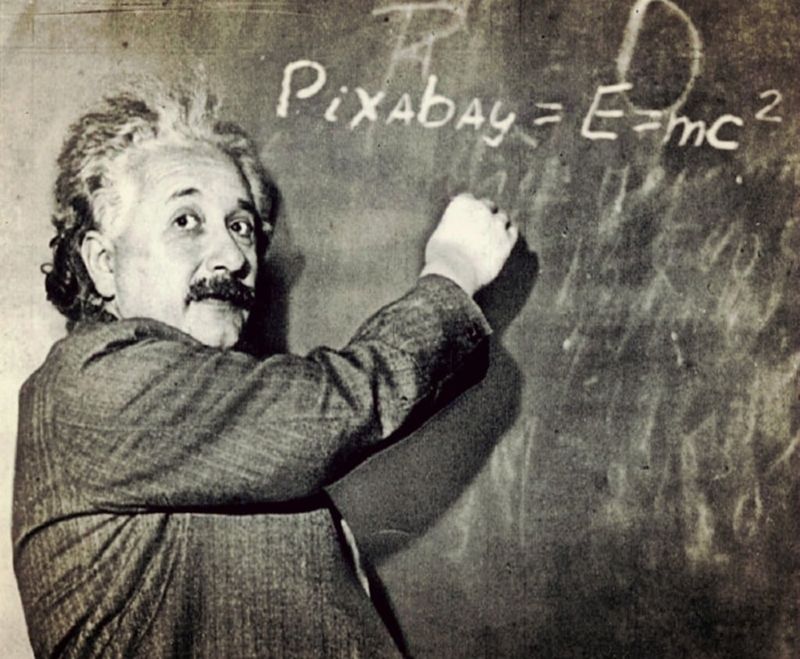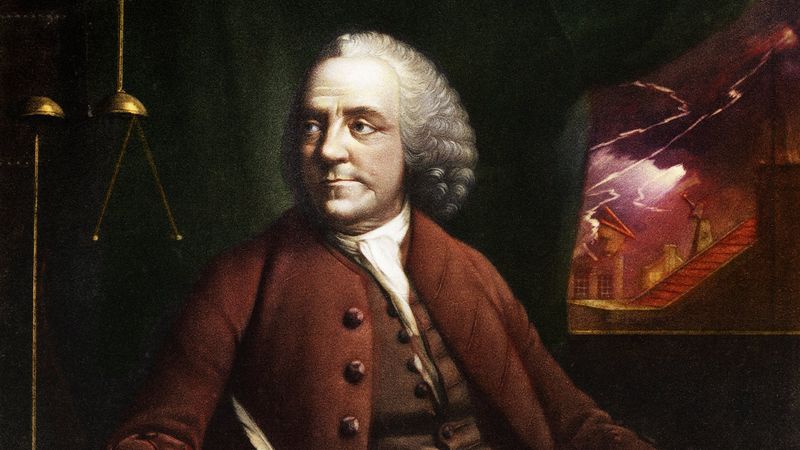Throughout history, remarkable individuals have used their intelligence to reshape our understanding of the world and our place within it.
From groundbreaking theories to revolutionary inventions, these visionaries have left an indelible mark on the future. Join us as we explore the lives and legacies of 25 such extraordinary people.
1. Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein revolutionized science with his theories of relativity, altering our understanding of space, time, and energy.
His famous equation, E=mc², established the relationship between mass and energy. Despite facing early academic setbacks, his curiosity and persistence led him to make profound contributions to physics.
2. Isaac Newton
Isaac Newton’s laws of motion and universal gravitation laid the groundwork for classical mechanics.
His work in calculus and optics also had a lasting impact on science and mathematics. Newton’s Principia Mathematica remains one of the most influential books in the history of science.
3. Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo da Vinci epitomized the Renaissance humanist ideal, mastering art, science, and invention.
His relentless curiosity and inventive spirit led to designs of flying machines and anatomical studies, displaying a blend of creativity and scientific inquiry that remains inspirational.
4. Aristotle
Aristotle’s work in philosophy, biology, and ethics formed the foundation of Western intellectual tradition.
His teachings expanded across numerous disciplines, influencing the way we understand logic, science, and politics. His legacy persists in modern philosophical and scientific methodologies.
