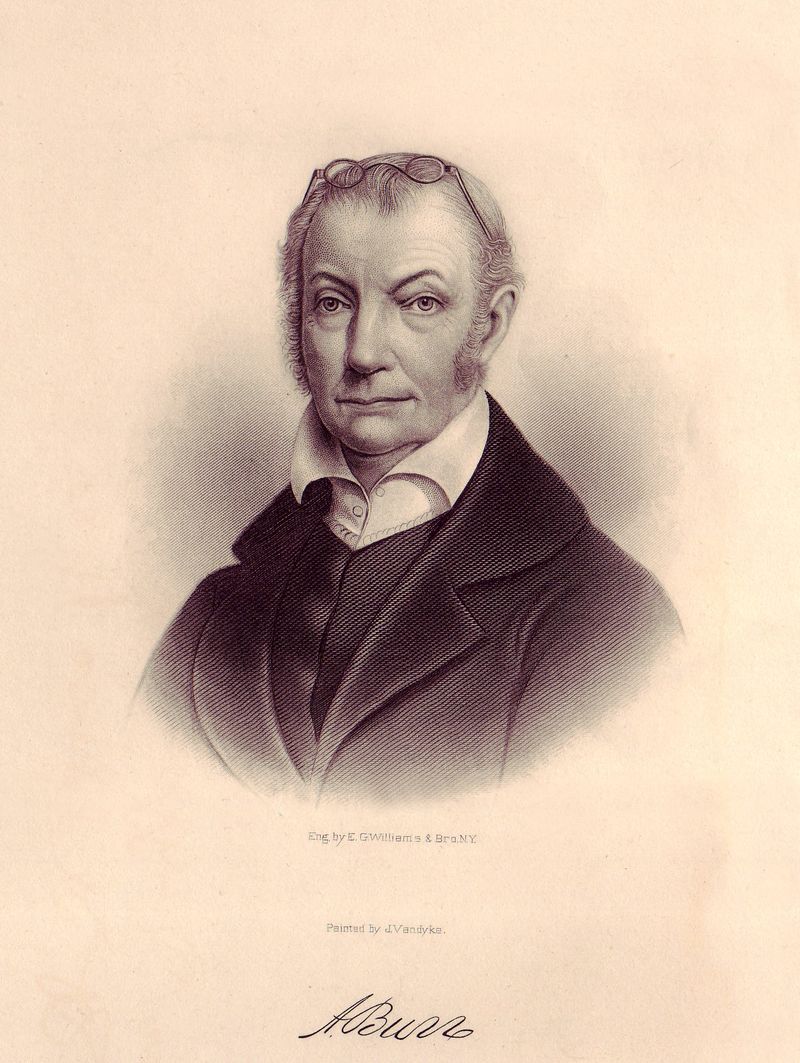February 19th is a date that has witnessed remarkable events throughout history. From ancient battles to significant political shifts, each moment has contributed to shaping the world as we know it.
Let’s explore 30 profound moments that occurred on this day, offering insights into the diverse tapestry of our past.
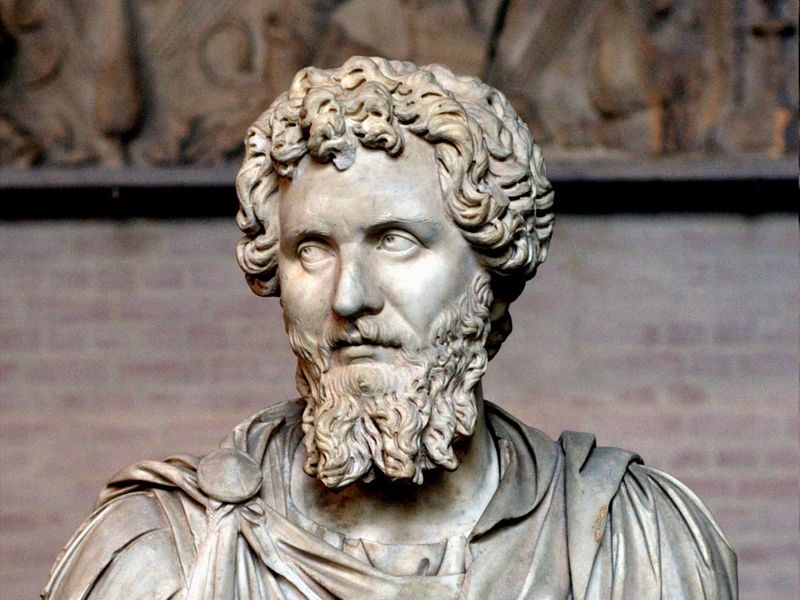
1. 197 – Battle of Lugdunum: Septimius Severus defeats Clodius Albinus.
The Battle of Lugdunum in 197 marked a decisive victory for Septimius Severus over Clodius Albinus, securing his position as Roman Emperor. This conflict was among the largest battles of the Roman civil wars, involving a massive number of troops.
Strategically fought near modern-day Lyon, France, the battle demonstrated Severus’s military prowess and tactical decisions. His victory ensured stability within the empire, shaping its future course.
The aftermath solidified Severus’s authority, enabling him to implement reforms that strengthened the empire. This pivotal moment highlighted the complexities of Roman politics and power struggles.
2. 356 – Roman Empire bans pagan idol worship.
In 356, the Roman Empire took a significant step by banning pagan idol worship. This edict, part of Emperor Constantius II’s efforts, aimed to consolidate Christianity’s influence.
The decree marked a pivotal shift, emphasizing the empire’s transition from polytheism to Christianity. Many temples were closed or repurposed, symbolizing the changing religious landscape.
While this move faced resistance, it played a crucial role in shaping religious practices. The ban on idol worship was a landmark in the historical shift towards monotheism, highlighting the dynamic interplay between religion and politics in ancient Rome.
3. 1594 – Sigismund III crowned King of Sweden.
Sigismund III’s coronation as King of Sweden in 1594 was a momentous occasion. Born into the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, his ascension symbolized the union of the two realms.
