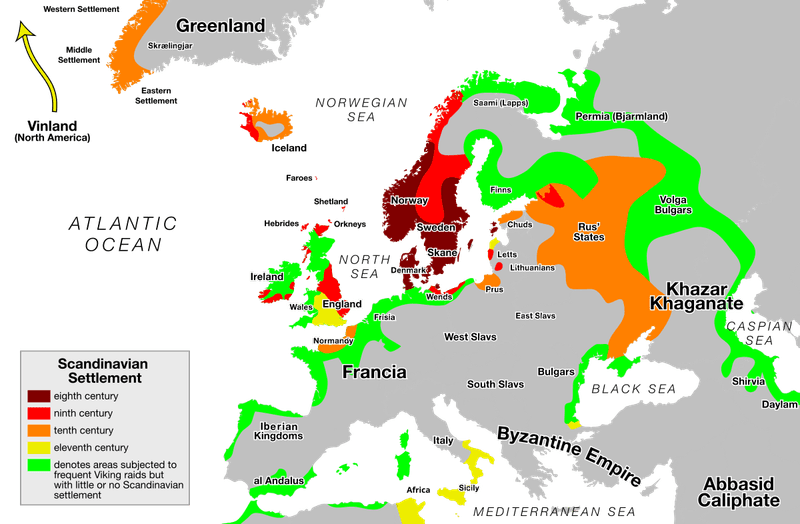
Explore the fascinating hidden truths about the Vikings’ journey to America. These Norse adventurers reached the New World long before Columbus, leaving behind traces of their presence in places like Newfoundland and narratives in the Icelandic Sagas.
From their initial settlements to interactions with native peoples, the Vikings’ voyages are filled with intriguing details and mysteries.
Discover the earliest known European settlement, their brief occupations, and the cultural exchanges that took place. Dive into archaeology-backed evidence and the stories that shape our understanding of the Vikings in America.
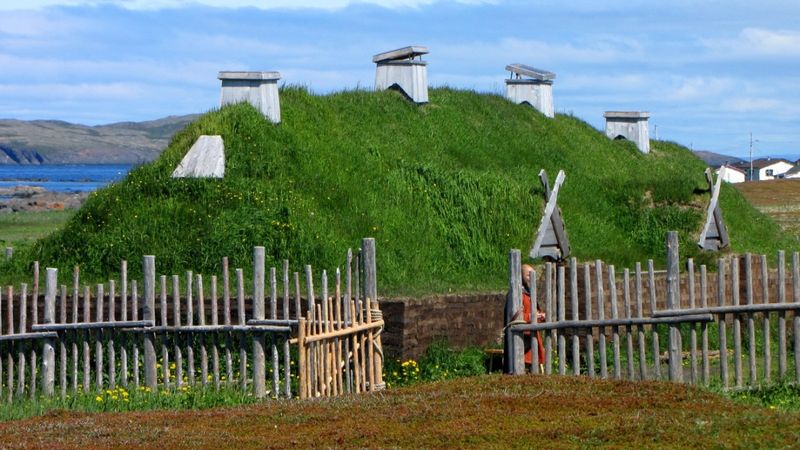
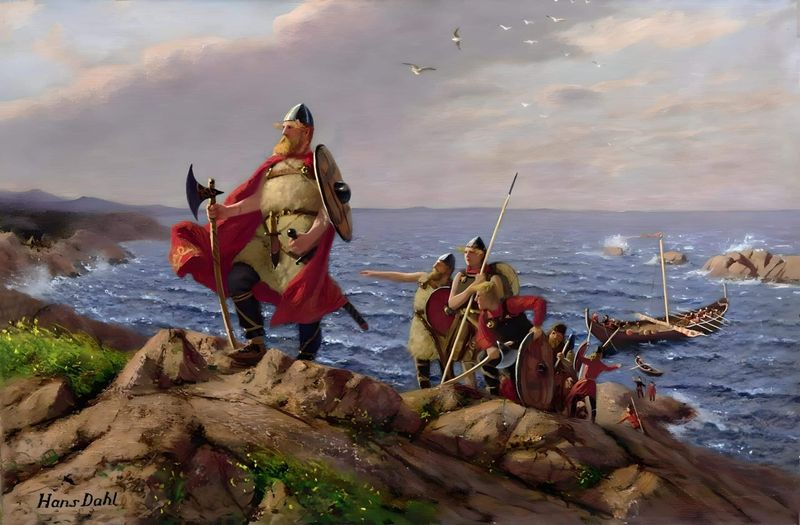
1. Settlement in L’Anse aux Meadows (Newfoundland, Canada)
Nestled in Newfoundland, L’Anse aux Meadows marks the beginning of Viking exploration in North America. This settlement stands as a testament to the Norse’s adventurous spirit.
Archaeological discoveries confirm its existence around AD 1000, making it the earliest known European settlement on the continent.