5. Archimedes
Archimedes was a pioneering mathematician and inventor, known for his principle of buoyancy and the invention of the Archimedean screw.
His relentless pursuit of understanding through experimentation exemplifies the spirit of scientific inquiry that continues to inspire.
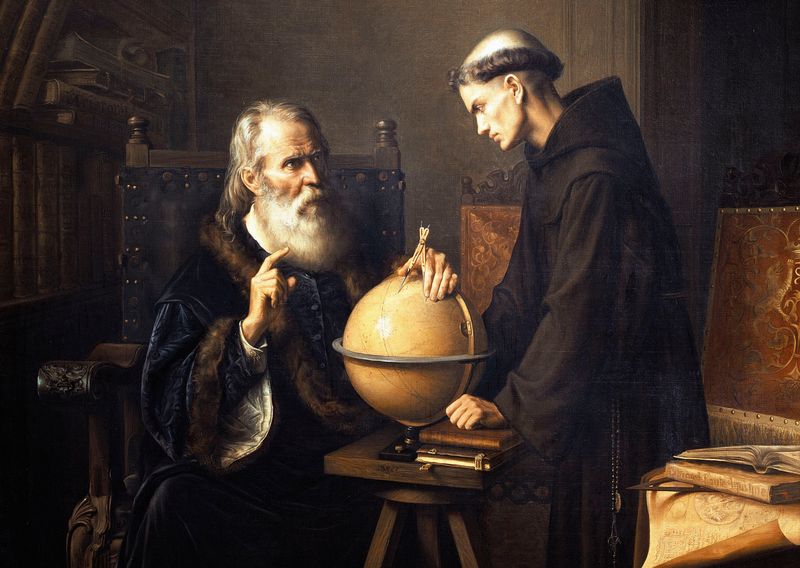
6. Galileo Galilei
Galileo Galilei’s advocacy for the heliocentric model of the solar system challenged established beliefs and laid the groundwork for modern astronomy.
His improvements to the telescope and subsequent astronomical discoveries marked a pivotal shift in scientific thought.
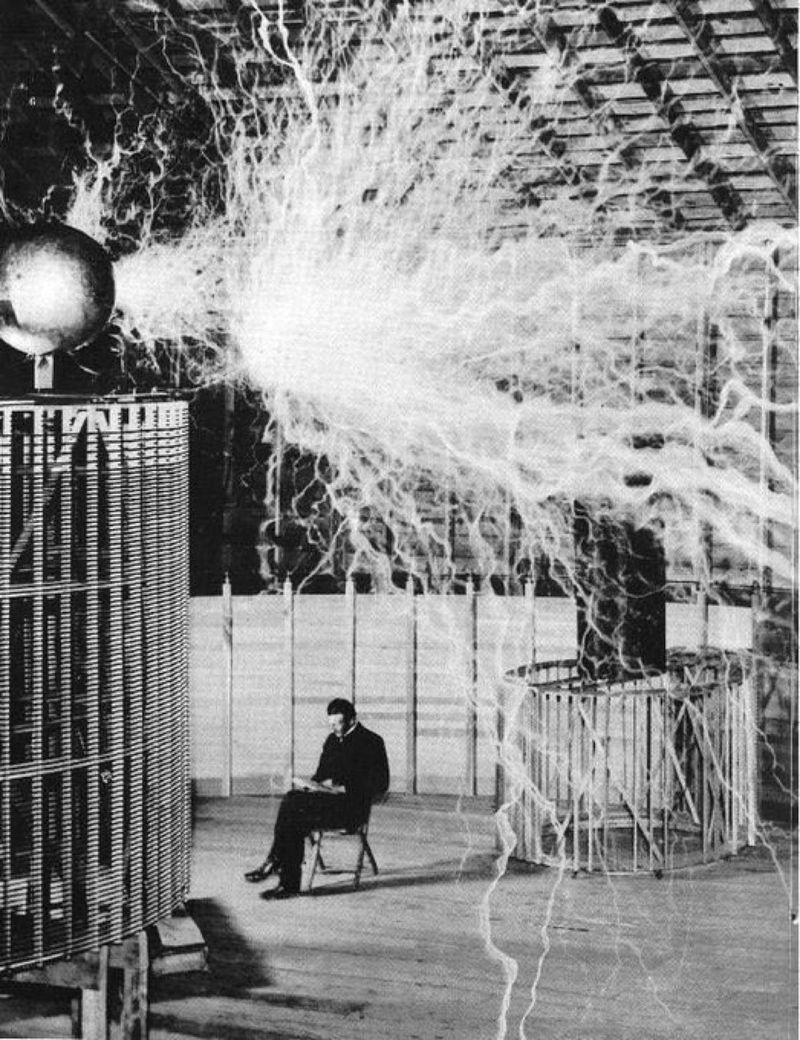
7. Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla’s innovations in electrical engineering, especially his development of alternating current (AC) electricity, transformed how we use power.