The ceremony was filled with grandeur, reflecting the political and cultural significance of the event. However, Sigismund’s reign was marked by tensions between his Catholic beliefs and Sweden’s Protestant majority.
These religious differences eventually led to his deposition, but his legacy persisted through his efforts to integrate Polish and Swedish interests. His crowning moment remains a fascinating study of monarchy, religion, and cultural exchange.
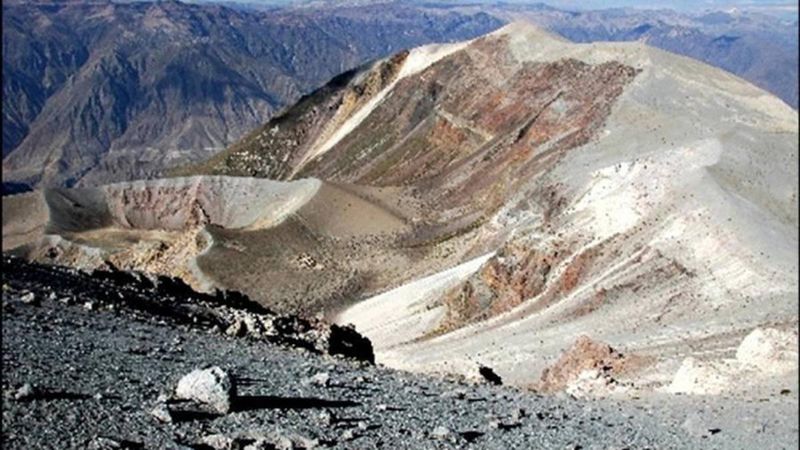
4. 1600 – Huaynaputina volcano erupts violently in Peru.
On February 19, 1600, Huaynaputina erupted with unprecedented force in Peru, becoming the largest volcanic event in South America’s recorded history. The eruption released vast amounts of ash, affecting global climates.
Local communities were devastated, with farmland covered in ash and livestock perishing. The explosion’s impact was felt far beyond Peru, contributing to the ‘Little Ice Age’ and causing crop failures worldwide.
This catastrophic event serves as a reminder of nature’s power and its far-reaching consequences. Understanding the eruption helps scientists study climate change and volcanic activity’s role in ecological shifts.
5. 1674 – Treaty of Westminster ends Third Anglo-Dutch War.
The Treaty of Westminster, signed in 1674, concluded the Third Anglo-Dutch War, restoring peace between England and the Dutch Republic. This treaty marked the end of hostilities that had strained relations and economics.
The agreement allowed both nations to refocus on trade and colonial expansion, fostering a period of relative stability. It included provisions for territorial adjustments and trade rights, reflecting the era’s geopolitical intricacies.
This treaty is a testament to diplomacy’s power in resolving conflicts and shaping international relations. The peace achieved paved the way for future collaborations and rivalries in European politics.
6. 1714 – Battle of Napue fought between Sweden and Russia.
The Battle of Napue in 1714 was a critical confrontation between Sweden and Russia during the Great Northern War. Fought in harsh winter conditions, the battle tested the resilience of both armies.
Sweden, led by General Carl Gustaf Armfeldt, faced a formidable Russian force. Despite their valiant efforts, the Swedes were defeated, marking a turning point in the war.
This battle underscored the challenges of warfare in extreme climates and highlighted the shifting power dynamics in Northern Europe. The outcome significantly influenced Sweden’s military strategy and its position in the region.
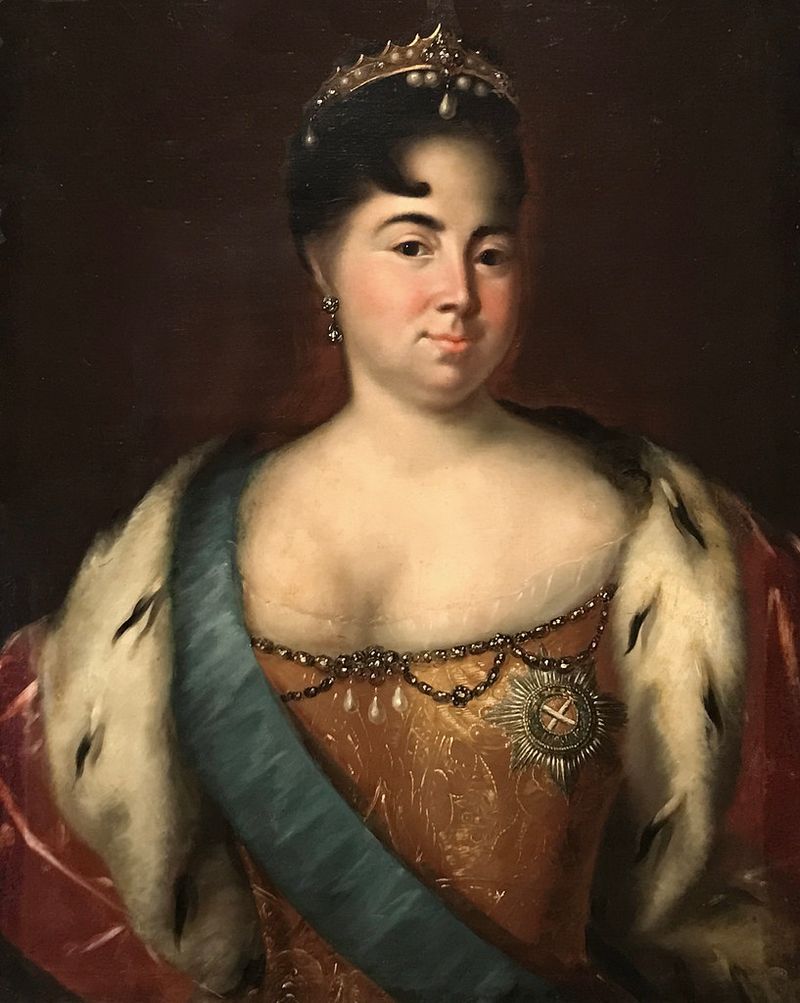
7. 1726 – Russia establishes the Supreme Privy Council.
