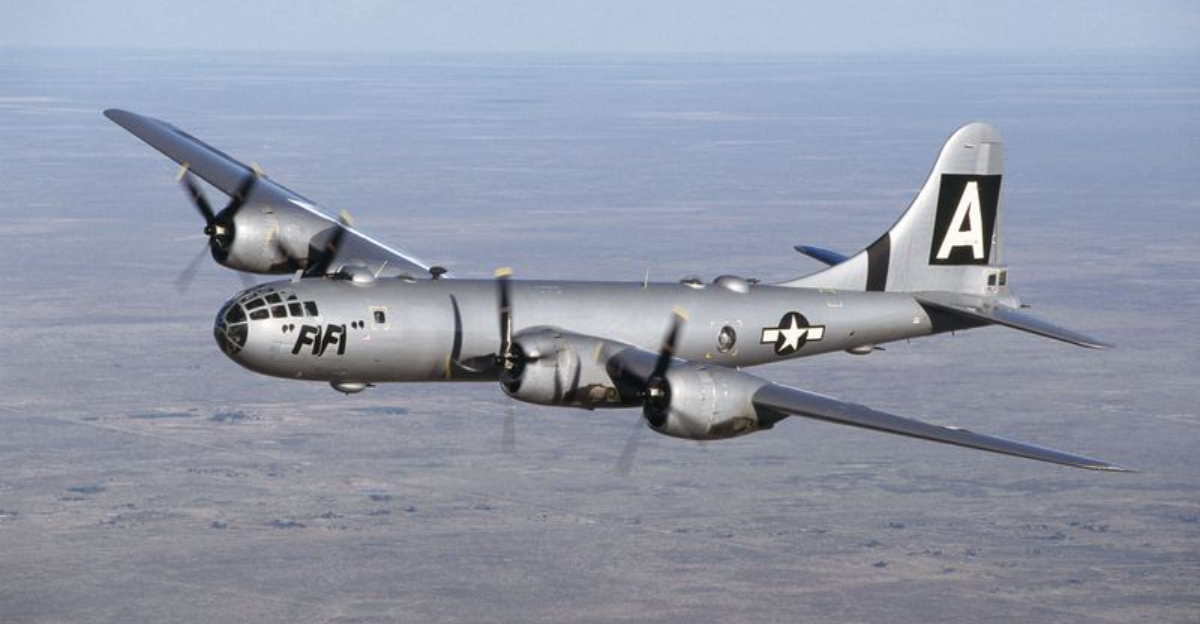
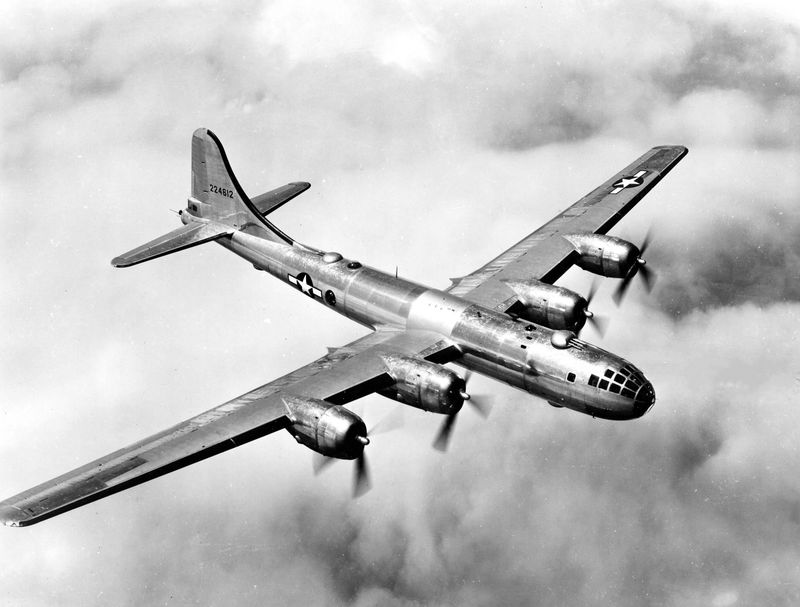
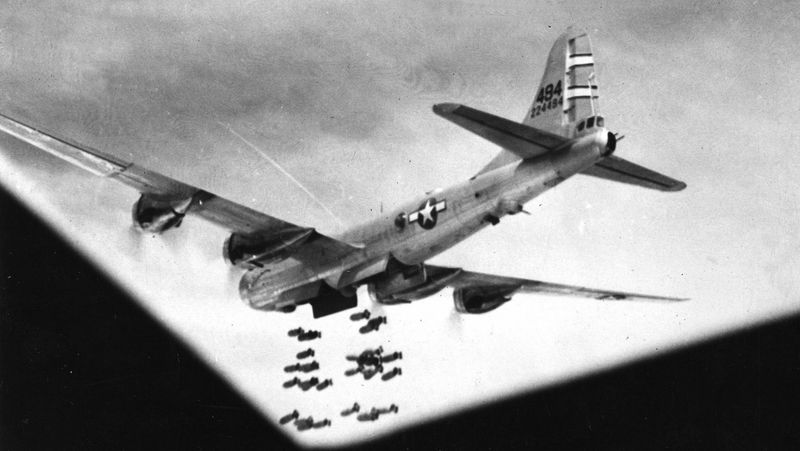
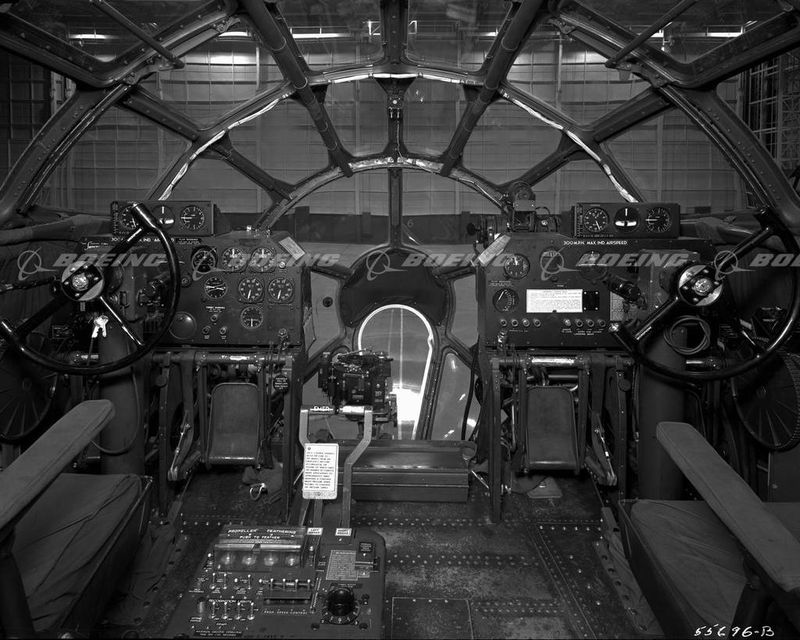
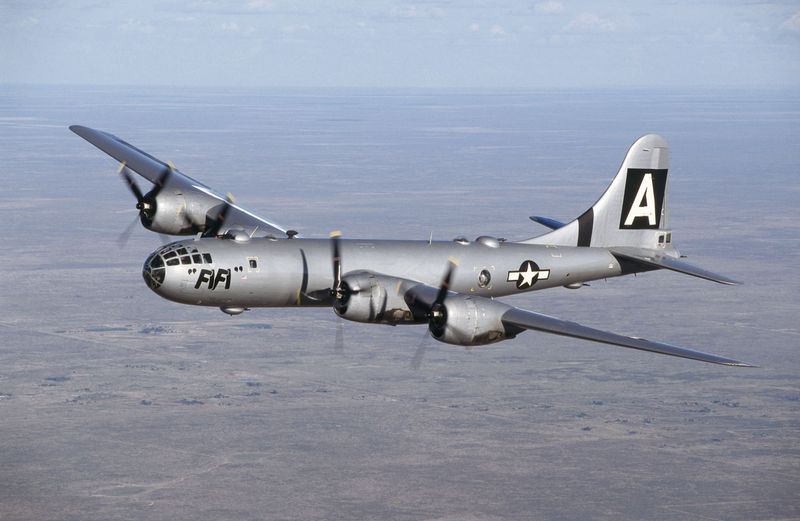