His visionary ideas and inventions, such as the Tesla coil, continue to influence modern technology and capture the imagination.
8. Stephen Hawking
Stephen Hawking’s work on black holes and cosmology advanced our understanding of the universe’s origins and structure.
Despite battling a debilitating disease, his intellectual fortitude and sense of humor inspired millions around the world to explore the mysteries of space.
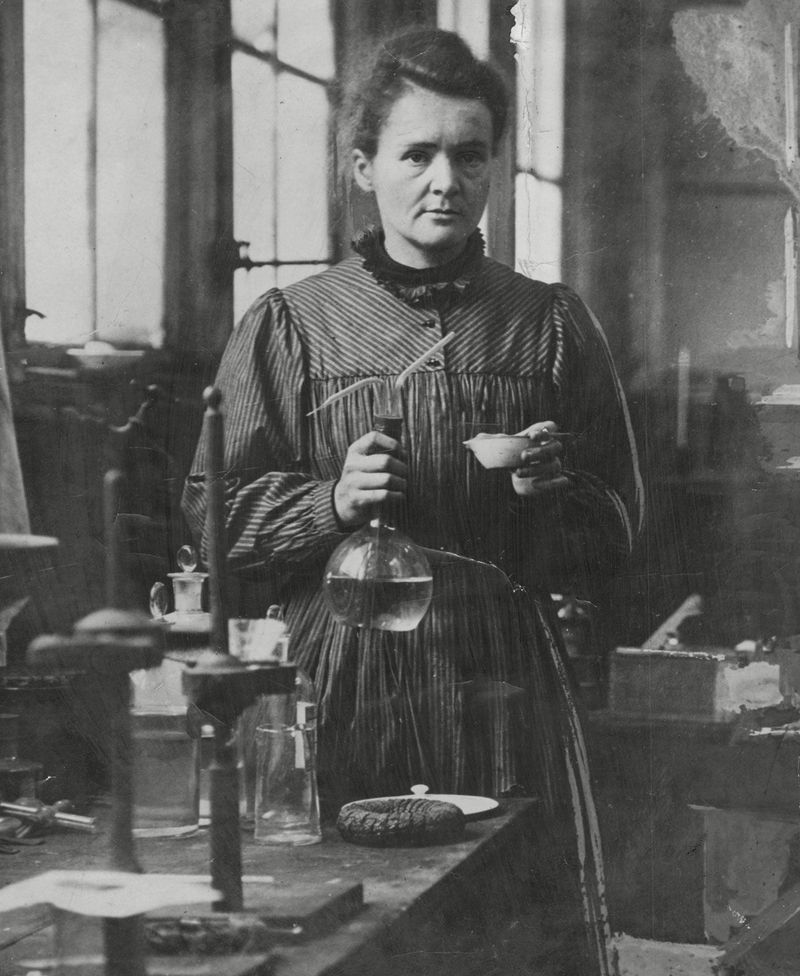
9. Marie Curie
Marie Curie’s pioneering research on radioactivity paved the way for significant advancements in medical and scientific fields.
As the first woman to win a Nobel Prize, and the only person to win in two different sciences, her legacy is one of perseverance and groundbreaking discovery.
