Explore 20 surprising and enlightening facts about Native Americans that showcase their diverse cultures, historical significance, and enduring legacy.
From ancient civilizations to modern contributions, these insights challenge common stereotypes and highlight the rich tapestry of Indigenous heritage across North America.
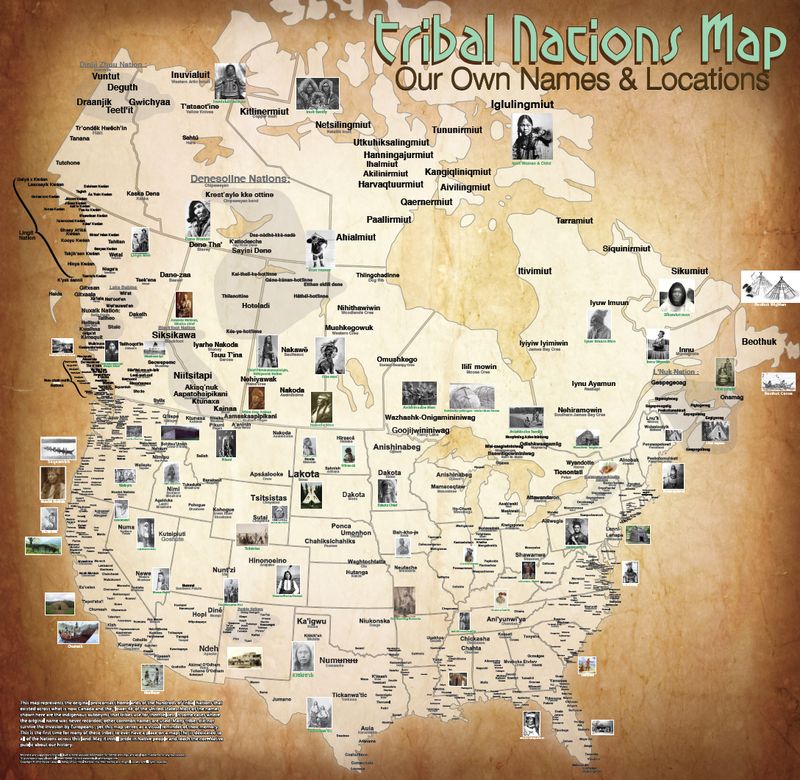
1. Hundreds of Distinct Nations
Contrary to the perception of a monolithic group, there are currently 574 federally recognized tribes in the United States, each with its own unique language, culture, and governmental system.
This diversity is a testament to the rich and varied history of Indigenous peoples across North America. By understanding the distinct identities of these tribes, we can appreciate the complexity and richness of Native American heritage.
These tribes continue to thrive and promote their traditions today, offering a vibrant mosaic of cultures and histories that enrich the nation as a whole.
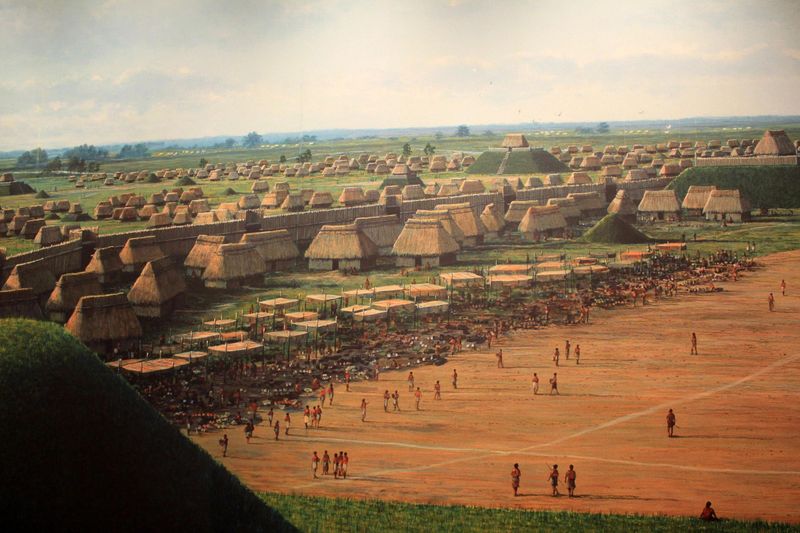
2. Ancient Urban Centers
Long before European contact, Indigenous peoples built sophisticated city-states like Cahokia, near present-day St. Louis. At its peak around 1100 CE, Cahokia may have rivaled or even exceeded the population of contemporary European cities.
