The origins of Native Americans have long been a subject of fascination and debate among historians, archaeologists, and geneticists.
While the predominant theory suggests a migration from Siberia across the Bering Land Bridge, research exploring potential links to Japan has sparked intriguing discussions.
Through genetic studies, cultural similarities, and archaeological evidence, we aim to unravel the complex tapestry of human migration that has shaped the identities of Indigenous populations in the Americas.
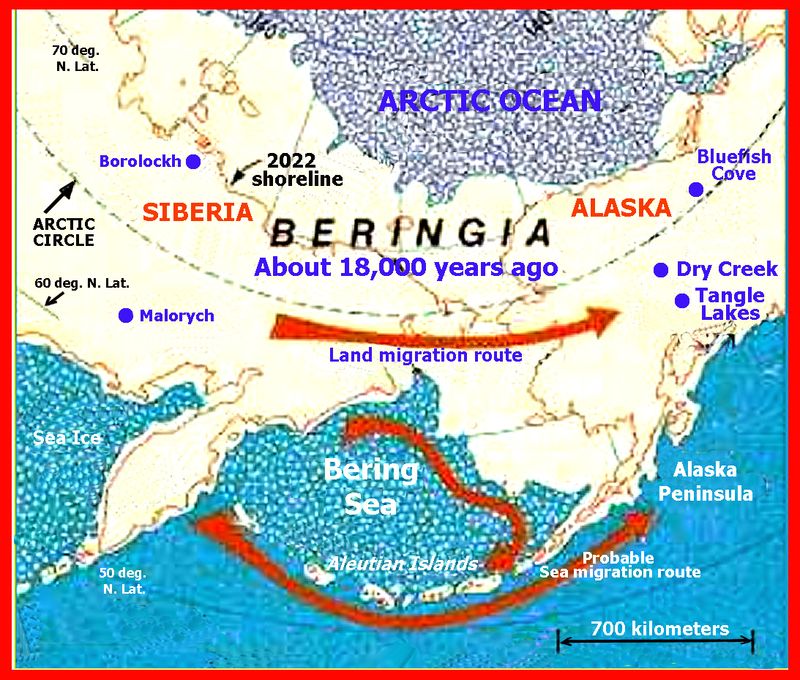
1. The Journey Begins: Migration Across Beringia
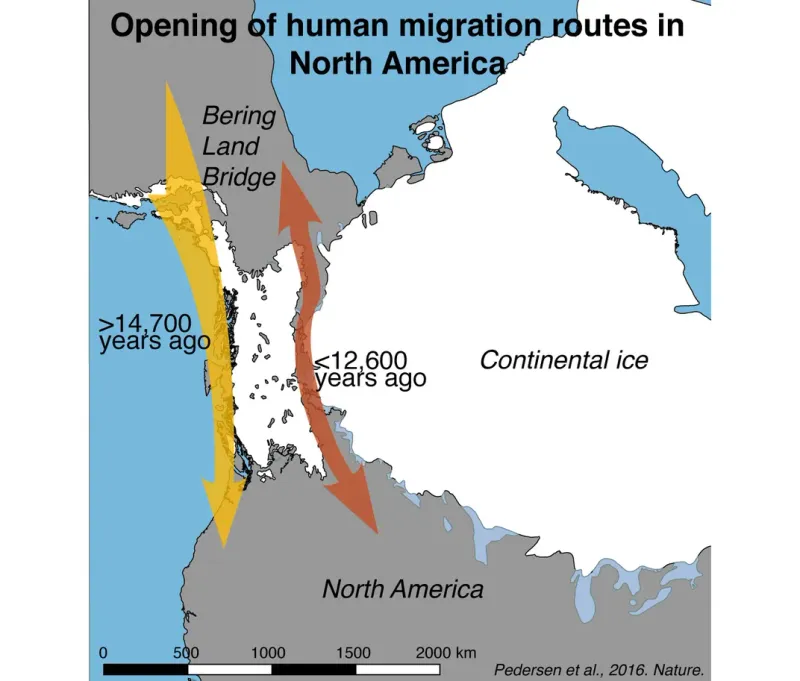
Native American ancestors embarked on a remarkable journey across Beringia, a now-submerged land bridge that connected Siberia and Alaska.
During the last Ice Age, this bridge provided a route for humans and animals to traverse from Asia into North America. The migration is believed to have occurred approximately 20,000 to 15,000 years ago.
Today, this region is submerged beneath the Bering Sea, but archaeological evidence supports the existence of this ancient pathway.
Understanding this journey offers insight into the resilience and adaptability of early humans as they expanded across new territories, shaping the future Indigenous cultures of the Americas.
