Throughout American history, certain battles have left indelible marks on the nation’s development. Some were fought on home soil, shaping the landscape and the national consciousness.
Others took place overseas, influencing international relations and America’s role on the world stage. These battles, whether they ended in victory or defeat, have helped define the United States.
This collection of 24 significant battles showcases the bravery, strategy, and fortitude that have characterized American military history. Each battle exemplifies a turning point, reflecting the challenges and triumphs faced by those who fought.
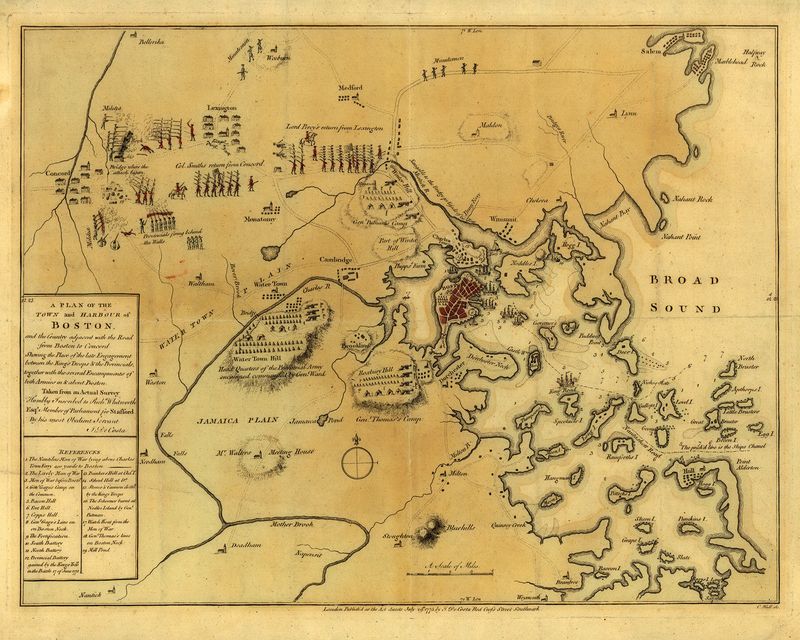
1. The Battle of Lexington and Concord
In April 1775, the first military engagements of the American Revolutionary War unfolded at Lexington and Concord. British troops, intending to seize colonial arms, faced American militiamen. The “shot heard ’round the world” marked the start of the revolution.
Early morning mist hung over the fields as tensions erupted into violence. American forces, though inexperienced, demonstrated resolve, forcing the British to retreat.
This battle galvanized colonial resistance and united the colonies in the fight for independence, setting the stage for the revolution and the birth of a new nation.
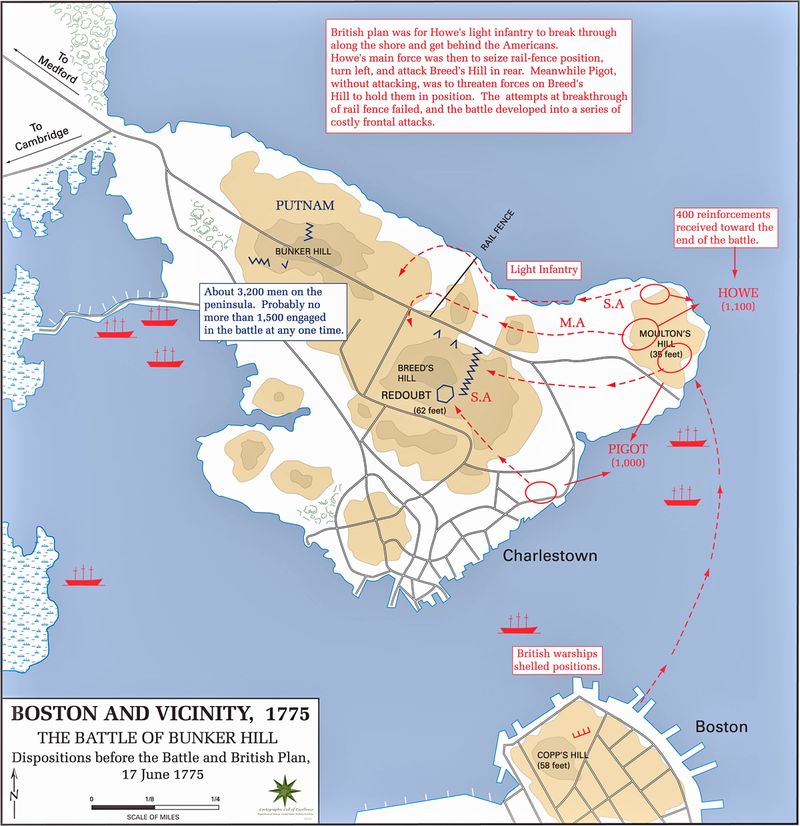
2. The Battle of Bunker Hill
Fought on June 17, 1775, the Battle of Bunker Hill was a pivotal early conflict in the American Revolutionary War. Although technically a British victory, it demonstrated the colonial forces’ capability to stand against the British army.
Colonial troops fortified Breed’s Hill in Charlestown, Massachusetts, leading to a fierce battle against British Redcoats. Despite their eventual retreat, the colonial forces inflicted significant casualties.
This battle gave the American forces a morale boost, proving that determination and strategic planning could challenge the might of the British Empire.
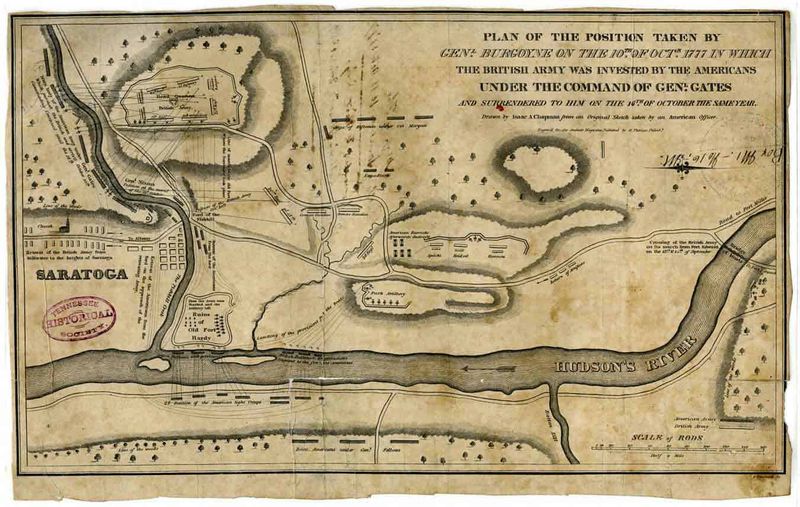
3. The Battle of Saratoga
In 1777, the Battle of Saratoga became a crucial turning point in the American Revolutionary War. Over several weeks, American forces, led by Generals Horatio Gates and Benedict Arnold, clashed with British troops in the dense forests of New York.