The site offers a glimpse into the lives of these early explorers, featuring Viking-style longhouses and remnants of their craftsmanship. Although not large, it served as a foothold for further exploration.
Today, it is a UNESCO World Heritage site, preserving the legacy of the Vikings’ brief, but impactful, presence in America.
2. Vinland, Markland, and Helluland
The Icelandic Sagas vividly describe three distinct lands: Vinland, Markland, and Helluland. These lands, rich in resources like timber and grapes, captivated the Norse explorers.
Vinland, possibly linked to L’Anse aux Meadows due to its mild climate, was known for its fertile grounds. Markland offered lush forests, while Helluland presented rugged, slab-like landscapes.
Despite their allure, these lands were challenging for permanent settlements. The sagas, partially legendary, provide a tapestry of Norse dreams and ambitions.
They capture the essence of exploration, guiding archaeologists and historians in understanding the scope of Viking journeys to these mysterious shores.
3. First Europeans in the New World (Before Columbus)
Long before Columbus’s famed voyage, the Vikings had already charted courses to the New World. Their adventures predate those of the famed Italian explorer by roughly 500 years.
The Norse’s brief, but significant, presence in North America marks the earliest documented European contact with the continent. While their settlements were not permanent, they represent a remarkable chapter in maritime exploration.
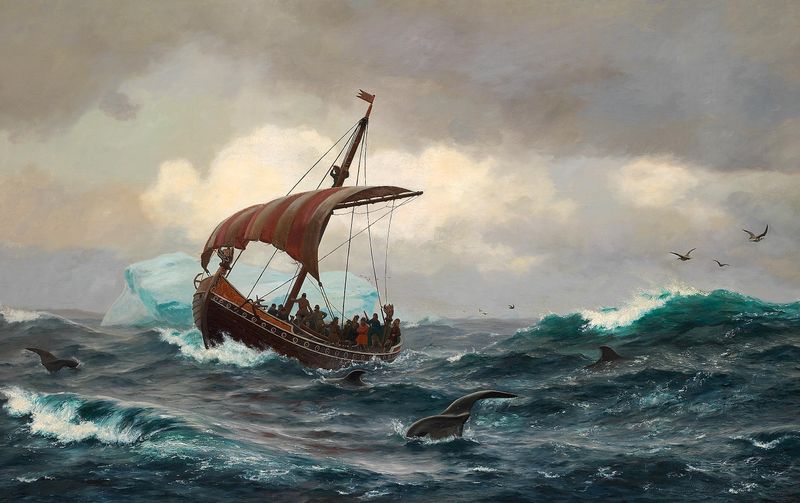
These voyages highlight the Vikings’ exceptional navigation skills and their relentless pursuit of new horizons. Despite being less celebrated, their journeys laid the groundwork for future explorations, showcasing their pioneering spirit and maritime prowess.
4. Archaeological Evidence at L’Anse aux Meadows
The archaeological site at L’Anse aux Meadows offers tangible proof of the Viking presence in North America. Excavations have unearthed Viking-style dwellings, iron-working residues, and artifacts such as a ringed pin.
These findings validate the Norse origins of the site, providing insights into their daily lives and skills. The presence of iron-working facilities suggests a community equipped for metalwork, crucial for tools and weaponry.
The site’s preservation allows historians and visitors alike to step back in time. This evidence, coupled with the sagas, paints a vivid picture of the Vikings’ adaptability and ingenuity in the New World.
5. Short-Lived Occupation
The occupation of L’Anse aux Meadows by the Vikings was notably brief. Evidence indicates that the settlement likely lasted a decade or two, serving as a seasonal camp or exploration outpost.
It was not a large colony, but rather a strategic base for further expeditions. The temporary nature of the settlement is reflected in its modest structures.
Despite its short-lived existence, the settlement played a crucial role in the Vikings’ exploratory missions.
The decision to abandon the site was influenced by various factors, including challenges in sustaining a larger community and interactions with Indigenous peoples. Its legacy, however, endures.
6. Contact with Indigenous Peoples
The Vikings’ encounters with Indigenous peoples, referred to as “Skrælings” in the sagas, were a complex mix of trade and conflict. These interactions played a pivotal role in shaping the Vikings’ experiences in North America.
The Norse were intrigued by the native cultures and sought to trade goods. However, misunderstandings and clashes were inevitable, leading to tensions. These relationships, though short-lived, left a mark on both cultures.
The sagas narrate these encounters with a mix of curiosity and caution, highlighting the challenges and opportunities faced by the Vikings as they navigated this new and diverse world.
7. Limited Expansion Southward
Despite the tantalizing prospects of Vinland’s milder climate, Norse expansion beyond Newfoundland was limited. Archaeological evidence of settlements further south remains elusive.
