In today’s fast-paced, technology-driven world, certain essential skills that were once second nature to previous generations are gradually fading away.
Gen Z, the first generation to grow up with smartphones and the internet at their fingertips, is experiencing a unique cultural shift.
While technology offers incredible conveniences, it also means that young people are missing out on learning crucial skills necessary for independence and self-reliance.
This blog post explores 20 key skills that Gen Z is losing and discusses the broader societal implications of this trend.
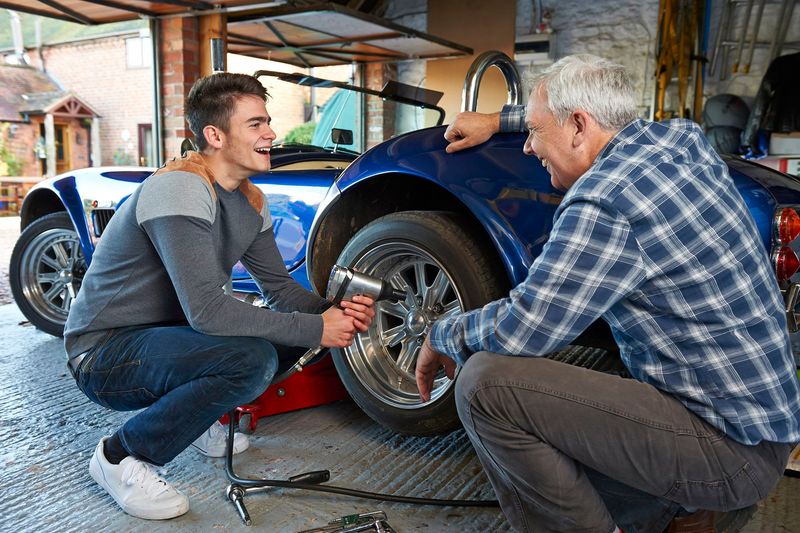
1. Basic Car Maintenance
Being able to perform basic car maintenance tasks like changing a tire, checking oil levels, or jump-starting a car is becoming less common among Gen Z. As cars become more technologically advanced, many young people rely heavily on roadside assistance and may not see the need to learn these skills.
This can lead to increased dependency on services and a lack of preparedness in emergency situations. Encouraging a hands-on approach and providing educational workshops can help bridge this gap. Such skills empower individuals to feel more confident and self-reliant when driving.
2. Handwriting and Cursive
The art of handwriting, particularly cursive writing, is becoming a lost skill in the digital age. With typing and texting dominating communication methods, many Gen Z individuals struggle with reading and writing in cursive. Schools are shifting focus from handwriting to digital literacy, leaving a gap in traditional writing skills.
This decline affects not only the ability to read historical documents but also personal expression through writing. Reintroducing cursive lessons in classrooms and encouraging handwritten notes can foster a deeper connection to language and improve cognitive skills.
3. Mental Math
Mental math, once a fundamental skill taught in schools, is waning with the widespread use of calculators and smartphones. Gen Z often relies on digital devices for even simple calculations, diminishing their ability to perform math mentally. This dependence can hinder problem-solving skills and numerical confidence.
Practicing mental math aids in developing a strong mathematical foundation and enhances critical thinking. Encouraging mental math exercises and creating engaging math challenges can help young people improve their arithmetic skills and boost overall academic performance.
4. Spelling Without Autocorrect
In an era dominated by digital communication, spelling proficiency is declining among Gen Z due to the convenience of autocorrect features. Many young people rely heavily on technology to correct their spelling mistakes, which can impede learning.
This reliance on autocorrect can lead to a lack of awareness in spelling nuances and reduce vocabulary development. Encouraging writing exercises without digital aids and promoting spelling games can enhance traditional spelling skills. By fostering these practices, individuals can develop a richer understanding of language and improve written communication.
5. Cooking from Scratch
The ability to cook from scratch is becoming a rare skill among Gen Z, who often opt for fast food, meal kits, or pre-packaged meals. With busy lifestyles and the convenience of ready-made food, traditional cooking skills are waning.