The American victory convinced France to join the war on the side of the colonies, providing essential support. This battle showcased the ability of the Continental Army to defeat British forces, marking a significant strategic shift.
The victory at Saratoga is often credited with altering the course of the war and securing American independence.
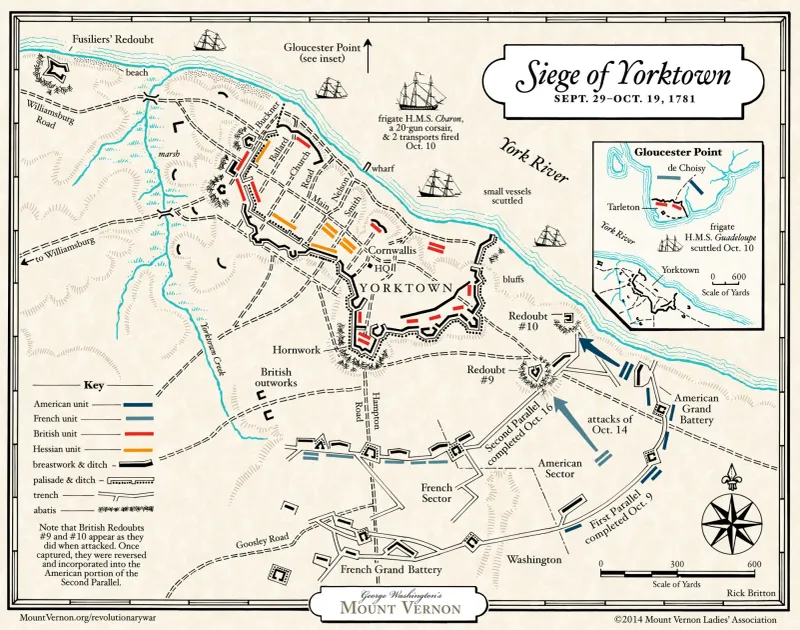
4. The Siege of Yorktown
The Siege of Yorktown in 1781 was a decisive victory for the American and French forces during the Revolutionary War. General George Washington, alongside French allies, surrounded British General Cornwallis’s troops in Yorktown, Virginia.
With the Chesapeake Bay blockaded by the French fleet, Cornwallis had no option but to surrender, effectively ending major military operations. This victory solidified American independence and demonstrated the power of international alliances. The surrender at Yorktown paved the way for peace negotiations, ultimately leading to the Treaty of Paris in 1783, which recognized American sovereignty.
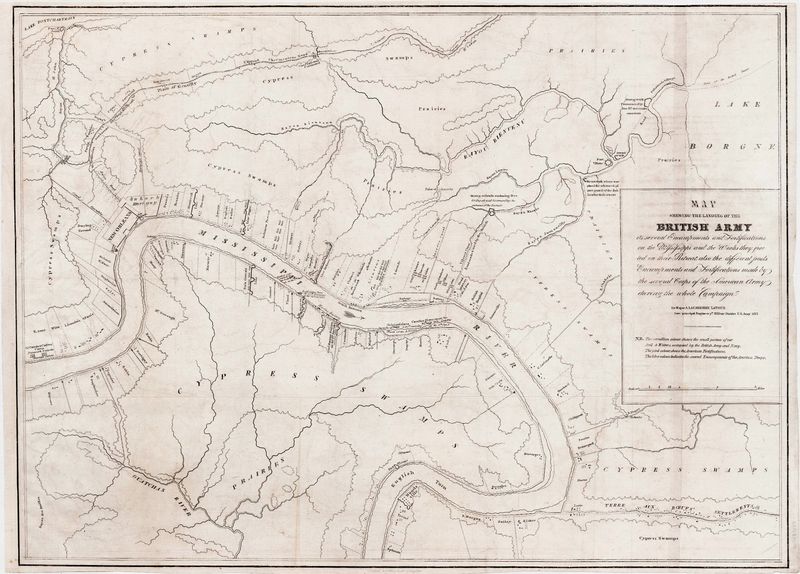
5. The Battle of New Orleans
The Battle of New Orleans, fought in January 1815, was the final major battle of the War of 1812. Led by General Andrew Jackson, American forces achieved a surprising victory against the well-trained British army.
The battle took place after the Treaty of Ghent had been signed but before news of the peace had reached the combatants. Jackson’s strategic use of the terrain and his diverse troop composition led to a decisive American victory.
This battle boosted national pride and helped solidify Andrew Jackson’s reputation as a national hero, shaping his future political career.
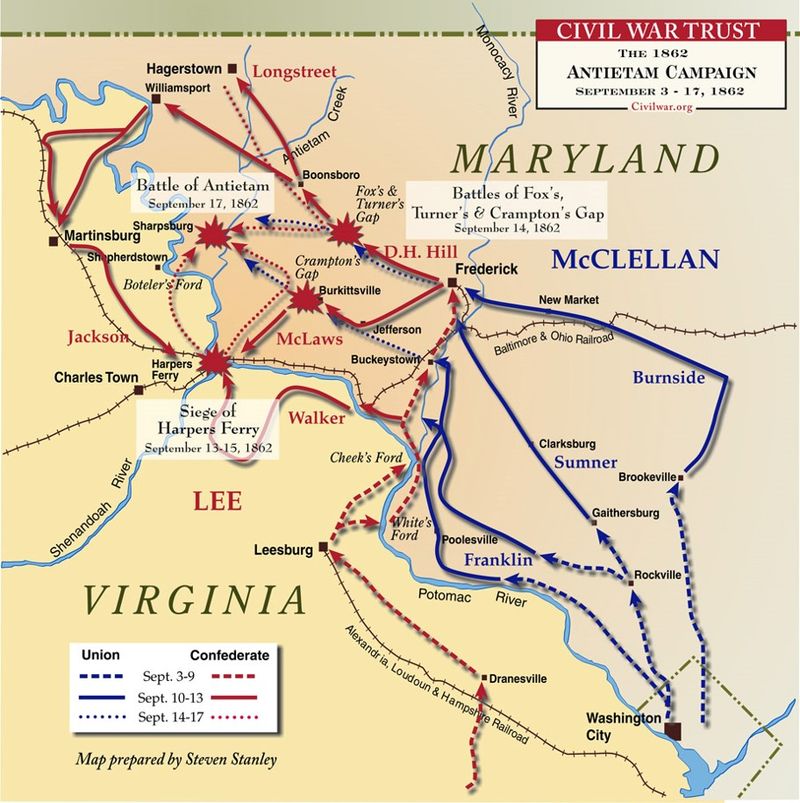
6. The Battle of Antietam
On September 17, 1862, the Battle of Antietam became the bloodiest single day in American military history. Union and Confederate forces clashed near Antietam Creek in Maryland, resulting in over 22,000 casualties.