These urban centers were hubs of trade, culture, and political life, demonstrating advanced societal organization and architectural prowess.
The monumental earthen mounds of Cahokia are a testament to the ingenuity and labor of its builders, reflecting complex social hierarchies and ceremonial practices.
Today, Cahokia stands as a symbol of the advanced civilizations that thrived in pre-Columbian North America.
3. Iroquois Influence on Democracy
The Iroquois Confederacy’s Great Law of Peace is often cited as an inspiration for certain concepts found in the U.S. Constitution, particularly ideas about federalism and participatory governance.
This confederacy, comprised of six nations, emphasized unity and collective decision-making, which resonated with early American leaders seeking to establish a democratic system.
The influence of the Iroquois model is a reminder of the significant contributions Indigenous governance systems have made to modern political thought.
By recognizing this legacy, we can better appreciate the depth of Indigenous influence on the development of democratic ideals.
4. Matrilineal Societies
Many tribes, including the Hopi, Navajo, and certain Iroquois nations, traditionally trace descent through the mother’s line, a system known as matrilineality.
This practice grants women significant influence in community decisions and property rights, challenging patriarchal norms.
Matrilineal societies highlight the central role women have played in maintaining cultural continuity and social structure within their communities.
Today, these practices continue to empower women and promote gender equality, demonstrating the progressive social systems that have existed among Indigenous peoples for centuries.
The resilience of these systems underscores the importance of recognizing diverse cultural frameworks.
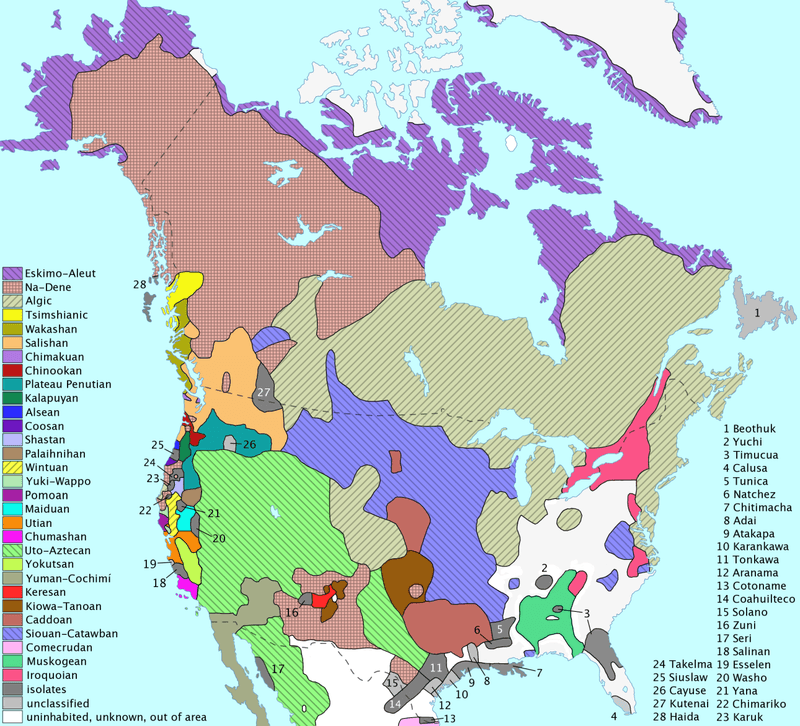
5. Diverse Language Families
Before European colonization, North America was home to hundreds of languages from more than a dozen major language families. This linguistic diversity reflects the rich cultural tapestry of Indigenous peoples across the continent.
Today, many efforts are underway to revitalize these languages, recognizing their importance in preserving cultural identity and heritage.
Language revitalization programs, including immersion schools and digital tools, are helping to ensure these languages continue to thrive.
By supporting these efforts, we acknowledge the vital role language plays in maintaining cultural continuity and fostering a deeper understanding of Indigenous histories and worldviews.
6. Sophisticated Agricultural Techniques
The “Three Sisters”—corn, beans, and squash—exemplify intercropping methods developed by Indigenous farmers. This agricultural technique utilizes the natural symbiosis between the plants to enhance soil fertility and prevent pests.