This decline can lead to unhealthy eating habits and a lack of culinary creativity. Learning to cook not only promotes healthier eating but also fosters independence and cultural appreciation. Encouraging cooking classes and providing simple, step-by-step recipes can inspire young people to explore the culinary world and enjoy homemade meals.
6. Sewing and Mending Clothes
Sewing and mending clothes are becoming obsolete skills for many in Gen Z, who often prefer replacing garments rather than repairing them. The fast fashion industry and a throwaway culture contribute to this trend, leading to increased waste.
Knowing how to sew can extend the life of clothing and promote sustainable living. It also offers a sense of accomplishment and creativity. Providing sewing workshops and DIY repair tutorials can empower young people to embrace these skills, reduce their environmental impact, and foster a more resourceful mindset.
7. Reading a Physical Map
With the advent of GPS technology, reading physical maps is becoming a lost skill among Gen Z. Many young people rely on digital navigation tools, which can lead to difficulties when technology fails or lacks coverage.
Understanding how to read a physical map enhances spatial awareness and problem-solving skills. Encouraging outdoor activities that require map reading and offering workshops on navigation can help revive this crucial skill. It also fosters a sense of adventure and independence, allowing individuals to connect with their surroundings more deeply.
8. Basic Home Repairs
Performing basic home repairs, such as fixing a leaky faucet or unclogging a drain, is becoming less common among Gen Z. As professional services become more accessible, many young people lack these hands-on skills. This dependency can lead to higher costs and less self-sufficiency.
Learning basic repairs can save money and increase confidence in handling everyday challenges. Offering home repair workshops and online tutorials can help young people gain practical experience. These skills promote independence and create a sense of pride in maintaining one’s living space.
9. Writing a Formal Letter
The art of writing a formal letter is declining as emails and texts replace traditional correspondence methods. Many Gen Z individuals struggle with professional communication, which can affect their career prospects.
Understanding the nuances of formal writing can enhance written communication skills and project professionalism. Encouraging letter-writing exercises and teaching the etiquette of formal correspondence can help young people develop these essential skills. This practice not only improves job prospects but also fosters a deeper appreciation for thoughtful communication.
10. Memorizing Important Phone Numbers
The ability to memorize important phone numbers is fading with the convenience of digital contact lists. Many Gen Z individuals store numbers in their smartphones without committing them to memory, which can be problematic in emergencies.
Knowing key phone numbers fosters independence and preparedness. Encouraging the practice of memorizing a few essential numbers can enhance security and confidence in unforeseen circumstances. This skill promotes mindfulness and reinforces the importance of being resourceful when technology is unavailable.
11. Using a Landline or Rotary Phone
Using a landline or rotary phone is becoming a foreign concept to many Gen Z individuals, who have grown up with mobile phones. This can lead to confusion in situations where traditional phones are still in use.
Understanding how to operate these phones bridges generational gaps and enriches historical knowledge. Encouraging young people to explore different communication devices fosters adaptability and appreciation for technological advancements. Hands-on experience with landlines can also provide insight into the evolution of communication technology.
12. Navigating Without GPS
The skill of navigating without GPS is becoming rare among Gen Z, who often rely on digital maps for directions. This dependence can pose challenges when technology fails or signals are weak.
Learning to navigate using landmarks and street signs enhances spatial awareness and problem-solving abilities. Encouraging exploration and providing guidance on traditional navigation methods can help young people develop these skills. It fosters a sense of adventure and independence, allowing for a deeper connection with one’s environment.
13. Face-to-Face Conflict Resolution
Face-to-face conflict resolution skills are declining as digital communication becomes the norm. Many Gen Z individuals find it challenging to address disagreements in person, which can affect personal and professional relationships.
Practicing direct communication fosters empathy and understanding. Encouraging face-to-face interactions and providing conflict resolution training can help young people develop these essential skills. This approach enhances interpersonal relationships and promotes a more harmonious and cooperative society.