In 1726, Russia established the Supreme Privy Council under the reign of Catherine I. This council became a central governing body, advising the Tsar and influencing key decisions.
Composed of prominent nobles, the council reflected the complexities of Russian imperial politics. It played a critical role in shaping policies and stabilizing the government during transition periods.
The establishment of the Supreme Privy Council marked a shift towards more structured governance, balancing the Tsar’s power with advisory input. It highlighted the evolving nature of Russian political systems and their adaptability to changing circumstances.
8. 1807 – Aaron Burr arrested for treason in Alabama.
In 1807, Aaron Burr, former Vice President of the United States, was arrested for treason in Alabama. Burr’s alleged conspiracy aimed to create an independent nation in the southwestern U.S.
His arrest followed a dramatic pursuit, highlighting political tensions in the young republic. Burr’s trial was a landmark in American legal history, testing the limits of executive power and constitutional rights.
Although acquitted, the trial tarnished Burr’s reputation. This event underscores the fragility of early American politics and the challenges of maintaining national unity amid ambitious individual pursuits.
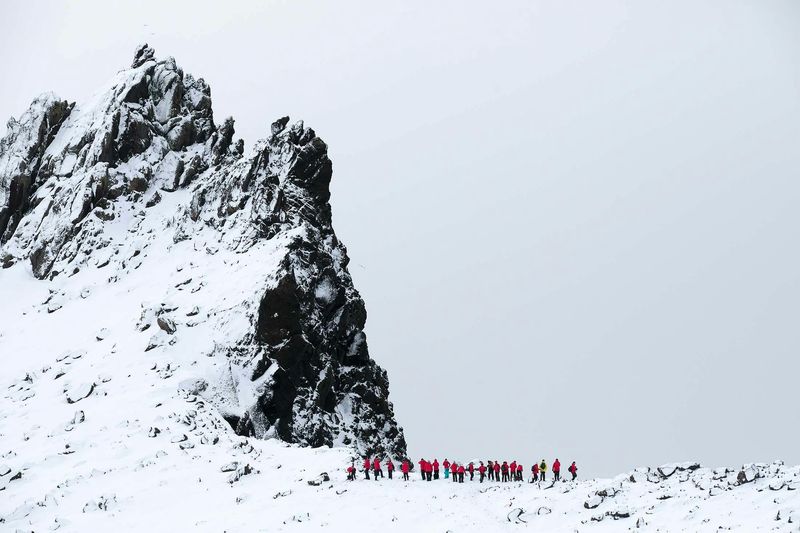
9. 1819 – British explorer discovers South Shetland Islands.
On February 19, 1819, British explorer William Smith discovered the South Shetland Islands, situated off the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula. This discovery expanded knowledge of the Antarctic region.
The islands became a hub for sealing and whaling, attracting explorers and traders. Smith’s findings highlighted the strategic importance of these islands in polar exploration and resource exploitation.
This moment in exploration history emphasizes the relentless human spirit in uncovering the mysteries of uncharted territories. It laid the groundwork for future Antarctic expeditions and international cooperation in the region.
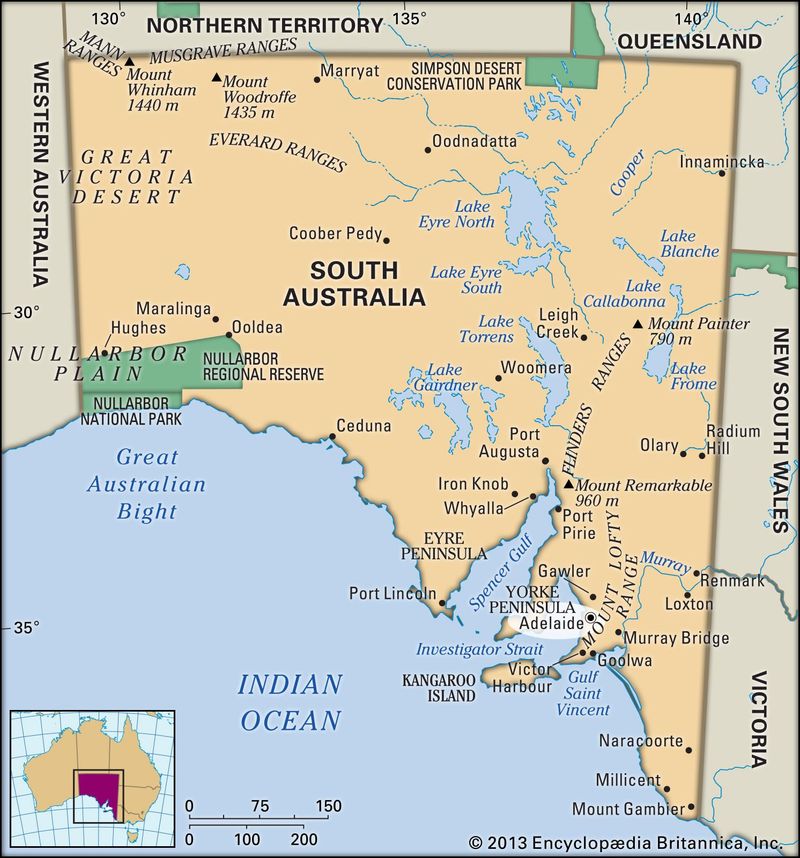
10. 1836 – King William IV establishes South Australia.
In 1836, King William IV officially established South Australia as a British province. This move was part of a broader colonial expansion strategy, emphasizing planned settlement rather than convict transport.
The colony was founded on principles of freedom and land ownership, attracting settlers seeking new opportunities. Its establishment laid the foundation for Adelaide and other settlements, fostering economic growth.
South Australia’s creation represented a shift in colonial policies, aiming for prosperity through cooperation with Indigenous peoples. This event highlights the complexities of colonization and its long-lasting impact on Australia’s development.
11. 1846 – Texas officially becomes a U.S. state.
On February 19, 1846, Texas officially became the 28th state of the United States. Previously an independent republic, Texas’s annexation was a contentious issue, affecting U.S.-Mexico relations.