Corn provides a structure for beans to climb, beans enrich the soil with nitrogen, and squash covers the ground to retain moisture. This method reflects a deep understanding of ecological principles and sustainable farming practices.
Indigenous agricultural knowledge continues to inspire modern sustainable farming techniques, highlighting the innovative and forward-thinking nature of these ancient practices. By embracing these methods, we promote environmental stewardship and food security.
7. Impressive Horse Cultures
Horses were reintroduced to the Americas by Spanish colonizers, and tribes like the Comanche and Lakota quickly became master horse riders and breeders.
The horse transformed their economies, warfare strategies, and social structures, becoming integral to their cultural identity. The adaptability and skill of these tribes in developing horse cultures demonstrate their resilience and ingenuity.
Today, the legacy of these equestrian traditions continues to thrive, celebrated in cultural events and ceremonies.
By understanding the significance of the horse in Indigenous cultures, we gain insight into the dynamic ways these communities adapted to changing circumstances.
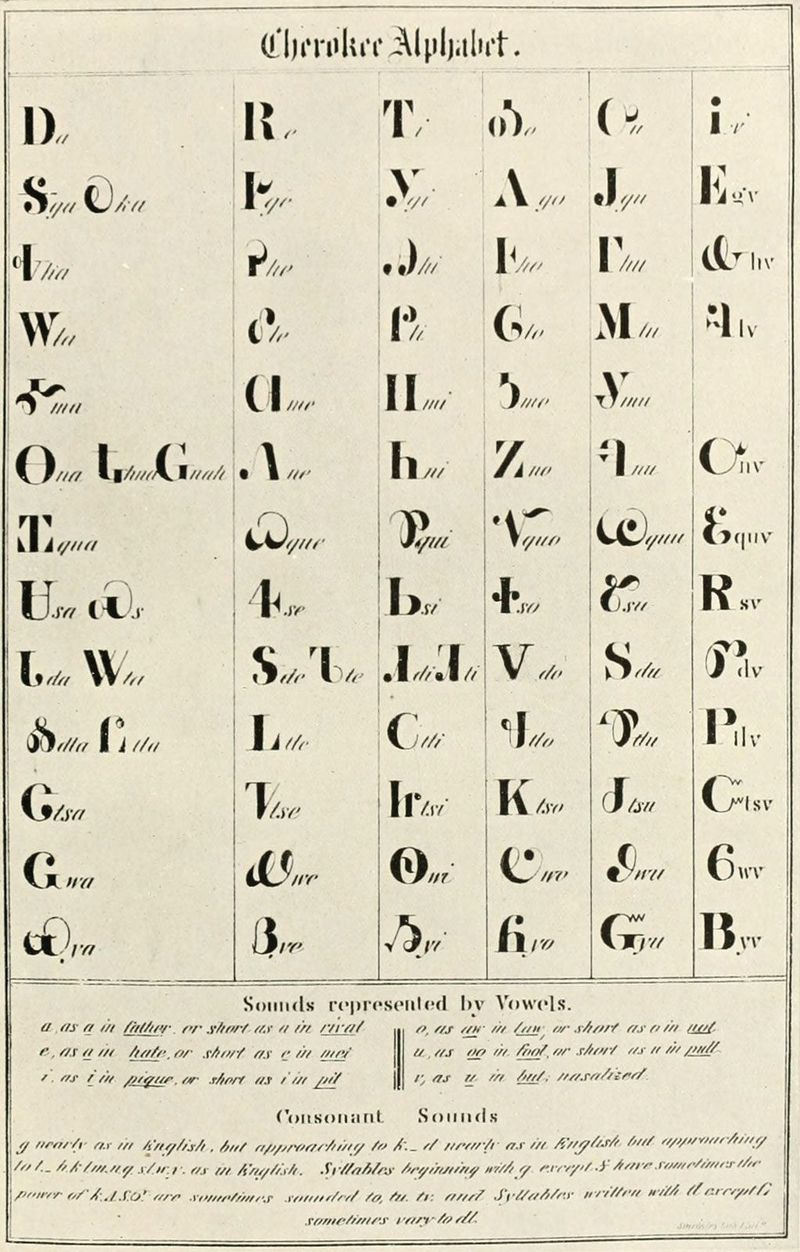
8. Cherokee Syllabary
In the early 19th century, Sequoyah developed a written syllabary for the Cherokee language, significantly boosting literacy rates in the Cherokee Nation.