The battle ended in a tactical draw, but it provided President Abraham Lincoln with the opportunity to issue the Emancipation Proclamation. This pivotal document redefined the purpose of the war, transforming it into a fight for the liberation of slaves.
Antietam’s strategic significance lay in its impact on both domestic and international perceptions of the Union’s cause.
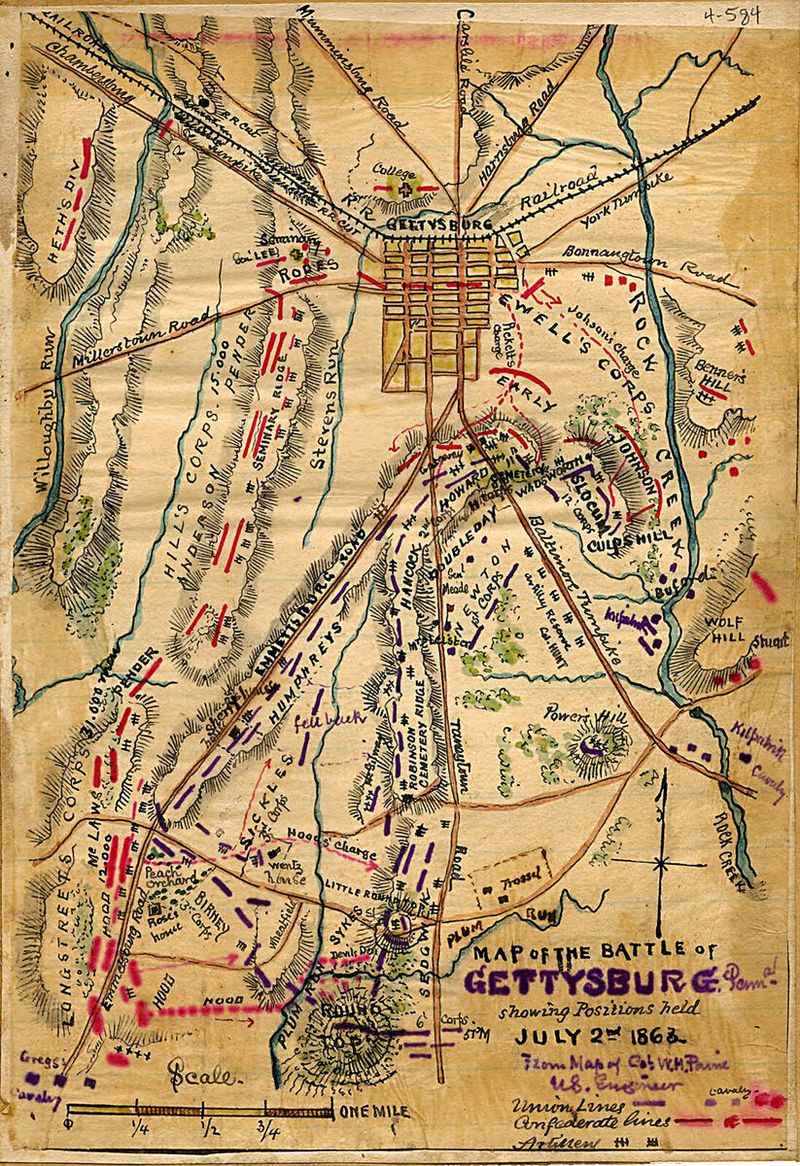
7. The Battle of Gettysburg
In July 1863, the Battle of Gettysburg marked a turning point in the American Civil War. Fought in the small town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, it was one of the fiercest battles, involving massive armies from both the Union and the Confederacy.
The Union victory ended General Robert E. Lee’s invasion of the North, inflicting irreparable losses on Confederate forces. Often considered the war’s turning point, Gettysburg shifted the momentum in favor of the Union.
The battle’s legacy is commemorated by President Lincoln’s Gettysburg Address, which redefined the nation’s values and commitment to liberty.
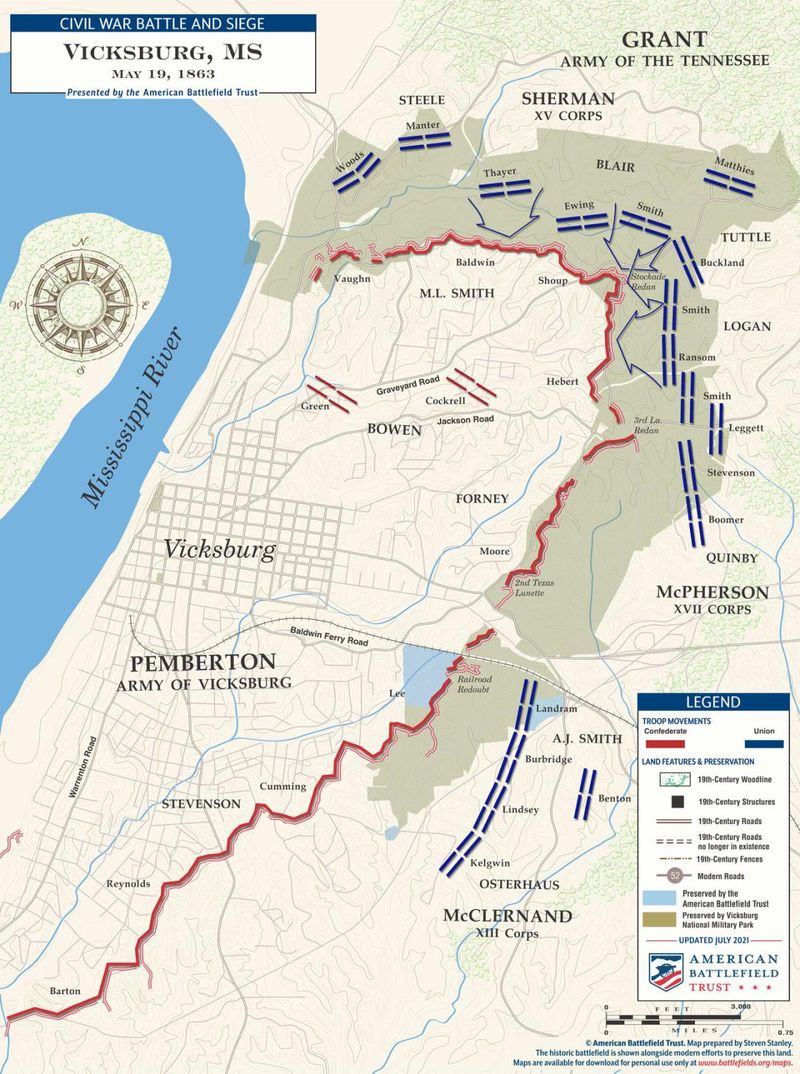
8. The Siege of Vicksburg
The Siege of Vicksburg in 1863 was a critical Union victory during the American Civil War. Union forces, led by General Ulysses S. Grant, besieged the Confederate-held city of Vicksburg, Mississippi, for over 40 days.