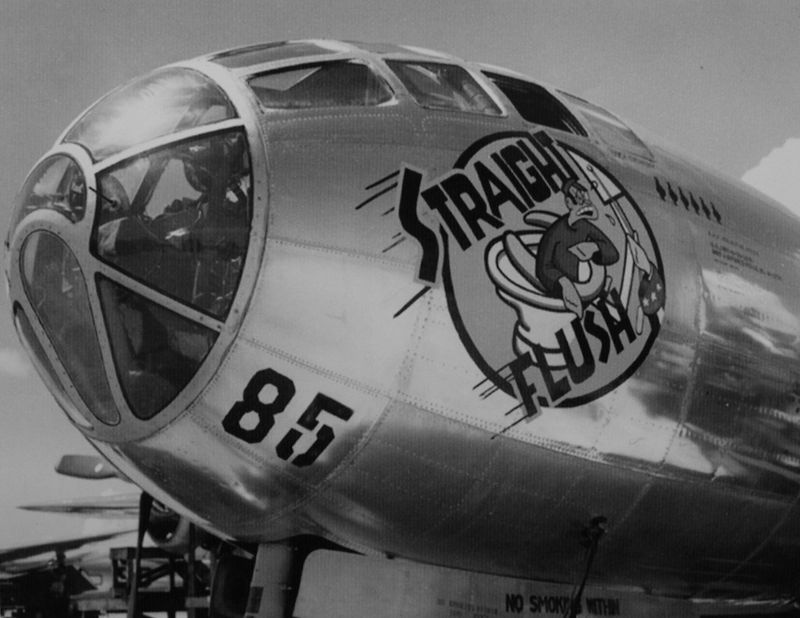
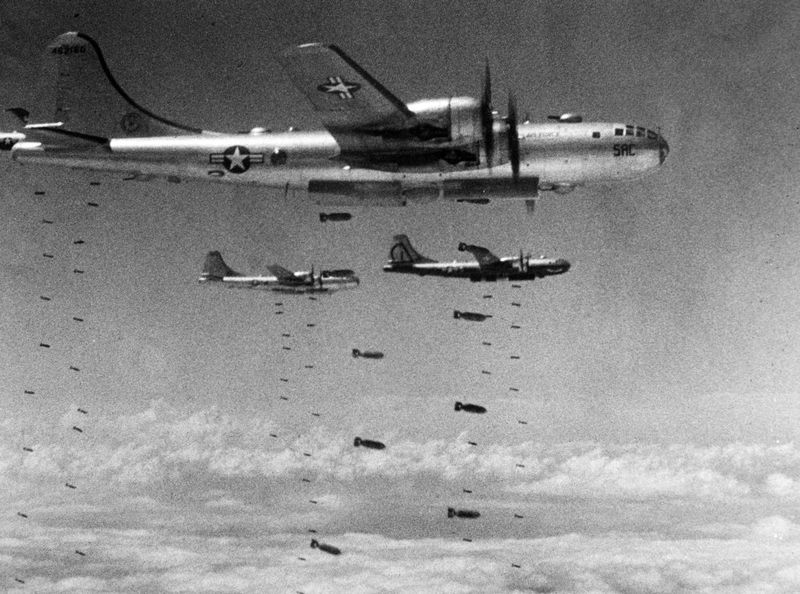
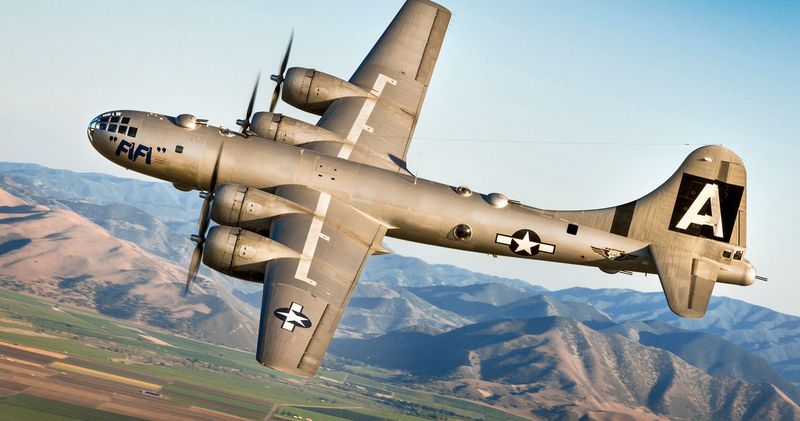
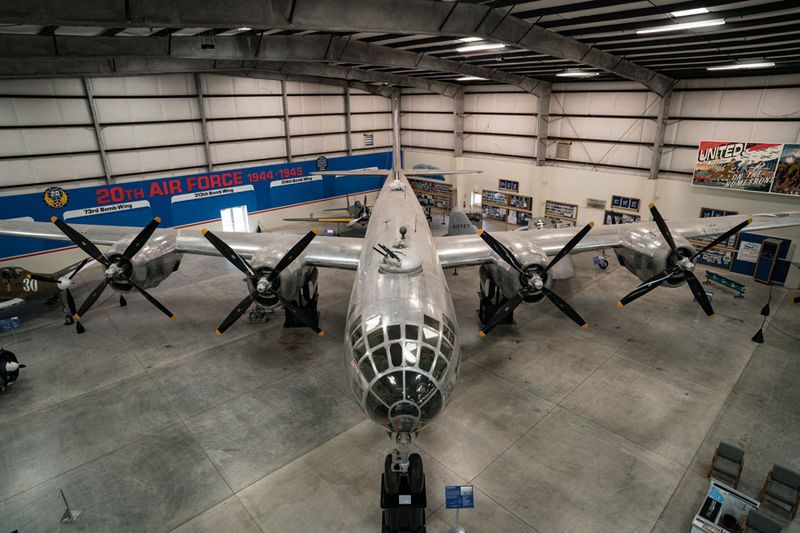
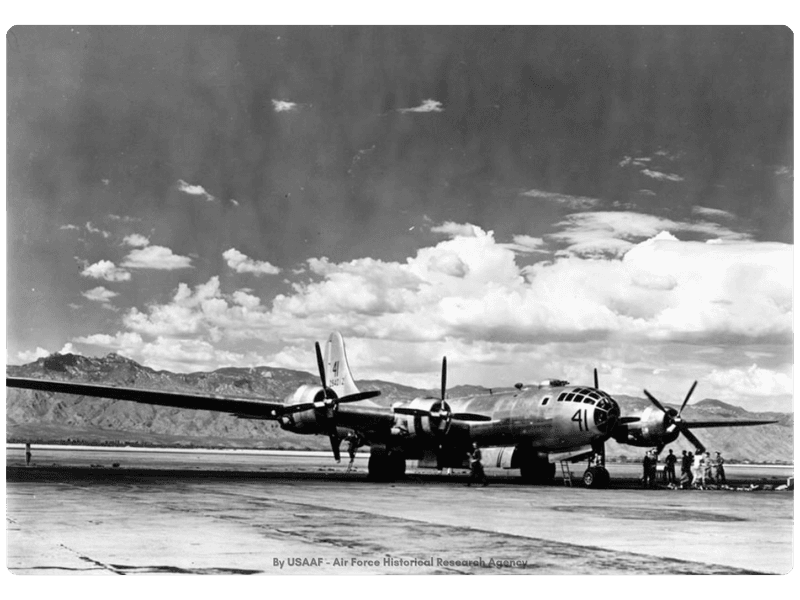
The B-29 Superfortress stands as one of the most iconic aircraft of World War II. Known for its advanced technology and significant role in the conflict, this bomber introduced innovations that changed the way air warfare was conducted. Its impact on the war effort and subsequent aviation developments is immense. Let’s explore 15 fascinating facts about this legendary aircraft.