This achievement surpassed literacy rates in many contemporary European populations, empowering the Cherokee people and preserving their language and culture.
The syllabary facilitated communication, education, and cultural continuity, reflecting the innovative spirit of Indigenous peoples. Sequoyah’s creation remains a symbol of linguistic and cultural resilience, inspiring modern language preservation efforts.
By celebrating this milestone, we honor the determination and creativity that have long characterized Native American communities in their pursuit of knowledge and cultural preservation.
9. Counting Coup
Among Plains tribes, “counting coup” was an alternative to lethal combat, emphasizing bravery and skill over violence. A warrior demonstrated courage by touching an enemy without harming them, often using a special stick.
This practice highlighted the value placed on honor and reputation rather than bloodshed. Counting coup fostered a culture of bravery and respect, where skill and strategy were revered.
This tradition challenges conventional perceptions of warfare and underscores the complexity of Indigenous cultural practices.
By recognizing the nuances of these traditions, we gain a deeper appreciation for the diverse ways Indigenous peoples have understood and approached conflict.
10. Early Environmental Stewardship
Many Indigenous cultures viewed land not as a commodity but as a communal resource to be honored and cared for. This perspective fostered sustainable land management practices and a harmonious relationship with nature.
Indigenous environmental stewardship is often framed as a precursor to modern environmental consciousness, emphasizing reciprocity and interconnectedness with the natural world.
These traditions continue to inform contemporary conservation efforts, highlighting the enduring wisdom of Indigenous ecological knowledge.
By integrating these principles, we can develop more sustainable and equitable approaches to environmental management, ensuring the health and vitality of our planet for future generations.
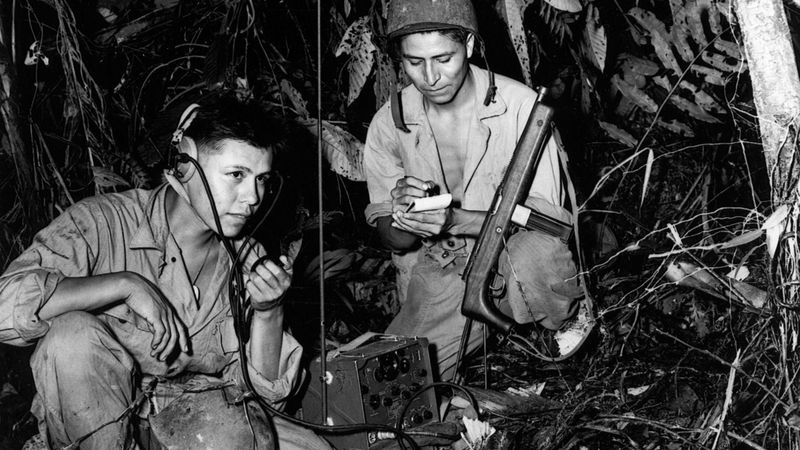
11. Code Talkers in WWII
During World War II, Navajo and other Indigenous language speakers played crucial roles as code talkers, using their languages to create unbreakable military codes. These codes secured Allied communication lines, contributing significantly to the war effort.
The code talkers’ achievements highlight the strategic importance of linguistic diversity and the vital contributions of Indigenous peoples to global events.
Their legacy is a testament to the resilience and ingenuity of Native American communities, whose languages became tools of warfare.
Today, their story inspires efforts to preserve Indigenous languages and celebrate the unique skills and perspectives they bring to the world.