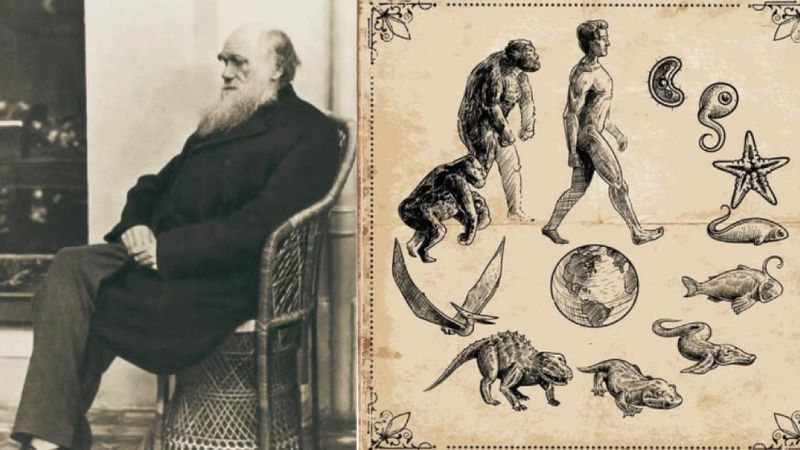
10. Charles Darwin
Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection revolutionized biological sciences.
His observations during the voyage of the HMS Beagle led to insights that changed our understanding of life’s diversity and interconnectedness, impacting numerous scientific disciplines.
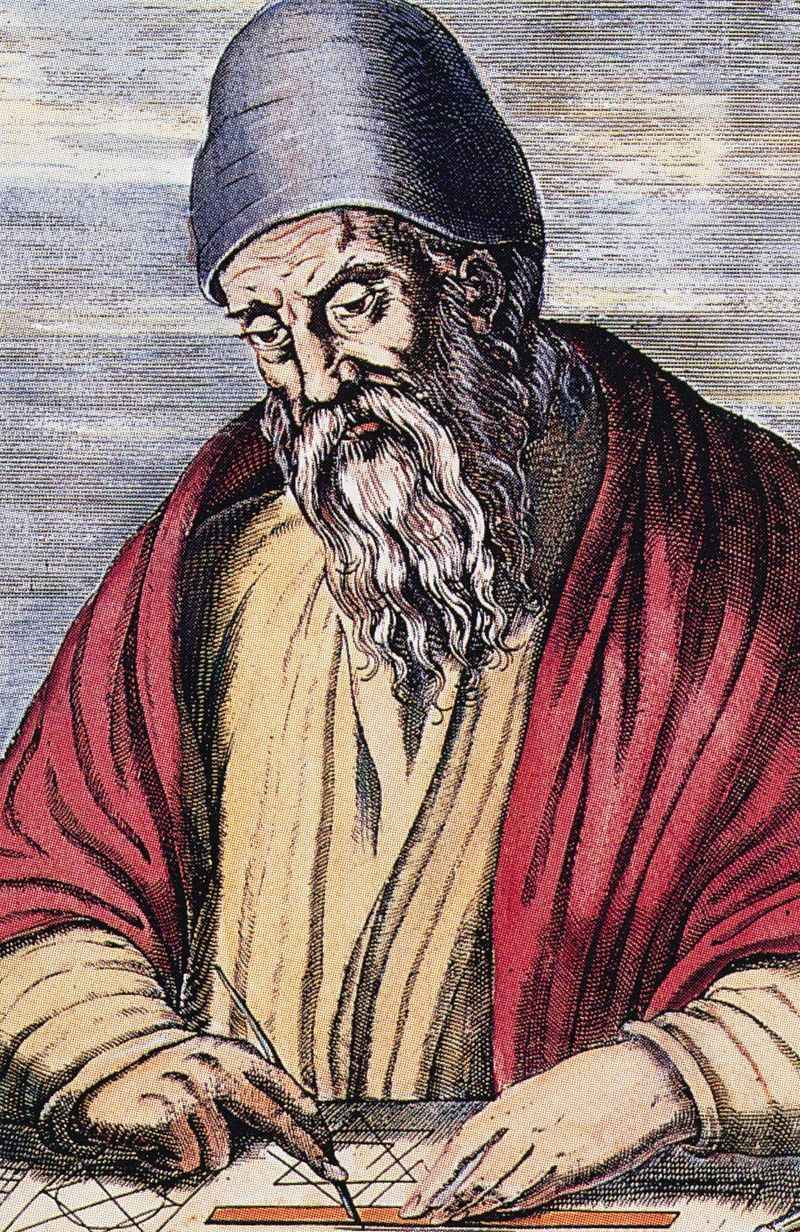
11. Euclid
Euclid, often called the “Father of Geometry,” established fundamental principles that have influenced mathematics for centuries.