1. Revolutionary Design
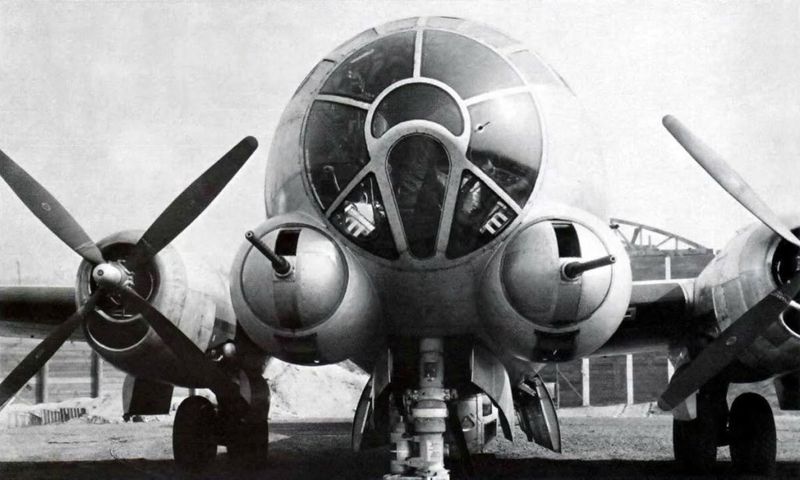
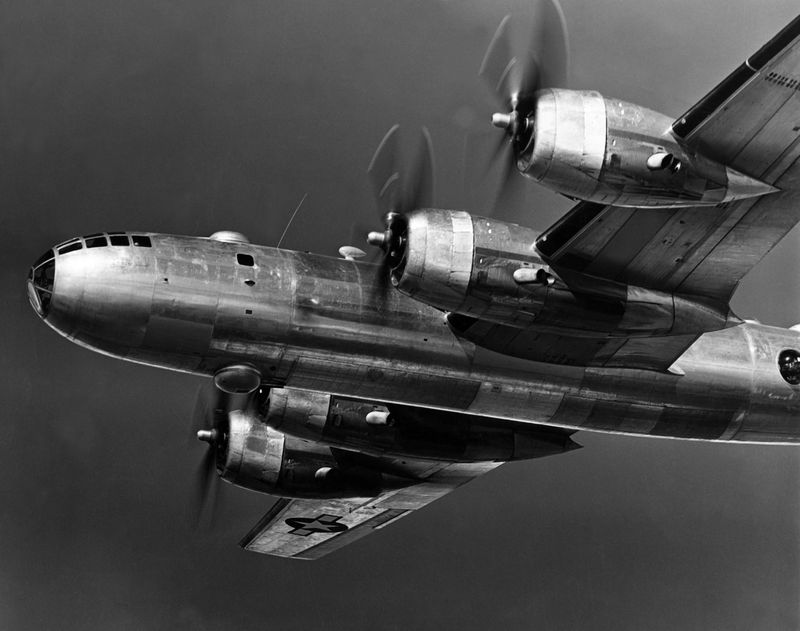
The B-29 Superfortress boasted a revolutionary design for its time, featuring a pressurized cabin, which allowed it to fly at higher altitudes. This innovation provided a tactical advantage, enabling the aircraft to avoid enemy anti-aircraft fire more effectively. The sleek and elongated fuselage gave it an imposing presence in the skies. Pilots appreciated the advanced technology which included remote-controlled gun turrets. Such design elements set a new standard for future bomber aircraft. The B-29’s elegant lines and robust construction made it a marvel of engineering during the war.
2. Combat Debut in 1944
The B-29 made its combat debut in June 1944, over Japan. Its first mission demonstrated the aircraft’s long-range capabilities, as it flew from bases in China to targets deep within Japanese territory. The mission marked a pivotal point in the air campaign against Japan. Crew members were trained extensively for these long missions, showcasing the aircraft’s endurance. The debut was not only a test of the bomber’s technical abilities but also of the strategic planning involved. It was a bold statement of American air power.
3. Pressurized Cabin
One of the standout features of the B-29 was its pressurized cabin. This allowed crews to operate in relative comfort at high altitudes, a significant departure from the freezing conditions faced in other bombers. The cabin was divided into three sections, each sealed independently, offering a sense of safety and modernity. Crew members could move between sections using a pressurized tunnel, a unique marvel at the time. This innovation greatly enhanced the effectiveness of missions, as crews could perform for longer periods without the extreme fatigue associated with low temperatures.
4. Enola Gay and the Atomic Bomb
Perhaps the most famous B-29 is the Enola Gay, which dropped the first atomic bomb on Hiroshima on August 6, 1945. This mission dramatically altered the course of the war and global history. The aircraft’s name has become synonymous with the dawn of the nuclear age. The mission highlighted the B-29’s capability to carry heavy payloads over long distances. For the crew, it was a mission with profound implications, altering their lives forever. The Enola Gay is now preserved at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum.
5. Advanced Armament Systems
The B-29 was equipped with advanced remote-controlled gun turrets, which were revolutionary for the time. This system allowed gunners to operate from a central position, improving defensive capabilities. The turrets could be controlled by multiple gunners, enhancing the bomber’s ability to fend off enemy fighters. This innovation reduced the weight and space required for additional crew members. The strategic placement of the turrets provided comprehensive coverage. These systems made the B-29 a formidable opponent in aerial combat, establishing a new benchmark for bomber defense.