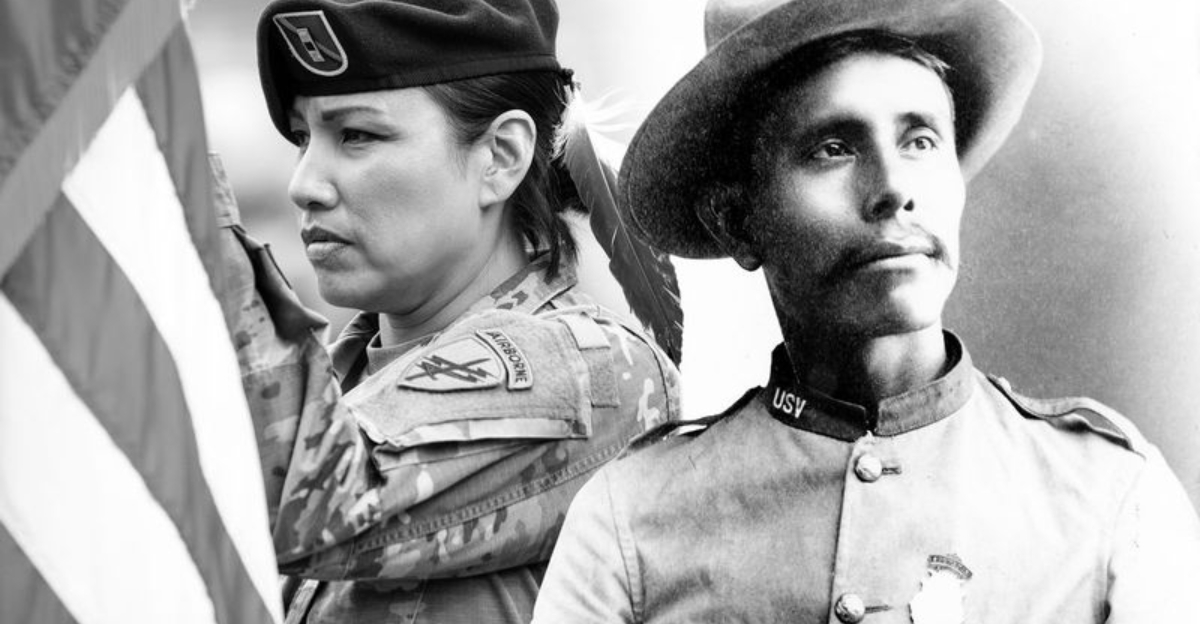
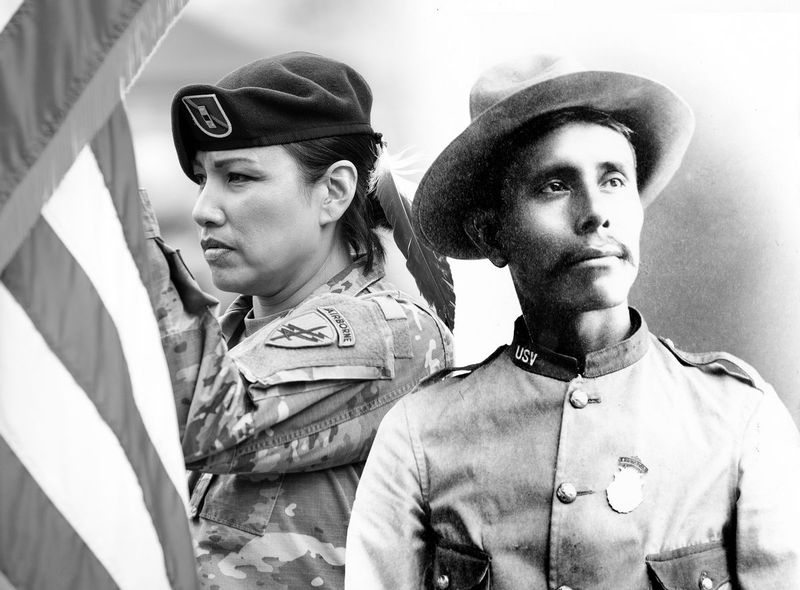
12. High Military Service Rate
Historically, Native Americans have served in the U.S. Armed Forces at one of the highest rates per capita of any demographic group. This dedication reflects both socioeconomic factors and longstanding warrior traditions within Indigenous cultures.
Military service offers opportunities for economic advancement and education, while also honoring a cultural legacy of courage and duty.
The high service rate among Native Americans underscores their significant contributions to the nation’s defense and security.
By acknowledging this history, we can better appreciate the complex motivations and enduring values that drive Indigenous service members in their commitment to the armed forces.
13. Contemporary Urban Life
While many associate Native Americans primarily with reservations, the majority now live in urban areas. Cities like New York and Los Angeles have large populations of diverse tribal members, reflecting the dynamic adaptability of Indigenous peoples.
Urban life offers new opportunities and challenges, as Native Americans navigate cultural preservation and modern realities. Community centers, cultural events, and advocacy groups play vital roles in supporting urban Indigenous populations.
By recognizing the vibrant presence of Native Americans in cities, we challenge stereotypes and embrace the diverse experiences and contributions of Indigenous peoples in contemporary society.