Ultimately, the Confederate surrender on July 4 split the Confederacy and gave the Union control of the Mississippi River. This victory was vital in the Union’s strategy of dividing and conquering the South.
The fall of Vicksburg, coupled with the Union’s triumph at Gettysburg, marked a significant turning point in the war, boosting Northern morale.
9. The Battle of Fort Sumter
In April 1861, the bombardment of Fort Sumter in Charleston Harbor signaled the start of the American Civil War. Confederate forces opened fire on the Union-held fort, marking the beginning of a conflict that would last for four years.
The fall of Fort Sumter rallied the North and solidified the resolve to preserve the Union. Although the fort’s surrender was a symbolic Confederate victory, it galvanized Union efforts.
The battle underscored the deep-seated divisions within the country, setting in motion a war that would ultimately reshape the nation’s political and social landscape.
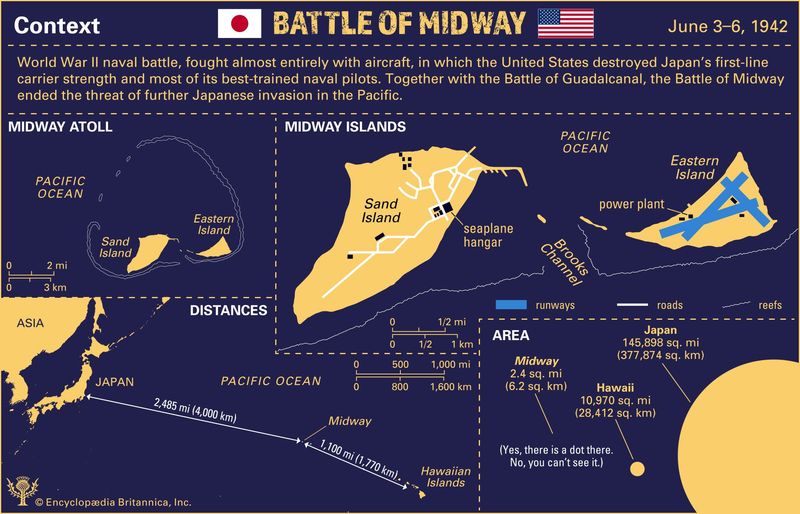
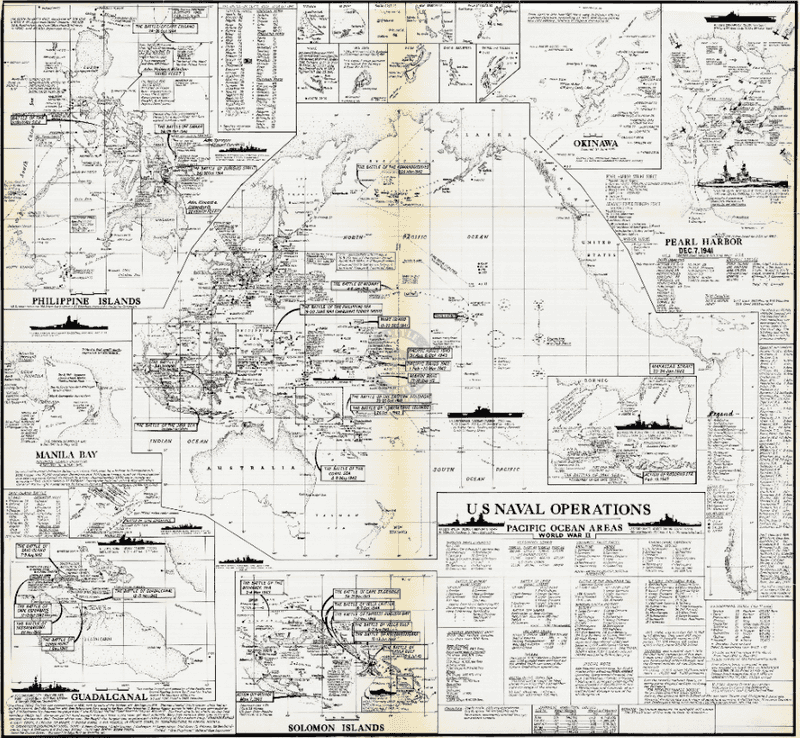
10. The Battle of Midway
In June 1942, the Battle of Midway became a pivotal moment in the Pacific Theater of World War II. American naval forces, utilizing advanced code-breaking techniques, ambushed the Japanese fleet near Midway Atoll.
The decisive American victory halted Japanese expansion and shifted the balance of power in the Pacific. This battle showcased the effectiveness of aircraft carriers and naval aviation, setting the stage for future naval engagements.
The victory at Midway is often seen as a turning point, demonstrating the strategic prowess of American forces and boosting morale on the home front.
11. The Battle of Iwo Jima
The Battle of Iwo Jima, fought in early 1945, was one of the most grueling battles in the Pacific Theater of World War II. American Marines faced entrenched Japanese defenders on the rugged volcanic island.
The iconic image of the flag raising on Mount Suribachi symbolizes the courage and determination of American forces. The battle was strategically important for its proximity to Japan and as a base for air operations.
Iwo Jima’s capture showcased the relentless spirit of the Marines and underscored the challenges of island warfare.
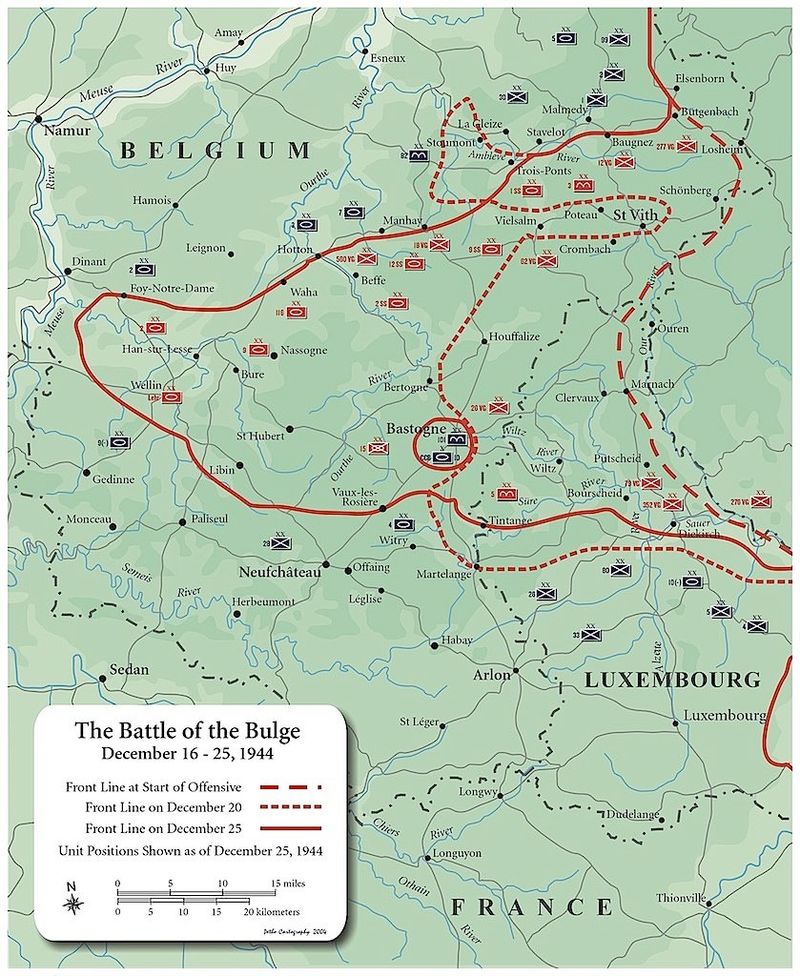
12. The Battle of the Bulge
In December 1944, the Battle of the Bulge unfolded in the dense Ardennes Forest, marking the last major German offensive of World War II. The surprise attack aimed to split Allied forces and capture Antwerp.