His work, “Elements,” is one of the most translated and studied mathematical textbooks in history, setting the standard for logical and mathematical reasoning.
12. Pythagoras
Pythagoras is best known for the Pythagorean theorem, a cornerstone of geometry that connects algebra and geometry.
His philosophical and mathematical explorations reflected a belief in harmony and order in the universe, inspiring future generations of mathematicians.
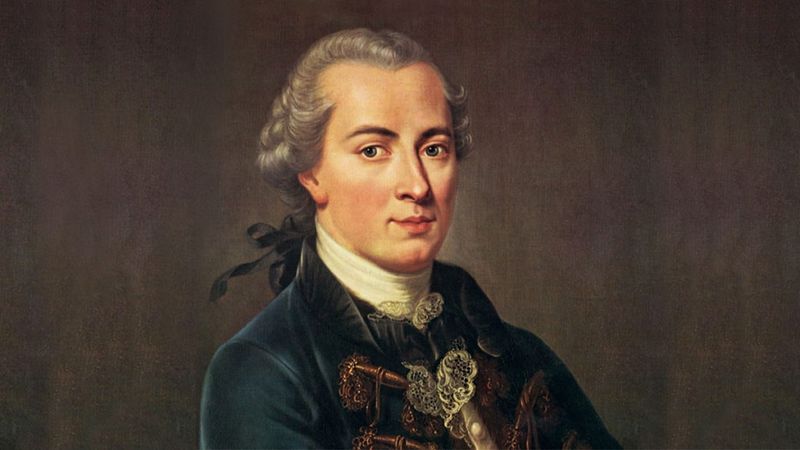
13. Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant’s critical philosophy reshaped modern thought, addressing the relationship between human experience and knowledge.
His ideas on morality, aesthetics, and metaphysics continue to influence contemporary philosophical discourse and ethical theories.
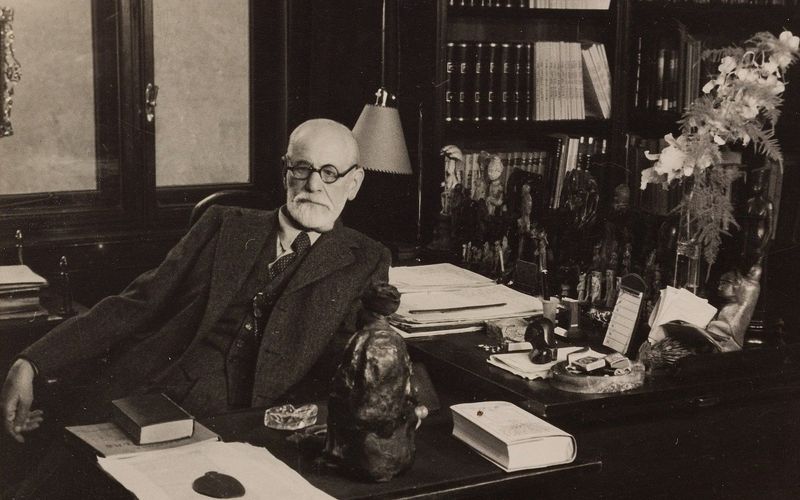
14. Sigmund Freud
Sigmund Freud’s development of psychoanalysis transformed the field of psychology, offering new insights into the human mind. His exploration of dreams, the unconscious, and human behavior laid the groundwork for various therapeutic techniques still used today.