The decision fueled debates over slavery’s expansion, reflecting the nation’s growing sectional divides. Despite tensions, Texas’s statehood contributed to the U.S.’s territorial expansion and economic growth.
This milestone in American history underscores the complexities of state formation, sovereignty, and identity. Texas’s integration into the Union was pivotal in shaping the nation’s political landscape and its future trajectory.
12. 1847 – Rescuers reach the stranded Donner Party.
In 1847, rescuers reached the stranded Donner Party in the Sierra Nevada, marking a harrowing chapter in American westward expansion. Trapped by snow, the emigrants faced starvation and dire conditions.
The rescue efforts, led by a determined team, showcased human resilience and compassion. However, the ordeal’s tragic outcomes, including cannibalism, highlighted the perilous nature of pioneer journeys.
This event remains a poignant reminder of the challenges faced by settlers seeking new lives. The Donner Party’s story is a testament to survival against the odds and the harsh realities of frontier life.
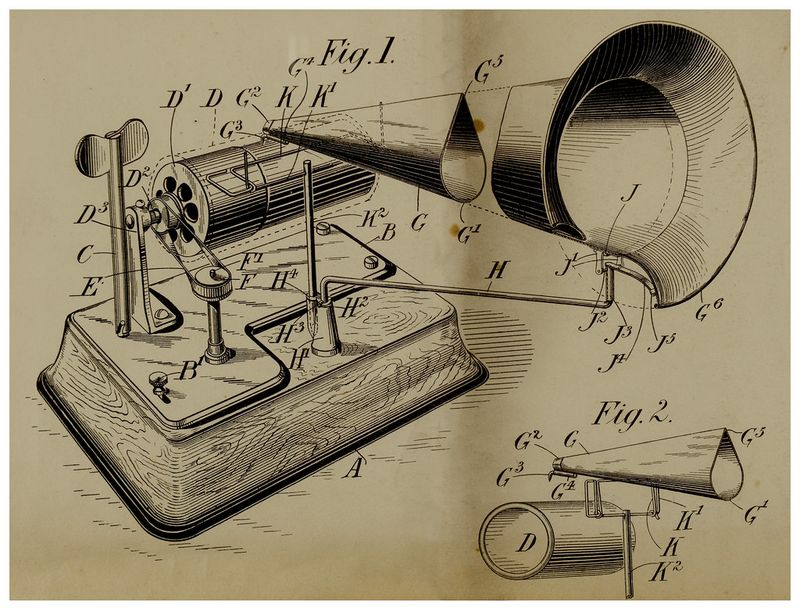
13. 1878 – Thomas Edison patents the phonograph.
On this day in 1878, Thomas Edison patented the phonograph, revolutionizing sound recording and reproduction. Edison’s invention marked the dawn of the audio age, enabling voices and music to be captured and replayed.
The phonograph’s impact was profound, influencing entertainment, communication, and education. Edison’s ingenuity and persistence exemplified the era’s spirit of innovation.
The phonograph paved the way for future technological advancements in audio and media. Edison’s achievement remains a cornerstone in the history of inventions, illustrating the transformative power of human creativity and curiosity.
14. 1884 – Major tornado outbreak strikes the U.S. South.
In 1884, a major tornado outbreak struck the U.S. South, causing widespread destruction and loss of life. The event, known as the Enigma Outbreak, affected multiple states, leaving communities in disarray.
The tornadoes underscored the region’s vulnerability to natural disasters, prompting discussions on preparedness and response strategies. Despite the devastation, communities rallied together in recovery efforts.
This historical weather event highlights the unpredictable nature of tornadoes and the importance of resilience in the face of adversity. The lessons learned from the outbreak continue to inform modern meteorological practices and emergency planning.
15. 1913 – Pedro Lascuráin serves as Mexico’s president for 45 minutes.
On February 19, 1913, Pedro Lascuráin served as Mexico’s president for just 45 minutes, the shortest presidency in history. His brief term was part of a political maneuver during a turbulent period known as the Ten Tragic Days.
Lascuráin’s primary role was facilitating a legal transfer of power amidst a coup. His presidency highlighted the volatility and complexities of Mexican politics at the time.
Despite his short tenure, Lascuráin’s contribution ensured constitutional legitimacy. This unique moment illustrates the intricate power dynamics and rapid changes often seen in political landscapes.
16. 1915 – First naval attack on the Dardanelles.
In 1915, the first naval attack on the Dardanelles took place, marking a critical phase in World War I. Allied forces aimed to secure a sea route to Russia, targeting the strategic strait.
The operation faced formidable Ottoman defenses, resulting in significant losses for the Allies. This campaign highlighted the challenges of naval warfare and strategic planning.
The Dardanelles attack had far-reaching implications, affecting military strategies and alliances. Despite its failure, the operation underscored the importance of control over vital maritime passages in global conflicts.
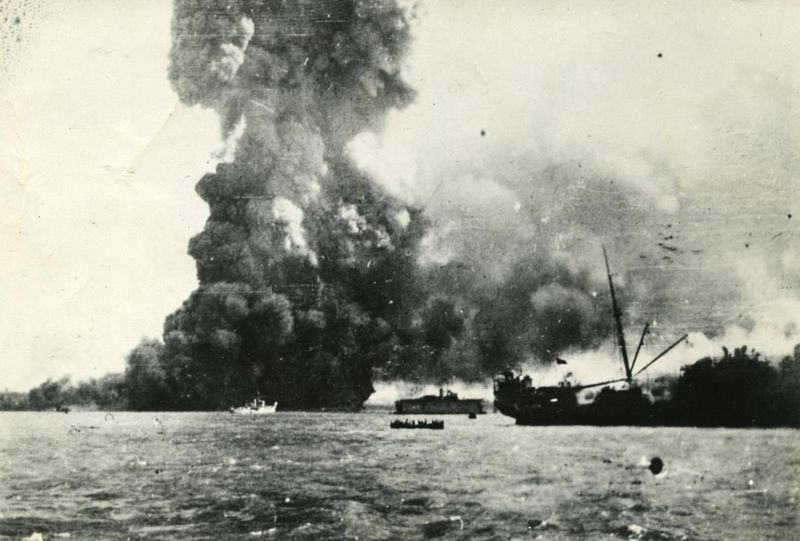
17. 1942 – Japanese warplanes bomb Darwin, Australia.