6. Long Range Capability
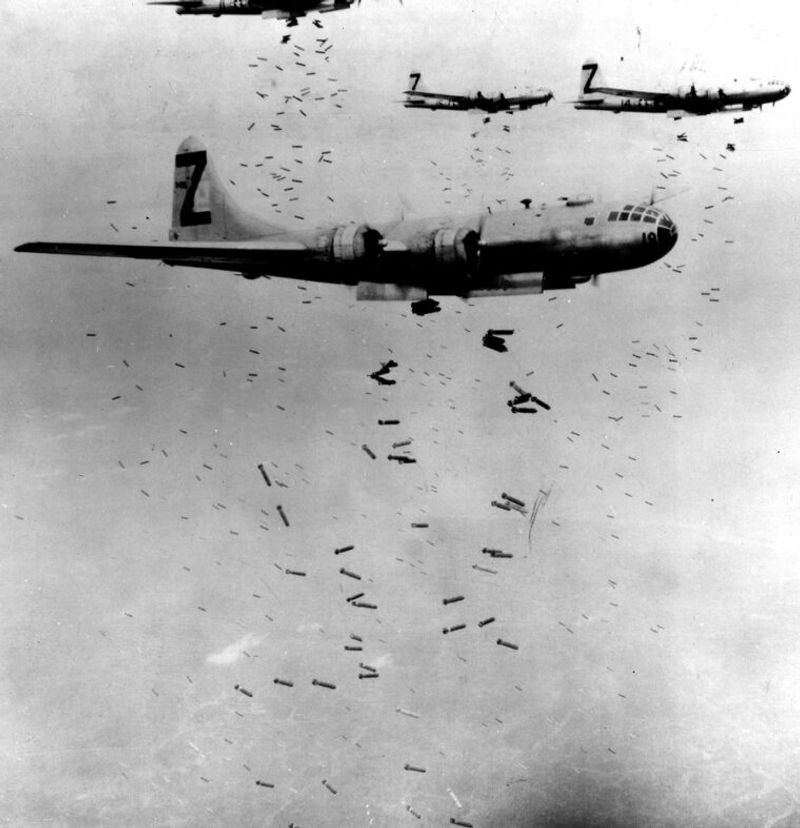
The B-29’s design allowed it to fly longer distances than any other bomber of its time, with a range of over 3,000 miles. This capability was crucial for operations in the vast theaters of the Pacific, enabling strategic strikes deep into enemy territory. It could reach targets that were previously inaccessible, drastically altering military strategies. This long-range advantage meant that missions could be planned with greater flexibility and fewer logistical concerns. The B-29’s ability to carry out such missions was a game-changer in the Pacific War.
7. Boeing’s Engineering Marvel
Boeing was the mastermind behind the B-29 Superfortress, pouring immense resources into its development. The engineering team faced numerous challenges but succeeded in creating one of the most advanced bombers of the era. The project was one of the most extensive and expensive of WWII, reflecting the importance of the aircraft. Boeing’s commitment to innovation led to breakthroughs that would influence aircraft design for decades. The B-29 embodied the pinnacle of wartime engineering, with its development setting a precedent for future aviation projects.
8. Strategic Importance
The strategic importance of the B-29 cannot be overstated. It played a critical role in the Allied bombing campaign, significantly impacting Japanese industrial capabilities. The bomber was central to nighttime bombing raids, utilizing its advanced navigation and bomb systems. These missions disrupted supply lines and crippled production facilities, hastening the end of the war. The B-29’s presence was a constant threat to enemy forces, altering their defensive strategies. Its success in strategic missions demonstrated the essential role of air power in modern warfare.
9. Post-War Influence
After WWII, the B-29 continued to influence military aviation, serving in the Korean War and leading to developments in aerial technology. Its design principles were incorporated into subsequent aircraft, shaping the future of bombers. The lessons learned from the B-29’s deployment informed strategies and innovations for the Cold War era. The aircraft laid the groundwork for future bombers like the B-47 and B-52, becoming a template for modern military aviation. Its legacy extends beyond its wartime achievements, marking a transition in aviation history.
10. Impressive Speed
The B-29 was not only known for its range but also for its impressive speed, capable of reaching over 350 miles per hour. This speed allowed it to outrun enemy interceptors, increasing its survivability during missions. The combination of speed and altitude made it difficult for enemy aircraft to engage. Pilots admired the aircraft’s responsiveness and agility, considering it a joy to fly. This high-speed capability was a significant factor in its operational success, allowing it to perform various roles effectively during the war.