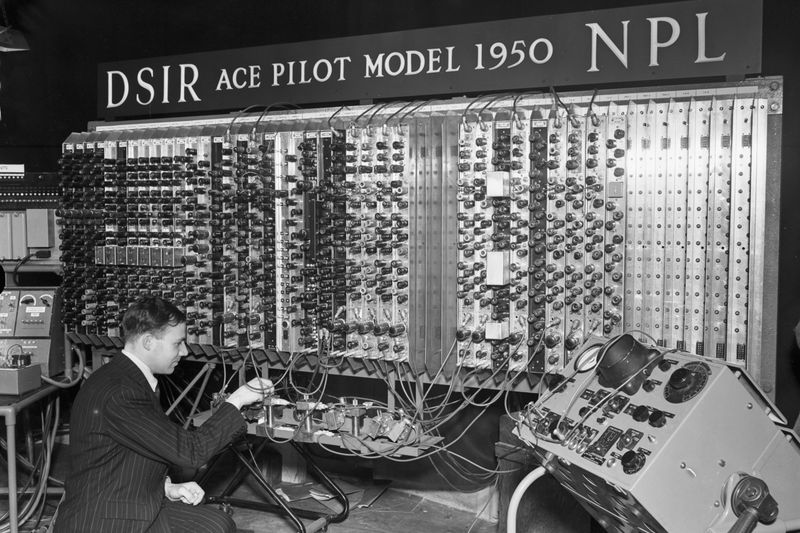
15. Alan Turing
Alan Turing’s pioneering work in computer science and artificial intelligence laid the foundation for modern computing. His code-breaking efforts during WWII were crucial to the Allied victory, showcasing the practical applications of his theoretical insights.
16. Richard Feynman
Richard Feynman’s contributions to quantum electrodynamics earned him a Nobel Prize, and his engaging teaching style made complex physics accessible. His curiosity and interdisciplinary approach inspired countless students and professionals in the field of science.
17. Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler’s laws of planetary motion provided key insights into the heliocentric model of the solar system. His work bridged the gap between Copernican theory and Newtonian physics, shaping our understanding of celestial bodies and their movements.
18. Socrates
Socrates is credited with founding Western philosophy through his method of questioning and dialogue. His emphasis on ethics and the pursuit of knowledge influenced his students and set the stage for future philosophical inquiry.
19. Plato
Plato, a student of Socrates, founded the Academy in Athens, cultivating an environment for philosophical and scientific exploration. His writings, particularly “The Republic,” continue to influence political theory and educational practices.
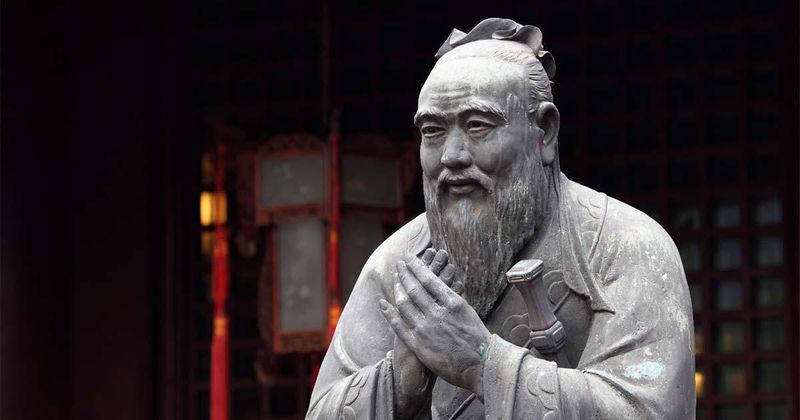
20. Confucius
Confucius’s teachings on ethics, governance, and personal conduct have deeply influenced Eastern thought. His emphasis on morality, family loyalty, and social harmony remains relevant in modern societies, guiding cultural practices and values.
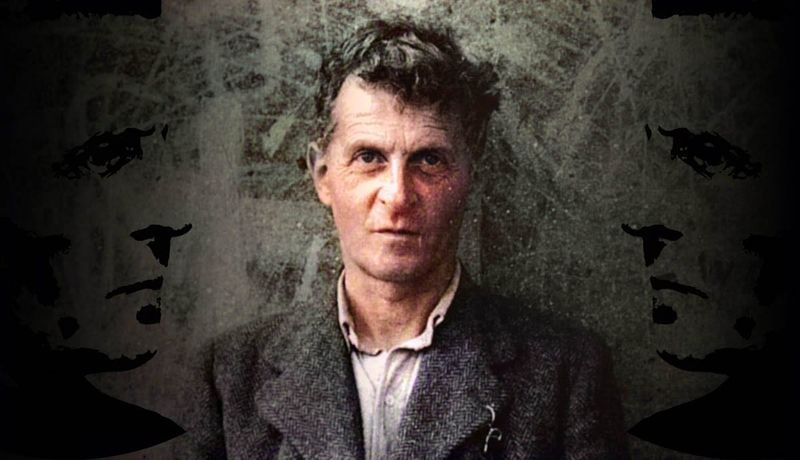
21. Ludwig Wittgenstein
Ludwig Wittgenstein’s work on language and logic transformed 20th-century philosophy. His ideas on the limits of language and meaning challenged conventional paradigms, influencing disciplines from linguistics to cognitive science.