On February 19, 1942, Japanese warplanes launched a surprise attack on Darwin, Australia, marking the largest single attack on the country in World War II. The bombing caused widespread damage and casualties.
This assault aimed to disrupt Allied operations and instill fear, highlighting the war’s reach into the Pacific. Despite the devastation, Australian defenses responded with resilience.
The bombing of Darwin underscored the vulnerability of territories to aerial warfare and the strategic significance of the Pacific region. It remains a pivotal moment in Australian military history, emphasizing preparedness and unity.
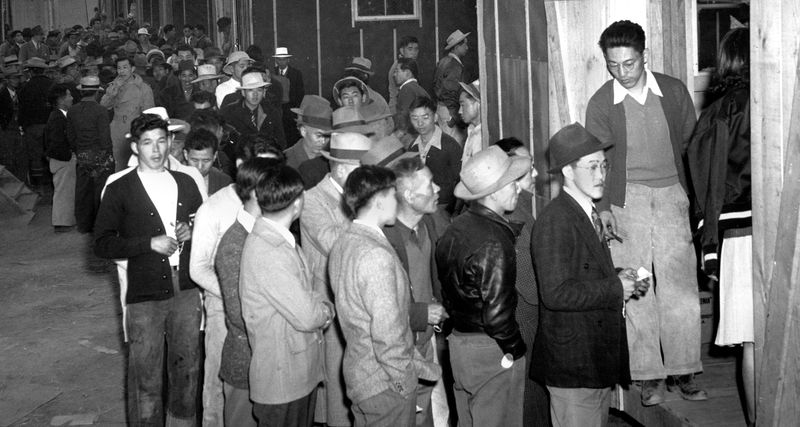
18. 1942 – Roosevelt signs order to intern Japanese Americans.
In 1942, President Franklin D. Roosevelt signed Executive Order 9066, authorizing the internment of Japanese Americans during World War II. This order led to the forcible relocation of over 120,000 individuals, a majority of whom were U.S. citizens.
The internment reflected wartime fears and prejudice, causing significant hardships and loss of civil liberties for those affected. The decision remains controversial, highlighting issues of race, security, and justice.
This event is a stark reminder of the impact of fear on policy decisions and the importance of safeguarding civil rights in times of crisis. Efforts to acknowledge and rectify this injustice continue today.
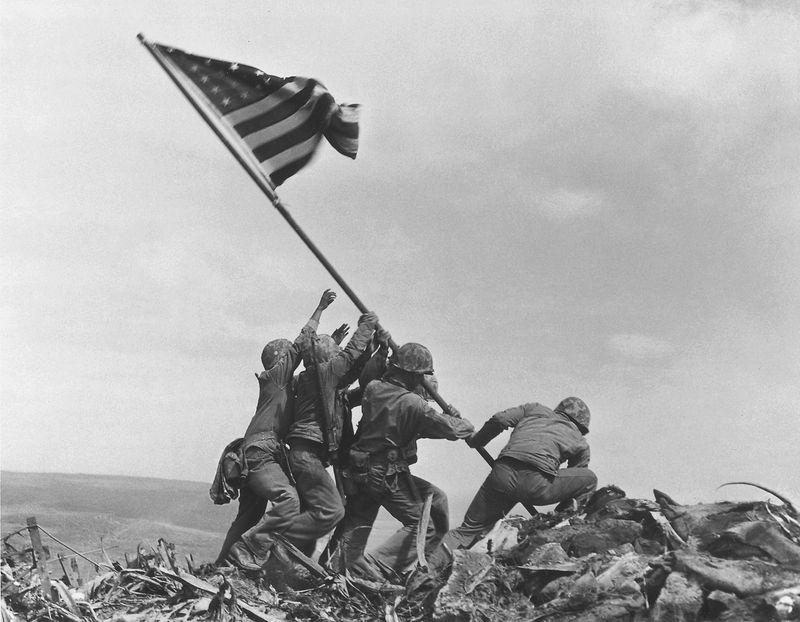
19. 1945 – U.S. Marines land in the Battle of Iwo Jima.
On February 19, 1945, U.S. Marines landed on Iwo Jima, initiating one of the most iconic battles of World War II. The island’s strategic importance for air operations made it a critical target.
The battle was fierce, with Marines facing entrenched Japanese defenses. The iconic image of the flag-raising on Mount Suribachi became a symbol of courage and perseverance.
Iwo Jima’s capture was pivotal in the Pacific campaign, showcasing the tenacity and sacrifice of the forces involved. The battle remains etched in history for its intensity and the profound impact on military strategy.
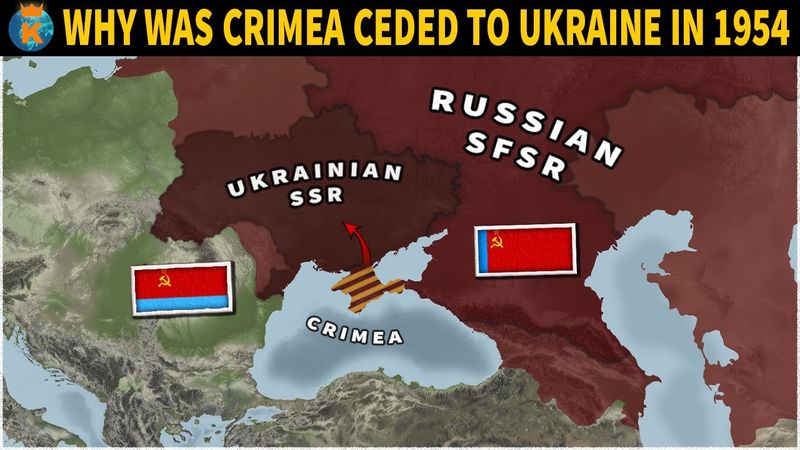
20. 1954 – Soviet Union transfers Crimea to Ukraine.