14. Dual Citizenship
Members of federally recognized tribes hold citizenship with both their own tribal nation and the United States, reflecting a unique government-to-government relationship.
This dual citizenship acknowledges the sovereignty of tribal nations while integrating Native Americans into the broader national framework.
It represents a complex legal and cultural identity, balancing traditional values with contemporary civic responsibilities.
Understanding this dual status is crucial for appreciating the distinct political and social dynamics of Native American life.
By respecting tribal sovereignty, we honor the autonomy and self-determination of Indigenous peoples in managing their affairs and preserving their heritage.
15. Varied Economic Enterprises
Beyond casinos, many tribes operate successful businesses in fields like energy, agriculture, entertainment, and manufacturing. Some own major wind farms, produce agricultural goods, or distribute globally recognized consumer products.
This economic diversity reflects the entrepreneurial spirit and adaptability of Native American communities. By exploring varied economic enterprises, tribes strengthen their sovereignty and create opportunities for development and self-sufficiency.
These endeavors challenge stereotypes and highlight the innovative contributions of Indigenous peoples to the national economy.
Supporting these efforts promotes economic justice and empowers Native American communities to thrive in a rapidly changing world.
16. Colonial Diseases’ Impact
Infectious diseases introduced by Europeans caused devastating population losses among Indigenous communities, sometimes wiping out entire groups long before direct contact occurred.
The spread of diseases such as smallpox, measles, and influenza had catastrophic effects, altering the social and cultural landscapes of Native America.
Despite these challenges, Indigenous peoples demonstrated remarkable resilience, adapting to new realities and preserving their cultures against the odds.
Understanding the impact of colonial diseases is essential for acknowledging the historical injustices faced by Native American communities.
This awareness fosters empathy and supports efforts to address contemporary health disparities among Indigenous populations.
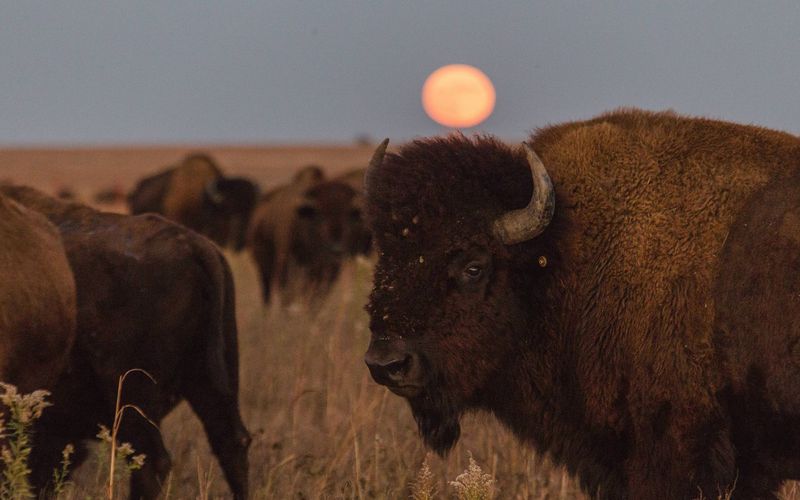
17. Bison Restoration Efforts
Indigenous-led programs are working to restore bison herds, which were nearly hunted to extinction in the 19th century. This reintroduction is culturally and ecologically significant, symbolizing resilience and restoration.
Bison hold a central place in the traditions and economies of many Plains tribes, serving as a source of food, materials, and cultural identity. The restoration efforts contribute to ecological balance and biodiversity, while also revitalizing cultural connections.
By supporting these initiatives, we honor the deep relationship between Indigenous peoples and the natural world, fostering partnerships that promote conservation and cultural revitalization.