Amid harsh winter conditions, American troops mounted a resilient defense, ultimately blunting the German advance. The battle’s intense fighting tested the mettle of Allied soldiers, but their determination led to a crucial victory.
The failure of the German offensive marked a turning point, as Allied forces regained the initiative, pushing towards ultimate victory in Europe.
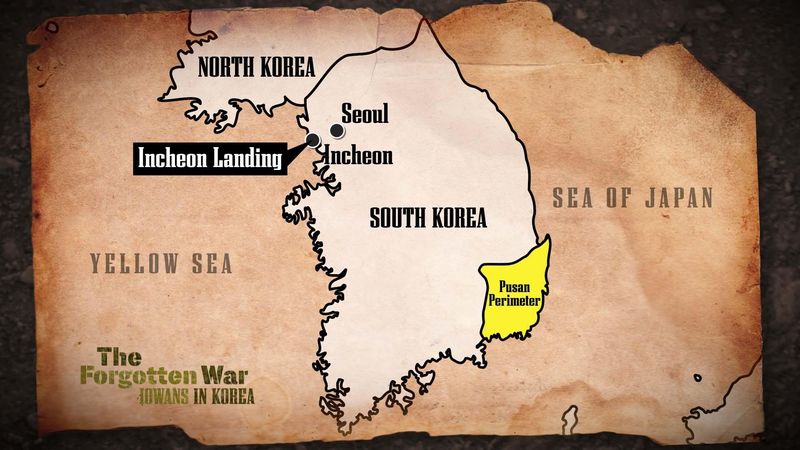
13. The Battle of Inchon
In September 1950, during the Korean War, the Battle of Inchon was a daring amphibious landing led by General Douglas MacArthur. The operation aimed to surprise and outflank North Korean forces.
The strategic success of the Inchon landing allowed United Nations forces to recapture Seoul and shift the war’s momentum. The battle showcased MacArthur’s bold strategy and the effectiveness of amphibious warfare.
Inchon’s success reinvigorated the efforts to defend South Korea, highlighting the importance of surprise and adaptability in military operations.
14. The Battle of Khe Sanh
In early 1968, the Battle of Khe Sanh became one of the most famous confrontations of the Vietnam War. U.S. Marines defended the remote outpost against a prolonged siege by the North Vietnamese Army.
The intense battle drew global attention, becoming a symbol of American resilience and determination. Despite the eventual lifting of the siege, the strategic significance of Khe Sanh remains debated.
However, the battle demonstrated the challenges of guerilla warfare and the complexities of fighting in Vietnam, shaping future military tactics and strategies.
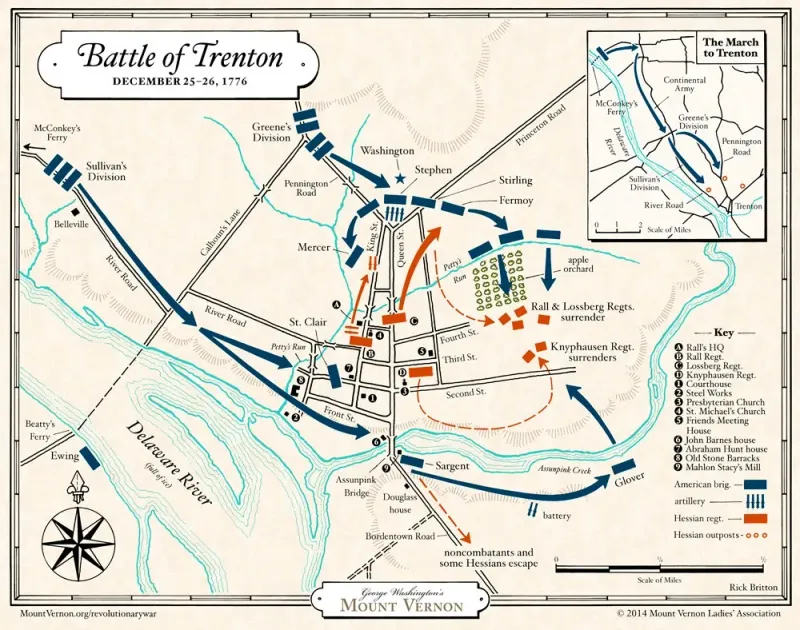
15. The Battle of Trenton
On December 26, 1776, the Battle of Trenton marked a pivotal moment in the American Revolutionary War. General George Washington led a surprise attack on the Hessian forces stationed in Trenton, New Jersey.
The daring crossing of the Delaware River in harsh winter conditions demonstrated Washington’s strategic brilliance. The victory boosted American morale and reinvigorated the revolutionary cause.
Trenton’s success proved that the Continental Army could defeat professional European troops, instilling hope and determination among the colonists as they continued their fight for independence.