In 1954, the Soviet Union transferred control of Crimea to Ukraine, a decision that would have lasting geopolitical implications. The transfer was symbolic, marking the 300th anniversary of Ukraine’s union with Russia.
At the time, the move was seen as an administrative decision within the USSR, but it later fueled tensions between Ukraine and Russia. The transfer underscored the complexities of national identity and territorial governance.
This historical event highlights the intricacies of Soviet policies and their long-term effects on regional stability. Crimea’s status remains a contentious issue in international relations today.
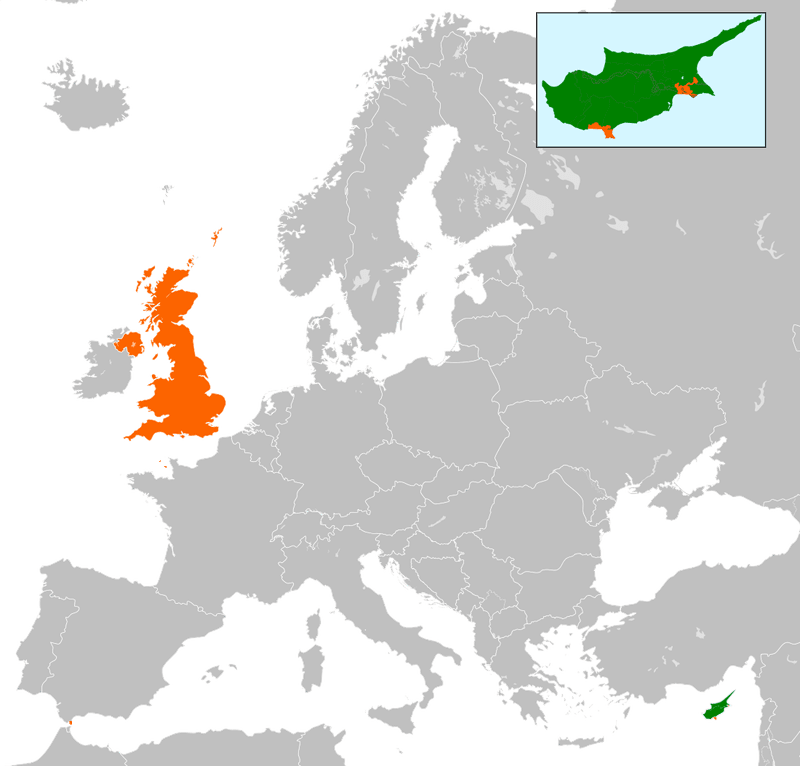
21. 1959 – UK grants Cyprus independence.
On February 19, 1959, the United Kingdom granted independence to Cyprus, ending decades of colonial rule. The agreement followed years of political struggle and negotiations involving Greece, Turkey, and the UK.
Cyprus’s independence marked a new chapter for the island, characterized by aspirations for self-governance and unity. However, ethnic tensions between Greek and Turkish Cypriots posed challenges to stability.
The independence of Cyprus is a testament to the complexities of decolonization and the pursuit of national identity. It underscores the ongoing efforts to achieve peace and reconciliation on the island.
22. 1963 – “The Feminine Mystique” reawakens U.S. feminism.
In 1963, Betty Friedan published “The Feminine Mystique,” a groundbreaking book that reignited the feminist movement in the United States. Friedan’s work challenged traditional roles assigned to women, sparking widespread discussion.
The book’s impact was profound, encouraging women to seek fulfillment beyond domestic duties and advocate for equal rights. It played a pivotal role in the second wave of feminism, influencing societal attitudes and policies.
“The Feminine Mystique” remains a crucial work in understanding gender dynamics and advocating for equality. Its legacy continues to inspire subsequent generations in the pursuit of women’s rights and empowerment.
23. 1976 – U.S. rescinds Japanese internment order.
In 1976, the United States formally rescinded Executive Order 9066, which had authorized Japanese American internment during World War II. This decision was part of a broader effort to address past injustices and restore civil rights.
The rescission symbolized a commitment to reconciliation and acknowledging historical wrongs. It paved the way for reparations and formal apologies in subsequent years.
This act of rescinding the order reflects the nation’s evolving understanding of civil liberties and justice. It serves as a reminder of the continual need to uphold rights and address systemic injustices in society.
24. 1978 – Egyptian commandos killed in Cyprus airport raid.
In 1978, a tragic incident unfolded at Larnaca International Airport in Cyprus, where Egyptian commandos attempting a hostage rescue were killed. The operation aimed to resolve a hijacking situation involving a Cypriot airliner.
Communication breakdowns and international tensions contributed to the operation’s failure, leading to loss of life. This event highlighted the complexities of international cooperation and counter-terrorism efforts.
Despite its tragic outcome, the incident underscored the importance of clear coordination in crisis situations. It remains a somber example of the challenges faced in protecting civilians and addressing global security threats.