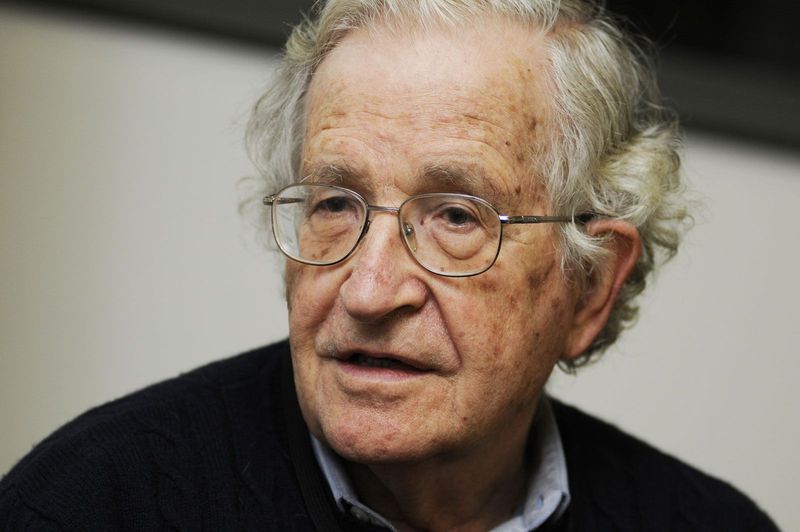
22. Noam Chomsky
Noam Chomsky’s groundbreaking theories in linguistics revolutionized our understanding of language acquisition and cognitive processes.
His political activism and critiques of media have also sparked widespread debate, underscoring his influence beyond academia.
23. Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin, a true polymath, made significant contributions to science, politics, and philosophy. His experiments with electricity and insights into civic responsibility continue to inspire innovation and public service.
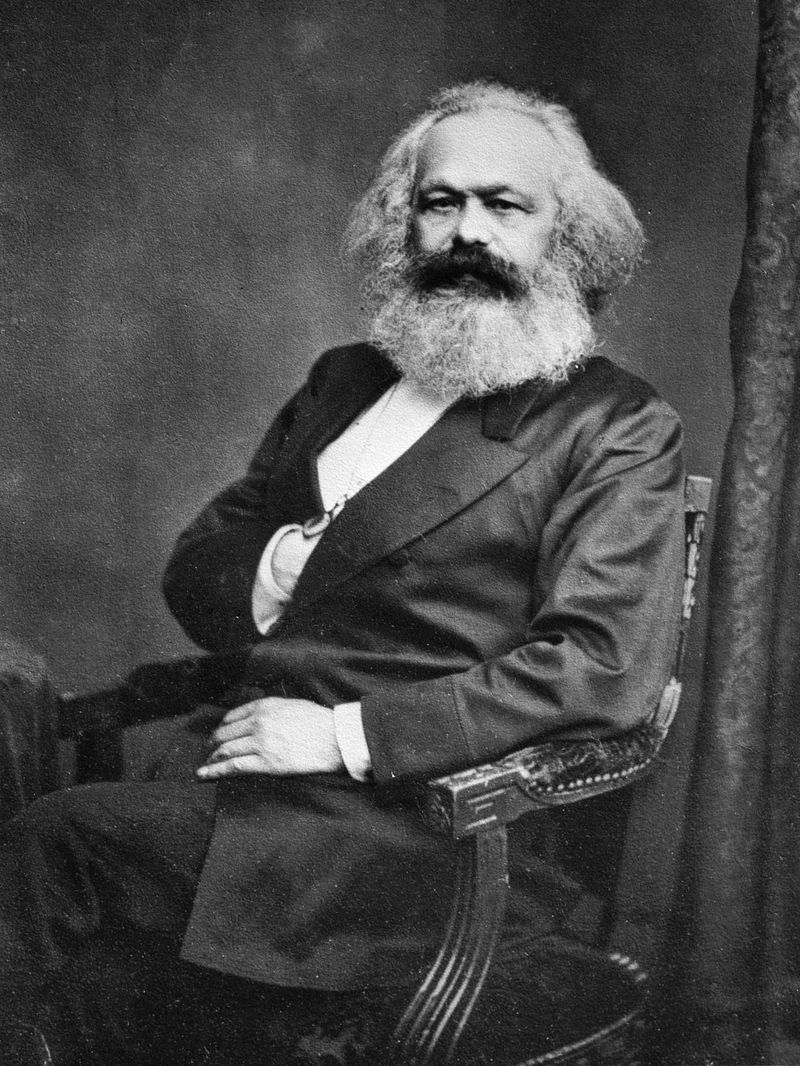
24. Karl Marx
Karl Marx’s critique of capitalism and his theories on class struggle shaped modern political and economic thought. His works, such as “The Communist Manifesto,” continue to influence discussions on equity and social justice worldwide.