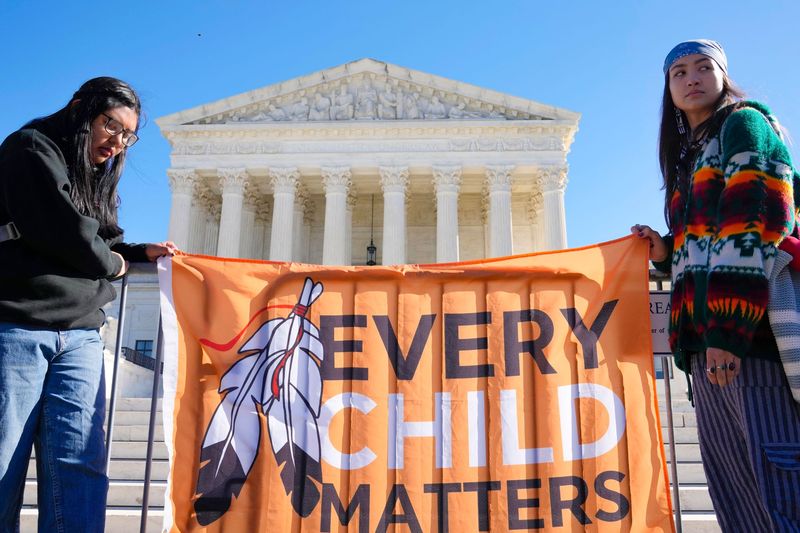
18. Indian Child Welfare Act (ICWA)
Enacted in 1978, the Indian Child Welfare Act (ICWA) gives tribal governments a strong voice in child custody proceedings. This legislation aims to prevent the separation of Indigenous children from their extended families and culture.
The ICWA recognizes the importance of cultural continuity and the unique rights of tribal nations in determining the welfare of their children.
By prioritizing placement with family or tribe members, the ICWA supports the preservation of Indigenous communities and their future generations.
This act underscores the value of cultural identity and the right of Indigenous peoples to raise their children within their traditions.
19. Modern Language Preservation
Tribes are using immersion schools, digital apps, and community classes to revitalize endangered languages, safeguarding cultural identity for future generations.
These efforts reflect a commitment to linguistic and cultural preservation, recognizing language as a vital component of heritage.
By harnessing modern technology and educational strategies, communities are ensuring that their languages continue to thrive in contemporary society.
Language preservation initiatives foster pride and connection to cultural roots, empowering Indigenous youth to carry their traditions forward.
Supporting these programs promotes cultural diversity and strengthens the resilience of Native American communities in the face of ongoing challenges.
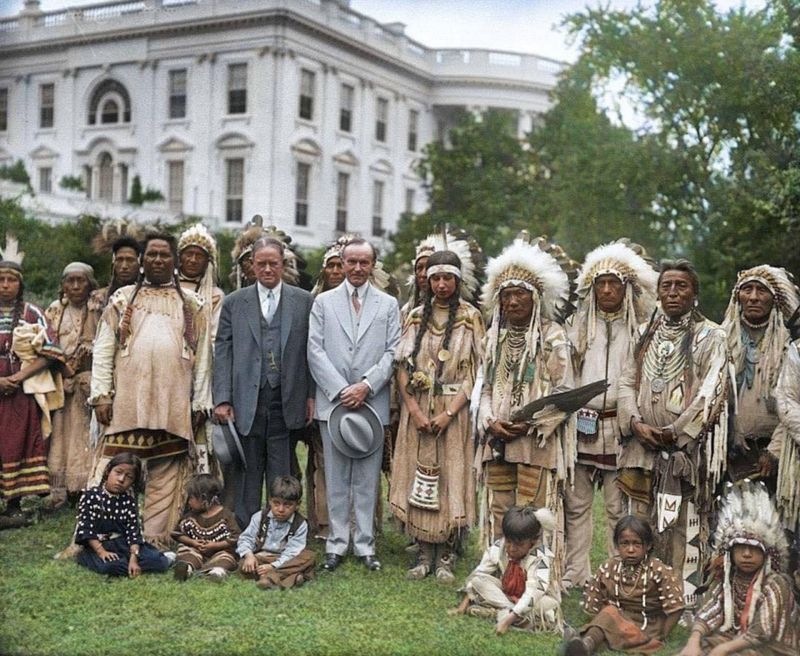
20. Tribal Sovereignty
Federally recognized tribes hold sovereign status under U.S. law, maintaining the right to govern themselves, manage resources, and uphold distinct legal and cultural practices on their lands.
Tribal sovereignty is a cornerstone of Native American identity, reflecting the autonomy and self-determination of Indigenous peoples.
This status enables tribes to negotiate with federal and state governments, manage economic enterprises, and preserve cultural traditions.
Understanding tribal sovereignty is essential for respecting the unique political and social dynamics of Indigenous communities. By supporting sovereignty, we honor the enduring legacy of Native American resilience and the right to self-governance.