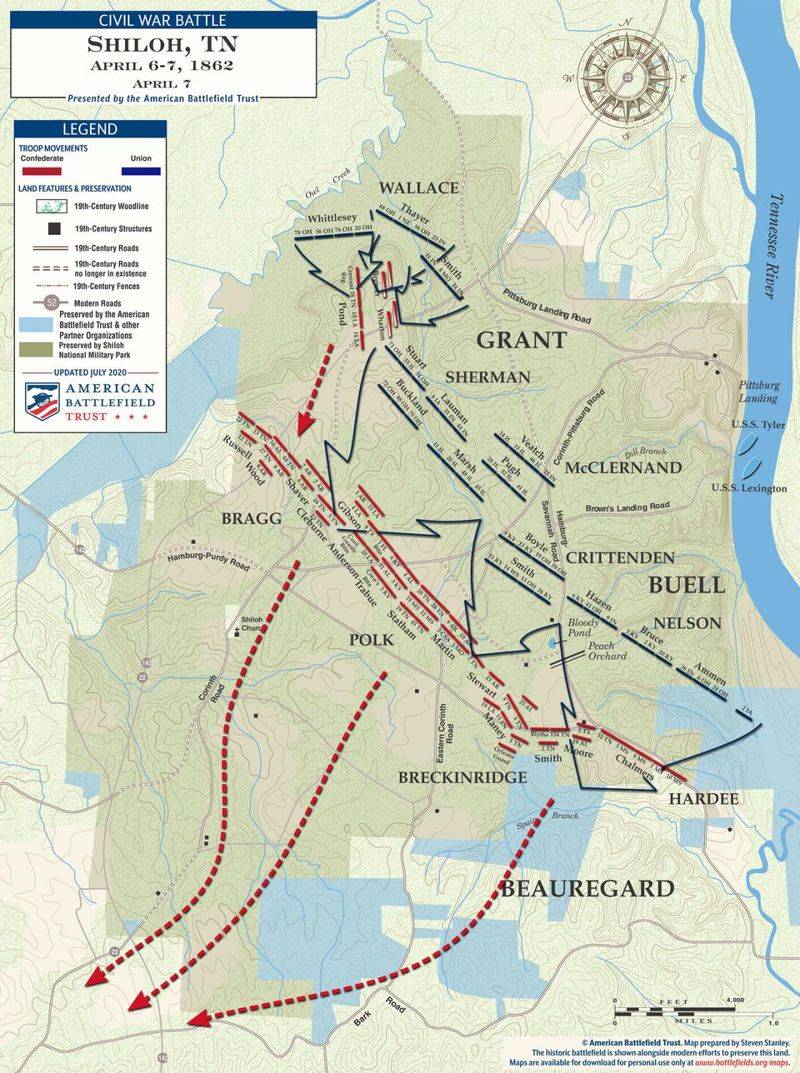
16. The Battle of Shiloh
In April 1862, the Battle of Shiloh was one of the early and intensely fought battles of the American Civil War. Union and Confederate forces clashed near the Tennessee River, resulting in heavy casualties on both sides.
The two-day battle highlighted the brutal nature of the conflict and the need for better preparation and leadership. Despite initial Confederate gains, Union reinforcements turned the tide, securing a critical victory.
Shiloh’s outcome emphasized the importance of logistics and the human cost of war, shaping future military strategies and engagements.
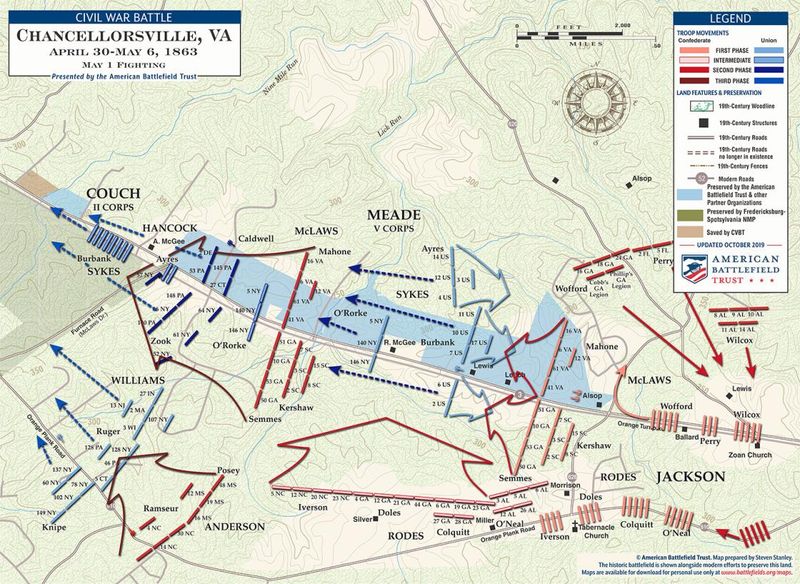
17. The Battle of Chancellorsville
In May 1863, the Battle of Chancellorsville showcased General Robert E. Lee’s tactical genius. Despite being outnumbered, Confederate forces achieved a significant victory over the Union army in Virginia.
Lee’s daring maneuvers and the bold use of terrain led to one of the Confederacy’s most celebrated victories. However, the battle also resulted in the tragic loss of General Stonewall Jackson to friendly fire.
Chancellorsville demonstrated the complexities of command and the impact of leadership on battlefield outcomes, influencing future military engagements during the Civil War.
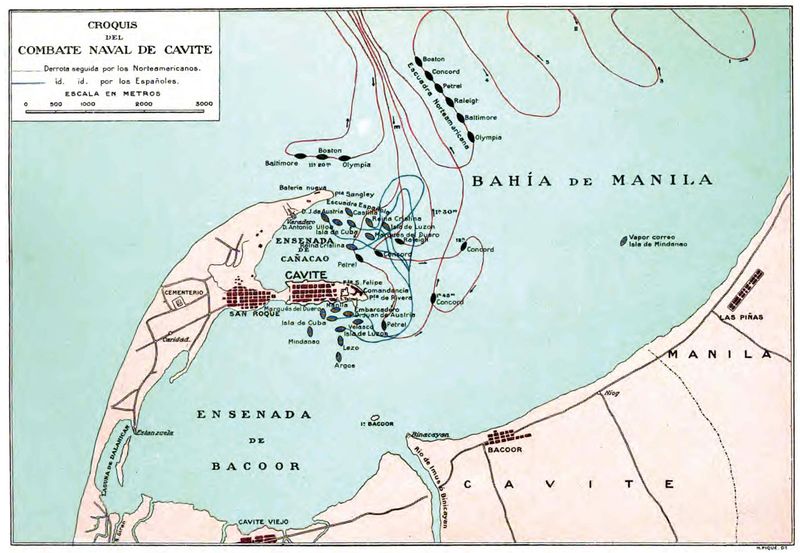
18. The Battle of Manila Bay
In May 1898, the Battle of Manila Bay marked a decisive American victory during the Spanish-American War. Commodore George Dewey led the U.S. Navy against the Spanish fleet in the Philippines.
Utilizing superior naval tactics and technology, the American forces quickly secured control of Manila Bay. This victory demonstrated the growing power of the U.S. Navy and signaled America’s emergence as a global maritime force.
The battle’s outcome contributed to the eventual end of Spanish colonial rule in the Philippines and expanded America’s influence in the Pacific region.