While the sagas mention fertile lands, the challenges of long-term habitation proved daunting. The harsh realities of supply lines and potential conflicts with Indigenous groups may have deterred further exploration.
Searches for additional sites have yielded mixed results, leaving many questions unresolved.
The Vikings’ cautious approach to expansion underscores their strategic considerations and the complexities of establishing a lasting presence. Their journeys, though ambitious, were marked by a balance of risk and reward.
8. The Role of the Sagas
The Vinland Sagas, while containing elements of legend, are invaluable in understanding the Norse voyages to America. These narratives provide critical clues about the timing, routes, and experiences of the explorers.
Cross-referenced with archaeological findings, they help piece together the puzzle of Viking exploration. The sagas capture the imagination, weaving tales of adventure and discovery.
They serve as a bridge between history and folklore, offering insights into the motivations and challenges faced by the Vikings. The sagas’ enduring appeal lies in their ability to convey the spirit of exploration and the allure of the unknown.
9. Mystery of Markland and Helluland
Markland and Helluland, mentioned in the Icelandic Sagas, remain shrouded in mystery. Believed to correspond to Labrador and Baffin Island, these regions were rich in natural resources.
Markland was noted for its abundant forests, while Helluland was characterized by its stark, icy landscapes. Despite their potential, no confirmed permanent Norse settlements have been found in these areas.
They may have served as sources of timber and furs for the Vikings. The sagas provide tantalizing glimpses into these lands, yet they leave many questions unanswered. The allure of Markland and Helluland continues to captivate historians and explorers alike.
10. The Kensington Runestone and Other Controversies
The Kensington Runestone and similar artifacts have sparked debates about the extent of Viking exploration in North America. Found in Minnesota, the runestone is inscribed with runes that some claim as evidence of Norse presence further inland.
However, mainstream scholars often dismiss it as a hoax or misinterpretation. These controversies underscore the challenges of verifying historical claims. While intriguing, the runestone remains a subject of skepticism.
The fascination with such artifacts highlights the enduring interest in Viking history. Despite doubts, these items inspire dialogue and exploration, encouraging a deeper examination of the Norse legacy in America.
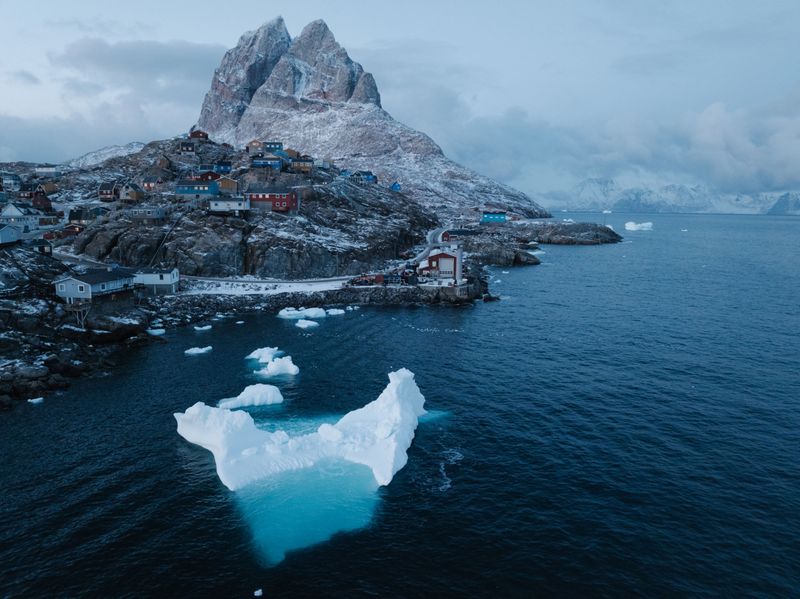
11. Greenland’s Importance
Greenland played a crucial role in Norse exploration of North America. The settlements in Greenland were a stepping stone, providing a base for voyages across the Atlantic. Harsh climates and resource needs prompted the Vikings to seek new lands.
The search for timber, essential for building and repair, was a significant driver of these explorations. Greenland’s challenging environment honed the Vikings’ resilience and adaptability.
It was from these icy shores that they launched expeditions, demonstrating their maritime capabilities. Greenland remains pivotal in understanding the Vikings’ exploratory endeavors, bridging their European origins with their American adventures.
12. End of the Norse in the Americas
The Norse departure from North America was influenced by multiple factors. Hostile relations with Indigenous peoples, coupled with limited resources, posed significant challenges.
The difficulty in maintaining supply lines from Greenland or Iceland further complicated their efforts. These challenges contributed to the decision to abandon the settlements.
Despite their withdrawal, the Norse left a lasting legacy, marked by their adventurous spirit. Their explorations paved the way for future contacts and exchanges.
The end of the Norse presence signals a chapter of resilience and adaptation, reflecting the broader narrative of exploration and retreat in the face of adversity.