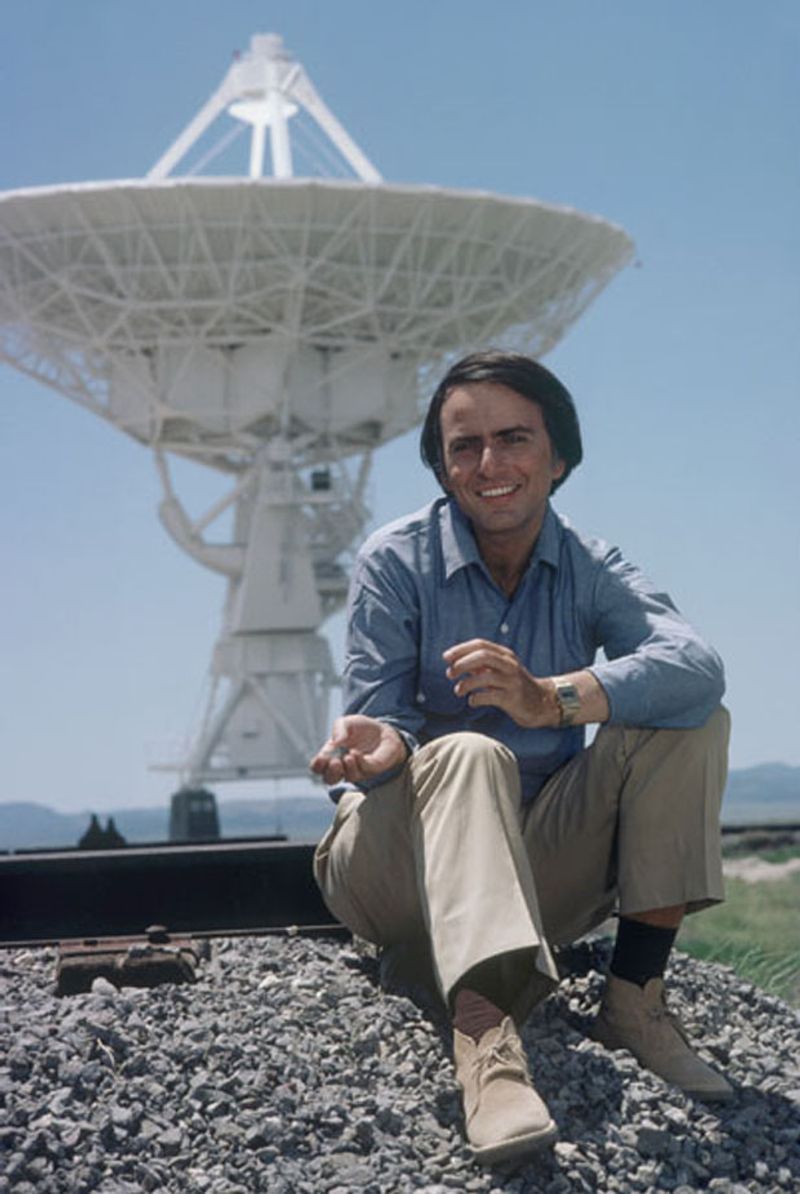
25. Carl Sagan
Carl Sagan’s work as an astronomer and science communicator inspired a generation to explore the universe. His ability to make complex scientific ideas accessible and his advocacy for scientific literacy have left a lasting legacy in both science and education.