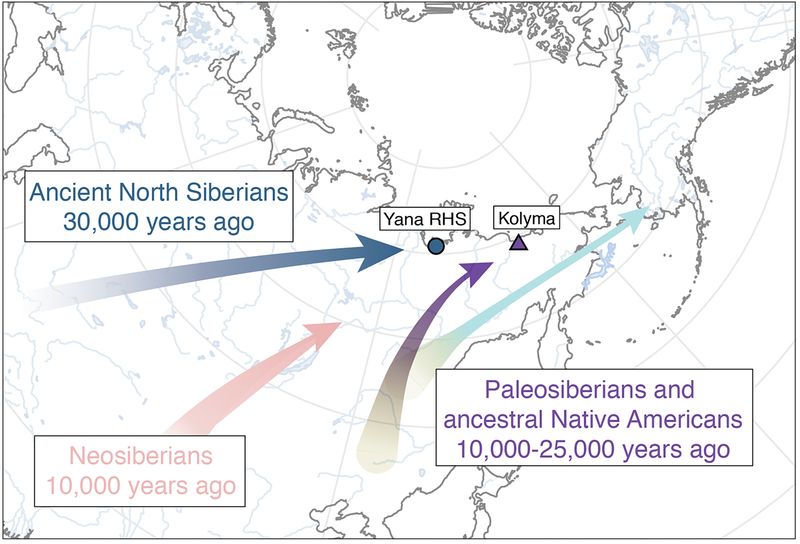
2. Tracing the Ancestors: Connections to Siberia
Genetic research has unveiled fascinating connections between Native Americans and ancient Siberian populations. These findings suggest that the ancestors of Native Americans were part of a migration wave from Siberia.
Approximately 20,000 years ago, these groups ventured into the Americas via the Bering Land Bridge. The genetic evidence illustrates a shared lineage, linking Native Americans with ancient Siberian peoples.
This ancestral connection highlights the interconnectedness of human societies and the shared evolutionary paths that different populations have taken throughout history, leading to the diverse cultures present in the Americas today.
3. The Role of the Jōmon People
The Jōmon culture of ancient Japan, dating back over 10,000 years, adds an intriguing layer to the migration narrative. Archaeologists have discovered distant genetic ties between the Jōmon people and Siberian groups.
This connection suggests a broader network of early migrations across East Asia. While these ties do not directly indicate that Native Americans descended from the Jōmon people, they underscore the complex web of ancient human movements.
The Jōmon culture’s unique pottery and tools offer a glimpse into their advanced craftsmanship and communal lifestyle, contributing to our understanding of prehistoric cultural exchanges.
4. Shared Innovations: Tools and Pottery
Artifacts found in Japan and early Native American sites reveal striking similarities in tools and pottery. These shared innovations raise questions about the interactions between ancient cultures.
While some suggest a direct migration from Japan, others propose that these similarities arose from parallel technological advancements. The exchange of ideas and techniques could have occurred through indirect contact or shared ancestral knowledge.
Exploring these artifacts helps historians piece together the puzzle of human innovation and cultural development, showing how different societies adapted to their environments using similar approaches, despite being separated by vast distances.
5. The Genetic Puzzle
Modern genetic studies have identified unique markers in Native American genomes. These markers distinguish Native Americans from other East Asian populations, including those from Japan.
After migrating into the Americas, Native Americans developed distinct genetic traits, setting them apart from their Asian ancestors. This differentiation highlights the evolutionary processes that occur when populations adapt to new environments.
Understanding these genetic differences offers valuable insights into human adaptation and migration patterns, emphasizing the diverse evolutionary paths that have shaped the genetic landscape of Indigenous peoples in the Americas.
6. Cultural Echoes Across Continents
Cultural parallels between Indigenous peoples in the Americas and ancient Asian societies have intrigued researchers. Shared artistic motifs and spiritual practices suggest deep ancestral influences that transcend continents.
These echoes of culture reveal how ancient societies may have maintained links through shared beliefs and traditions, despite geographical separation.
Such cultural similarities provide clues to the complex web of human history, where exchanges of ideas and practices occurred across vast distances, enriching the cultural tapestries of humanity.
Exploring these connections broadens our understanding of cultural evolution and the diverse heritage of Native American societies.
7. Why Not Japan?
Theories suggesting a direct migration from Japan to North America remain speculative. The majority of evidence supports Siberia as the origin of Native American ancestors.
While distant genetic ties to Japanese populations exist, they do not substantiate a direct lineage. Instead, these ties reflect broader ancient migrations in East Asia.
The prevailing view holds that Native Americans have roots in Siberia, with subsequent migrations shaping their genetic and cultural development in the Americas.
This conclusion underscores the importance of comprehensive evidence in tracing human ancestry, ensuring a nuanced understanding of migration history.
8. Understanding the Bigger Picture
The story of Native American origins is a complex tapestry woven from migrations, genetic evolution, and cultural exchanges. It reflects how ancient human populations were interconnected across the globe.
While theories about Japanese links are intriguing, the broader narrative encompasses a multitude of influences. Understanding this bigger picture offers a comprehensive view of human history, highlighting the resilience and adaptability of ancient peoples.
By examining genetic, archaeological, and cultural evidence, we gain insights into the rich heritage and diverse identities of Indigenous populations in the Americas, revealing a shared human journey that transcends borders.