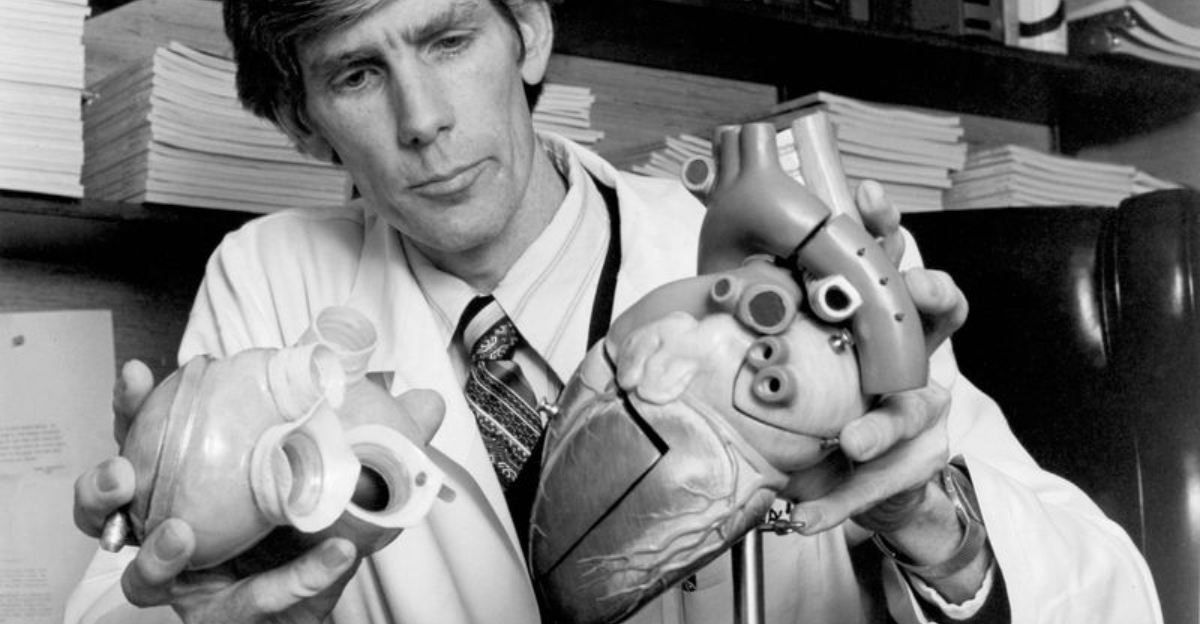
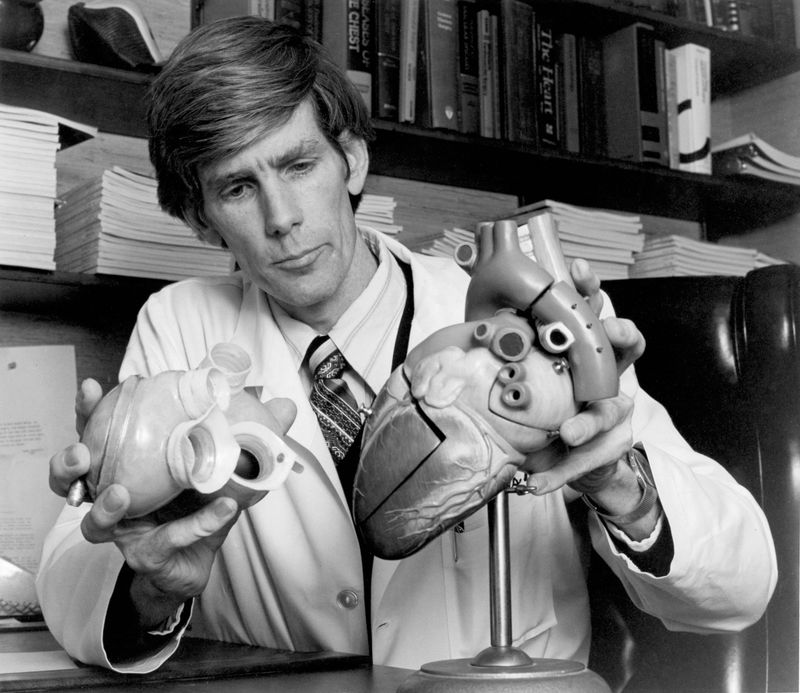
25. 1985 – First artificial heart recipient leaves the hospital.
In 1985, Dr. Barney Clark, the first recipient of an artificial heart, left the hospital, marking a milestone in medical technology. Clark’s journey was a testament to human ingenuity, offering hope to those with heart conditions.
The artificial heart represented a significant advancement in life-saving technology, sparking debates on ethics and quality of life. Clark’s experience provided valuable insights for future innovations.
His discharge symbolized the potential of medical breakthroughs to transform lives. The event remains a pivotal moment in healthcare, encouraging ongoing research and development in cardiac treatments.
26. 1989 – Flying Tiger Line Flight 66 crashes in Malaysia.
On February 19, 1989, Flying Tiger Line Flight 66 tragically crashed near Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, resulting in the loss of all crew members aboard. The accident was attributed to pilot error and adverse weather conditions.
The crash highlighted the complexities of air travel safety and the need for stringent protocols. It led to improved safety measures and training within the aviation industry.
This incident serves as a reminder of the importance of vigilance in air travel operations. The lessons learned contributed to advancements in navigation technology and safety practices, enhancing future aviation security.
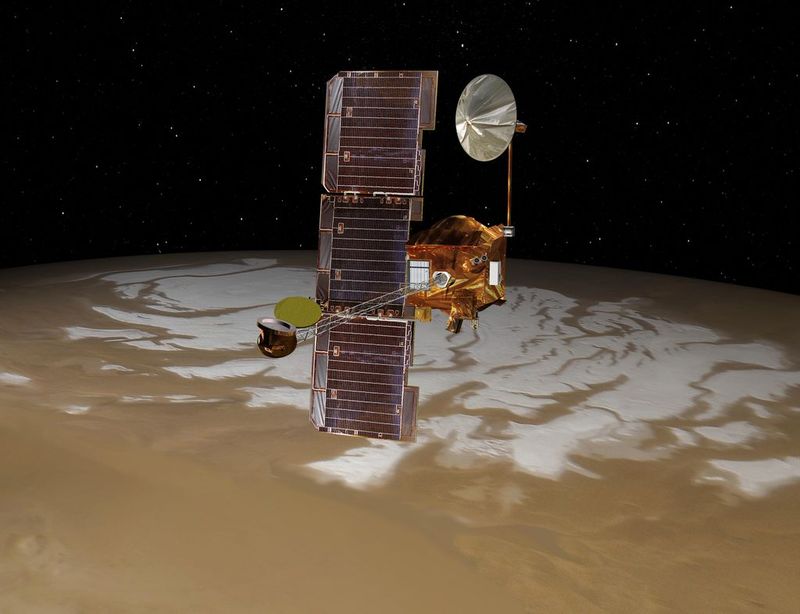
27. 2002 – NASA’s Mars Odyssey begins mapping Mars.
In 2002, NASA’s Mars Odyssey mission began mapping the Martian surface, providing unprecedented insights into the planet’s composition and climate. The spacecraft’s advanced instruments allowed scientists to detect water ice and study Mars’s geology.