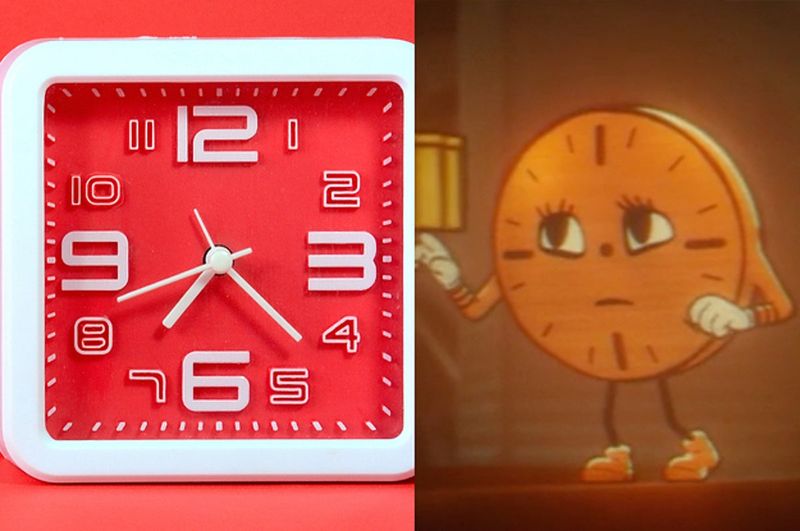
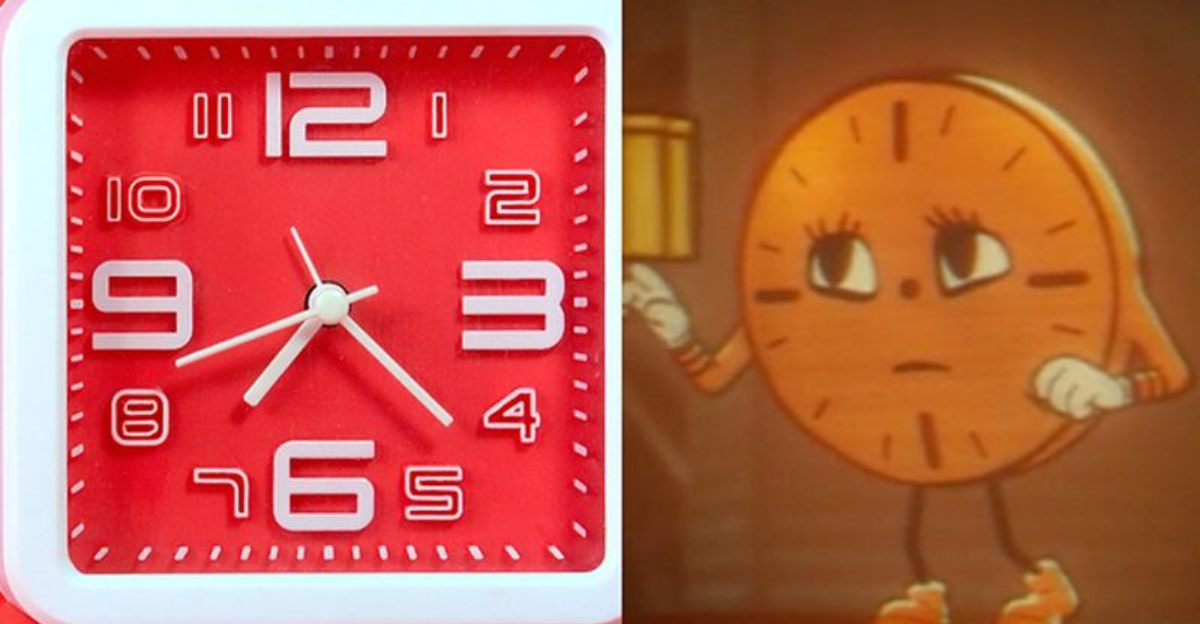
14. Understanding Analog Clocks
Reading analog clocks is becoming a lost skill as digital devices dominate timekeeping. Many Gen Z individuals struggle with understanding clock faces, which can hinder time management skills.