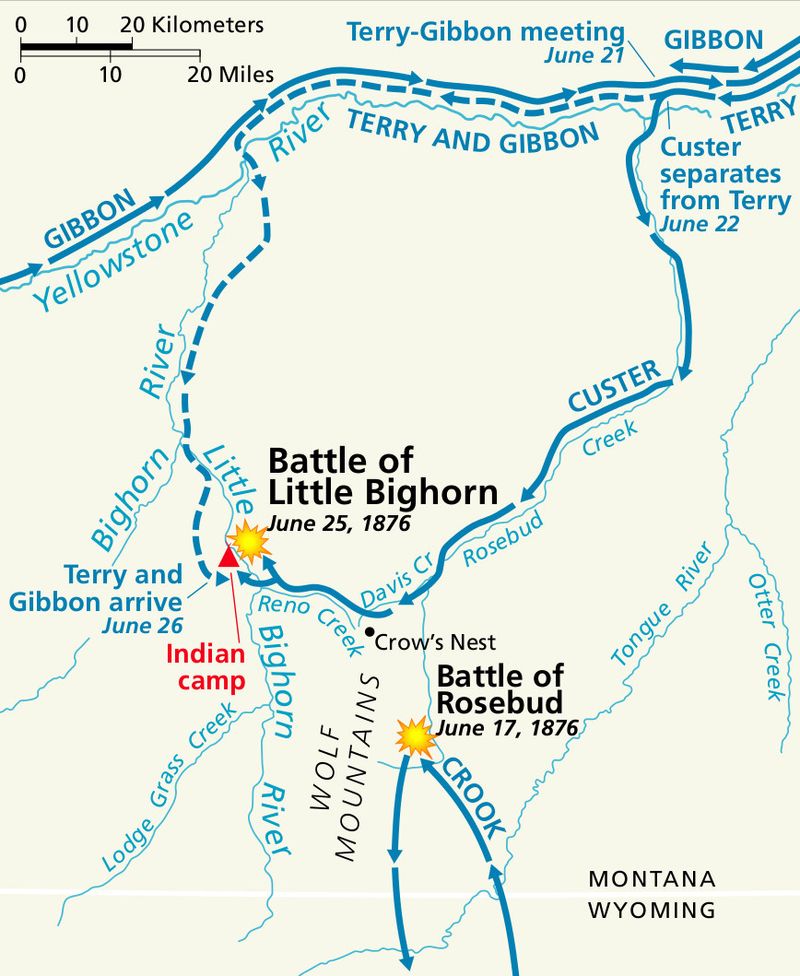
19. The Battle of Little Bighorn
In June 1876, the Battle of Little Bighorn became a defining conflict during the Great Sioux War. General George Armstrong Custer led the U.S. Army’s 7th Cavalry against a large coalition of Native American tribes.
Underestimating the Native forces, Custer and his troops were overwhelmed and defeated. The battle, often referred to as “Custer’s Last Stand,” highlighted the tensions between the U.S. government and Native American tribes.
The victory was a symbolic triumph for the Native Americans, underscoring their resilience and the complexities of westward expansion.
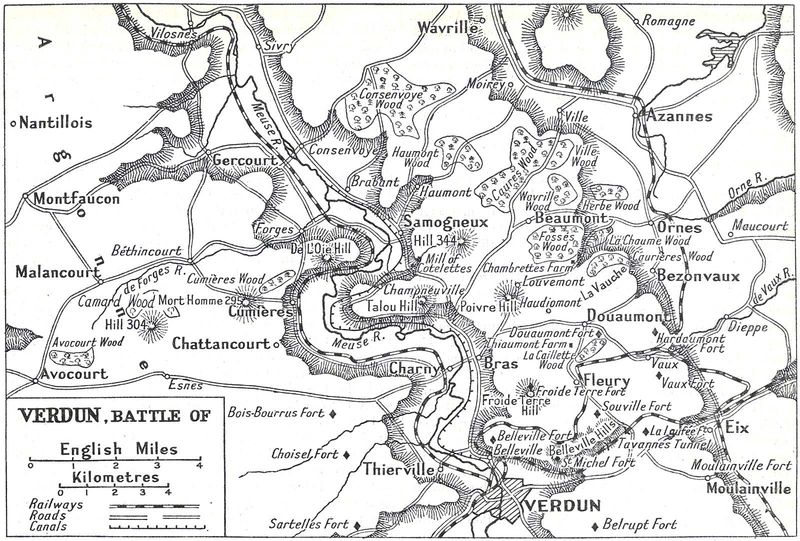
20. The Battle of Verdun
While not a direct American battle, the Battle of Verdun in 1916 had significant implications for World War I. French forces bravely held their lines against a relentless German assault.
The battle’s prolonged and brutal nature resulted in massive casualties and became a symbol of French determination. The American entry into the war in 1917 was partly influenced by the stalemate exemplified at Verdun, highlighting the need for Allied support.
Verdun’s legacy is a testament to the endurance and sacrifices of soldiers during one of history’s deadliest conflicts.
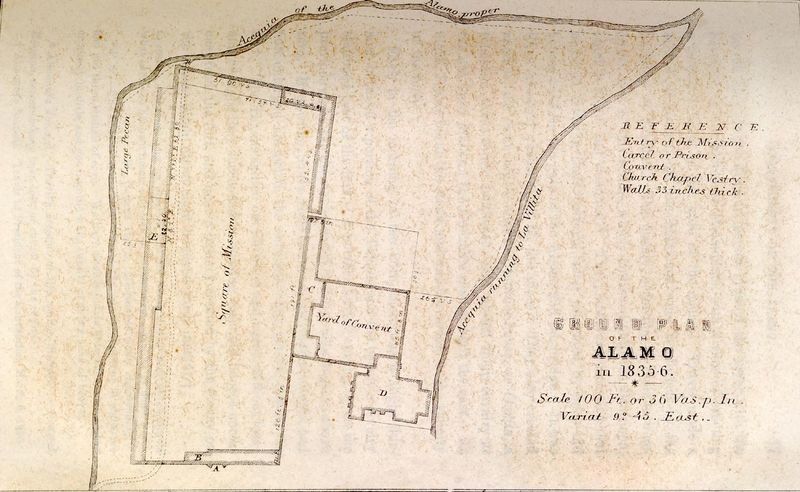
21. The Battle of the Alamo
In March 1836, the Battle of the Alamo became a legendary event during the Texas Revolution. Texian defenders, including famous figures like Davy Crockett, held out against the Mexican army at the Alamo Mission in San Antonio.
Despite being vastly outnumbered, the defenders’ courageous stand inspired the rallying cry “Remember the Alamo” for Texian forces.
The battle underscored the determination for independence and played a crucial role in galvanizing support for the Texian revolutionaries. Ultimately, the sacrifice at the Alamo became a symbol of heroism and the fight for liberty.