11. Production Challenges
Producing the B-29 was a massive undertaking, with factories across the United States involved. The complexity of the design led to numerous production challenges, requiring extensive coordination and resources. Delays were frequent, but the urgency of war efforts pushed teams to overcome obstacles. The scale of production was unprecedented, reflecting the strategic importance of the aircraft. Workforce training and resource allocation were critical in meeting production demands. Despite difficulties, the successful production of the B-29 demonstrated American industrial capabilities during WWII.
12. The Silverplate Program
The Silverplate program was a crucial modification initiative for the B-29, specifically to accommodate the atomic bombs. This involved structural changes to the bomb bay and other systems to ensure the safe delivery of nuclear payloads. The program was top-secret, reflecting the sensitivity of nuclear missions. These modifications were necessary for the success of missions like the Hiroshima and Nagasaki bombings. Silverplate B-29s were specially selected for their reliability and performance, representing the pinnacle of wartime technological adaptations.
13. Role in Korean War
The B-29 continued its service in the Korean War, adapting to new combat environments. Despite being older technology by then, it remained effective in bombing raids against North Korean and Chinese targets. Its ability to carry large bomb loads made it a valuable asset. The aircraft’s presence symbolized American air power, supporting ground operations and strategic bombing campaigns. The B-29’s adaptability to different roles highlighted its enduring design. It served as a bridge between WWII and Cold War aviation tactics, maintaining its relevance.
14. Military and Civil Uses
Beyond its military uses, the B-29 found roles in civilian applications, such as weather reconnaissance and aerial mapping. Its robust construction made it ideal for non-combat operations. The aircraft’s versatility was further demonstrated by its use in research and development projects. Post-war, the B-29 contributed to scientific advancements, including high-altitude atmospheric studies. This dual-use capability showcased the aircraft’s adaptability and engineering excellence. Its transition from wartime service to peacetime roles highlighted the enduring legacy of the B-29.
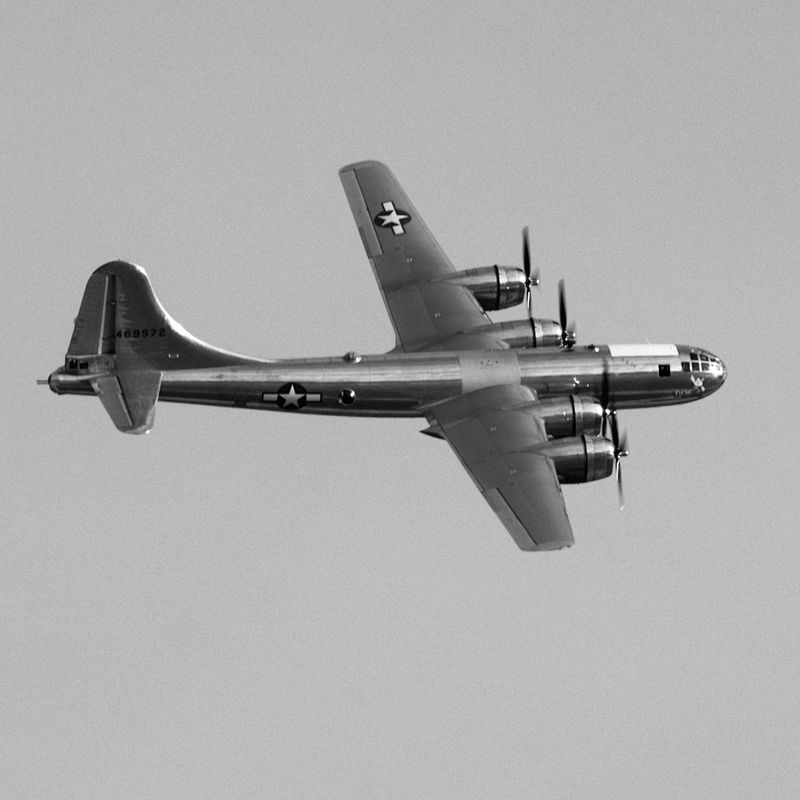
15. Survivors and Preservation
Today, a few B-29s survive in museums and private collections, serving as reminders of their historical significance. These preserved aircraft are meticulously maintained, often displayed in airshows to educate the public about their role in history. Restoration projects are ongoing, with enthusiasts dedicated to keeping them airworthy. The B-29’s enduring appeal lies in its engineering marvel and its impact on history. Museums worldwide exhibit these bombers, allowing new generations to appreciate their contributions to aviation and the broader narrative of WWII.