Learning to read an analog clock enhances cognitive development and reinforces time-related concepts. Encouraging the use of analog clocks in educational settings can help young people develop these skills. This practice promotes a comprehensive understanding of time and improves punctuality and scheduling abilities.
15. Handwriting a Signature
The traditional act of handwriting a signature is being replaced by e-signatures and digital approvals. Many Gen Z individuals are unfamiliar with crafting a personal signature, which remains an important part of identity.
Learning to create a unique signature is a crucial skill that fosters individuality and professionalism. Encouraging the practice of signature development can help young people appreciate its value. This skill not only enhances personal documentation but also strengthens one’s sense of identity and authenticity.
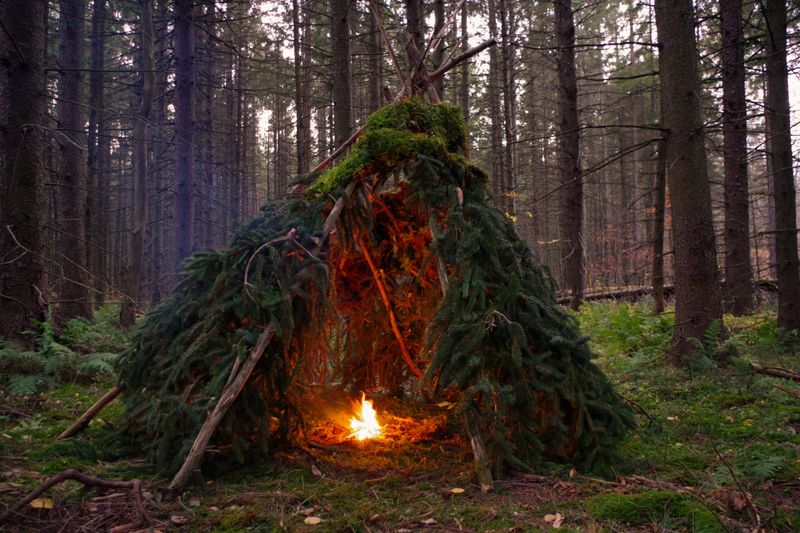
16. Outdoor Survival Skills
Outdoor survival skills, such as fire-starting and foraging, are becoming rare with urbanization. Many Gen Z individuals lack these essential techniques, which can be critical in emergency situations.
Learning survival skills promotes self-sufficiency and a deeper connection with nature. Encouraging outdoor education and survival workshops can help young people develop these abilities. This knowledge not only enhances personal safety but also fosters a respect for the natural world and its resources.
17. Public Speaking
Confidence in public speaking is waning as social media and texting reduce face-to-face communication. Many Gen Z individuals experience anxiety when addressing an audience, which can impact career opportunities.
Practicing public speaking enhances communication skills and boosts self-esteem. Encouraging participation in speech clubs and public speaking courses can help young people overcome fears. This skill promotes personal and professional growth, allowing individuals to express themselves effectively in various settings.
18. Etiquette and Manners
Etiquette and manners are fading as digital interactions replace traditional social norms. Many Gen Z individuals lack basic social graces, which can affect personal and professional relationships.
Learning etiquette enhances social interactions and fosters respect and kindness. Encouraging polite behavior and offering etiquette workshops can help young people develop these essential skills. This practice not only improves relationships but also creates a more respectful and considerate society.
19. Critical Thinking Without Google
The ability to think critically without relying on Google is diminishing as immediate internet access becomes the norm. Many Gen Z individuals struggle with independent problem-solving and analysis.
Developing critical thinking skills fosters innovation and adaptability. Encouraging independent research and problem-solving activities can help young people strengthen these abilities. This approach enhances cognitive development and empowers individuals to think creatively and make informed decisions.
20. Patience and Long-Term Focus
The capacity for patience and long-term focus is waning with the rise of instant gratification from social media and technology. Gen Z often experiences shortened attention spans, impacting perseverance.
Cultivating patience promotes mental resilience and goal achievement. Encouraging mindfulness practices and long-term projects can help young people develop these traits. This focus enhances personal growth and allows for deeper engagement with tasks and relationships, fostering a more balanced and fulfilling life.