This mission revolutionized our understanding of Mars, paving the way for future exploration and discovery. Mars Odyssey’s success highlighted the collaborative efforts of scientists and engineers in space exploration.
The data collected continues to inform research and inspire curiosity about the universe. Mars Odyssey remains a testament to humanity’s pursuit of knowledge and the wonders of our solar system.
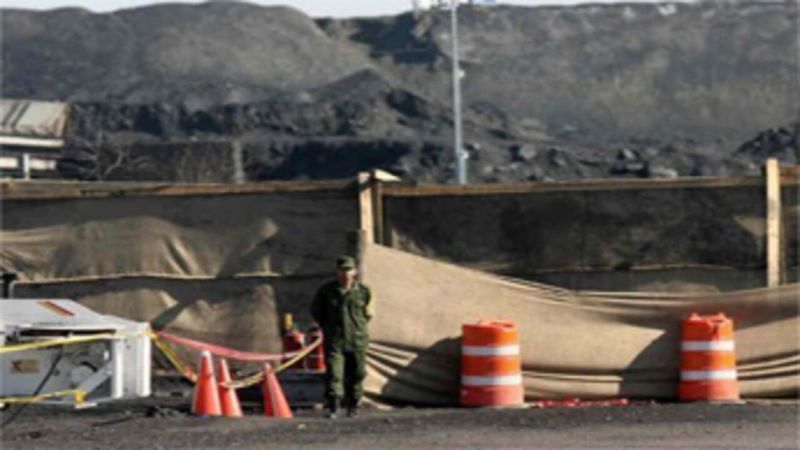
28. 2006 – Methane explosion kills 65 miners in Mexico.
In 2006, a devastating methane explosion occurred at the Pasta de Conchos mine in Mexico, claiming the lives of 65 miners. This tragedy highlighted the inherent dangers of mining and the need for stringent safety measures.
The explosion prompted investigations into mining practices and calls for improved regulations to protect workers. The incident underscored the human cost of industrial operations and the importance of safeguarding labor rights.
This event serves as a somber reminder of the risks faced by miners worldwide. Efforts to enhance safety standards and prevent similar disasters continue to be a priority in the industry.
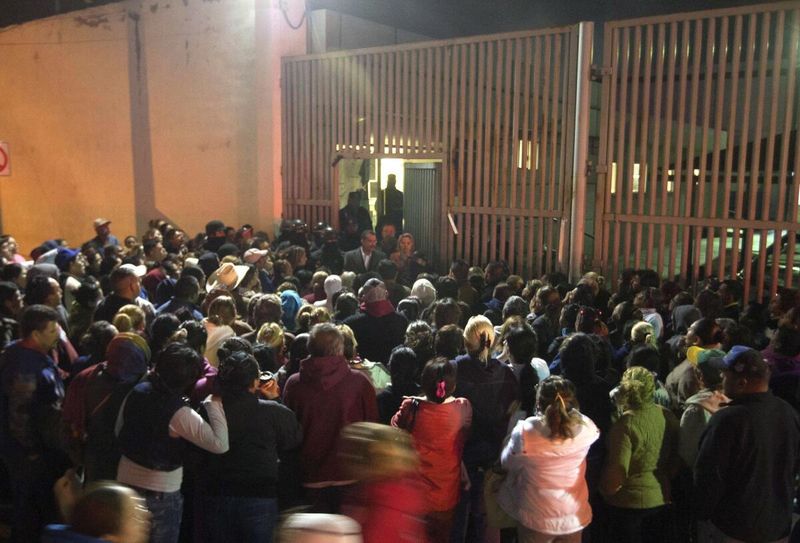
29. 2012 – Deadly prison riot in Nuevo León, Mexico.
In 2012, a deadly riot erupted at the Apodaca prison in Nuevo León, Mexico, resulting in the deaths of 44 inmates. The violence was linked to gang rivalries and highlighted systemic issues within the prison system.
The riot underscored the challenges of managing overcrowded and underfunded facilities. It prompted calls for comprehensive prison reforms and improved security measures.
This incident drew attention to the broader issues of crime and corruption affecting Mexico. It remains a critical case study in understanding the complexities of prison management and the need for effective rehabilitation programs.
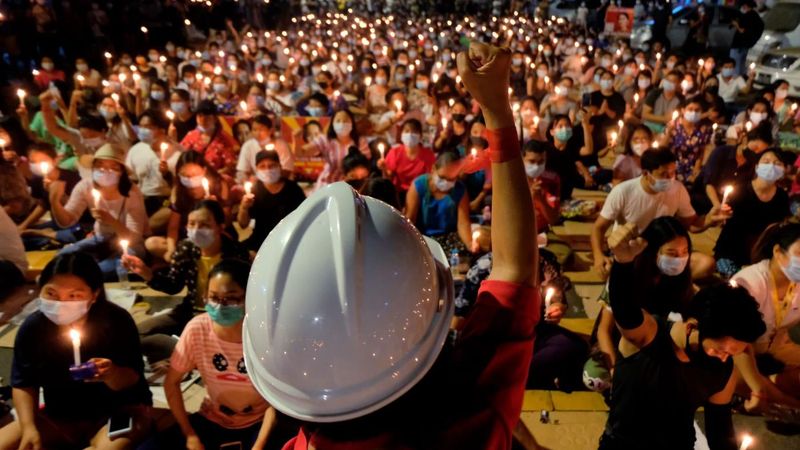
30. 2021 – First casualty in Myanmar anti-coup protests.
In 2021, the first casualty occurred during Myanmar’s anti-coup protests, marking a significant and tragic moment in the nation’s struggle for democracy. The protests followed a military coup that ousted the elected government.
The unrest illustrated the deep divisions and tensions within Myanmar, as citizens demanded the restoration of civilian rule. The loss of life intensified international scrutiny and calls for action.
This moment in Myanmar’s history underscores the ongoing fight for democratic governance and human rights. It serves as a sobering reminder of the sacrifices made in the pursuit of freedom and justice.