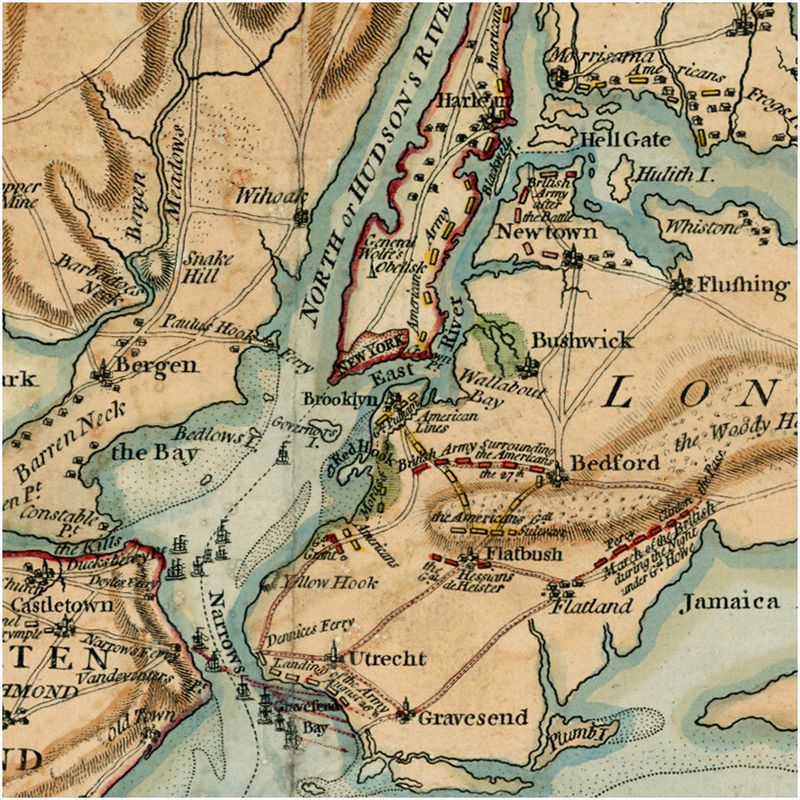
22. The Battle of New York
In the summer of 1776, the Battle of New York was a significant early defeat for American forces during the Revolutionary War. British troops launched a series of attacks, forcing General George Washington’s army to retreat.
The British victory secured control of New York City, highlighting the challenges faced by the Continental Army. Despite the setback, Washington’s strategic withdrawal preserved the army’s core, allowing for future successes.
The battle emphasized the importance of resilience and adaptability in the revolution, setting the stage for continued struggle and ultimate triumph.
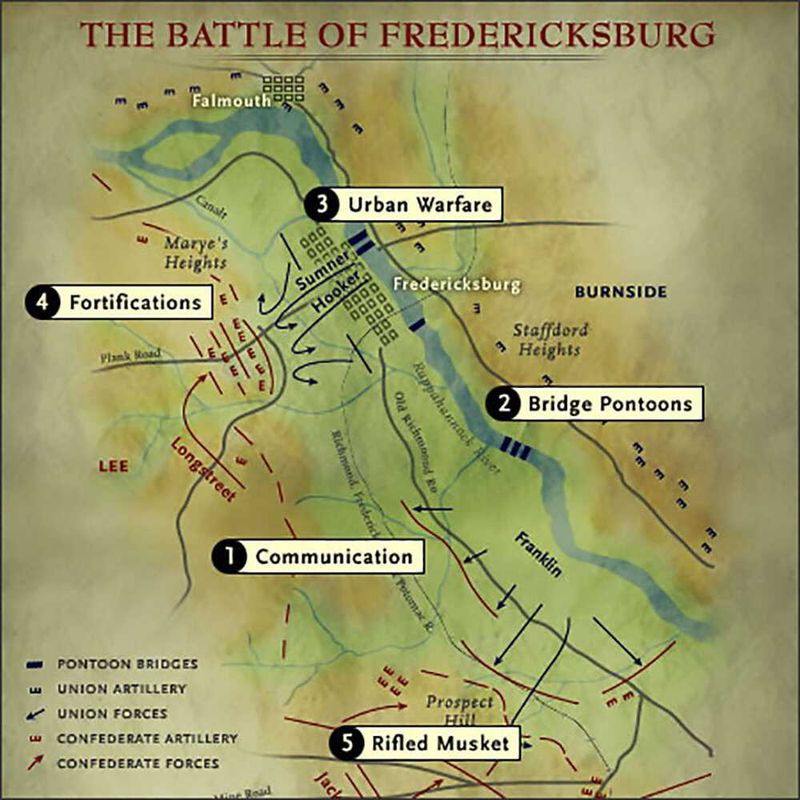
23. The Battle of Fredericksburg
In December 1862, the Battle of Fredericksburg was a significant Confederate victory during the American Civil War. Union forces, under Major General Ambrose Burnside, launched repeated assaults on well-fortified Confederate positions.
The battle resulted in heavy Union casualties and highlighted the challenges of frontal assaults against entrenched defenses. Fredericksburg underscored the importance of strategy and the need for effective leadership in wartime.
The Confederate victory bolstered Southern morale, while the Union learned valuable lessons for future engagements, shaping military tactics and decision-making in the war’s later years.
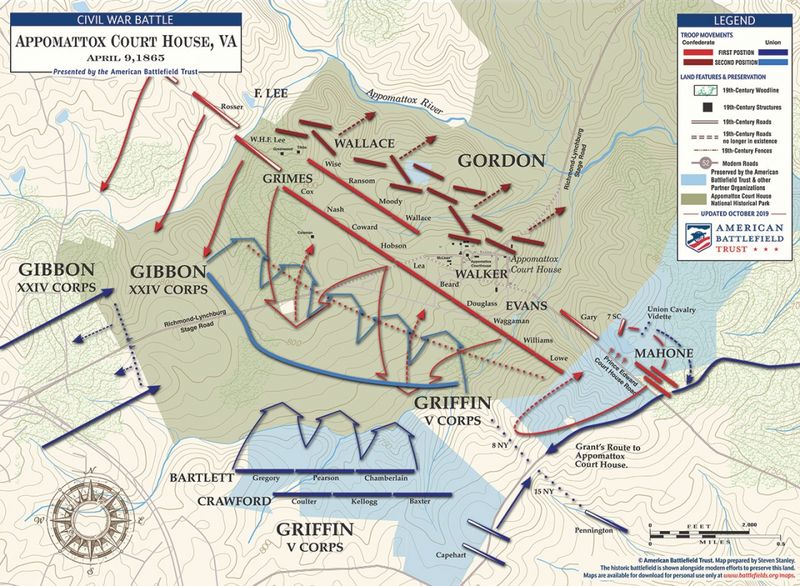
24. The Battle of Appomattox Court House
In April 1865, the Battle of Appomattox Court House marked the final engagement of the American Civil War. General Robert E. Lee’s Confederate Army, surrounded and outnumbered, was forced to surrender to Union General Ulysses S. Grant.
This surrender effectively ended the Civil War, paving the way for national reunification. The meeting between Lee and Grant set a tone of reconciliation, symbolizing hope for healing a divided nation.
Appomattox’s legacy endures as a turning point in American history, highlighting themes of unity, resilience, and the enduring quest for freedom.