March 16th has witnessed a multitude of significant historical moments that have shaped the world in various ways. From the establishment of empires and kingdoms to tragic massacres and pivotal political events, this date has a rich tapestry of stories.
Each event not only marks a moment in history but also offers lessons and reflections on the human experience.
Join us as we explore 30 notable events that occurred on this day, ranging from ancient declarations of power to modern geopolitical shifts and natural calamities.
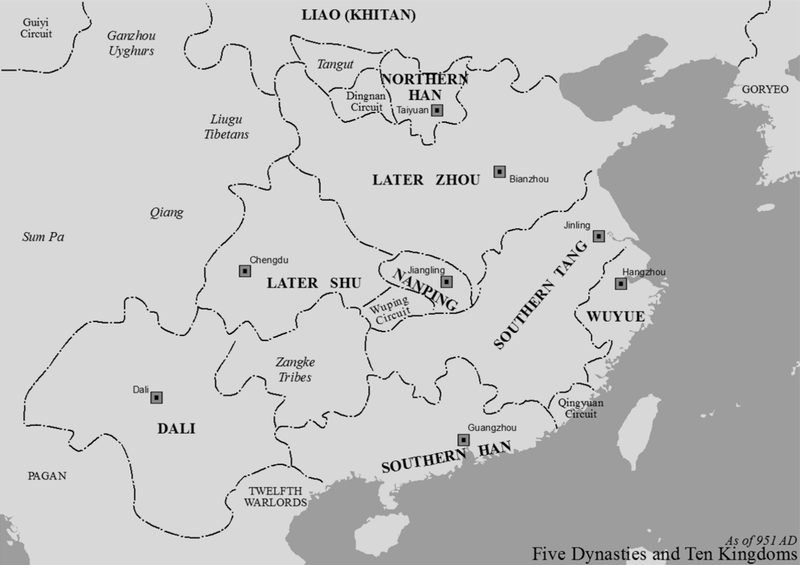
1. 934 – Meng Zhixiang Declares Himself Emperor and Establishes the Later Shu
March 16, 934, marked a turning point in Chinese history with Meng Zhixiang’s declaration as emperor, establishing the Later Shu dynasty. In ancient Sichuan, amid political fragmentation, Meng claimed the throne, asserting authority over the region.
His move was strategic, capitalizing on the Tang dynasty’s collapse. The declaration was not merely symbolic. It represented a shift in power dynamics, illustrating the era’s regional autonomy.
Meng’s reign saw efforts to stabilize the region, fostering economic growth and cultural development. His rule, though short-lived, left a lasting impact on the region, setting a precedent for future rulers.
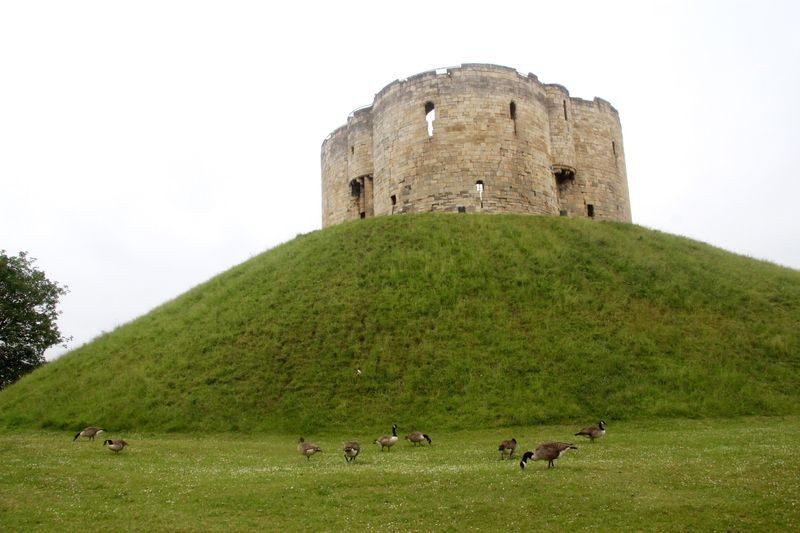
2. 1190 – Massacre of Jews at Clifford’s Tower, York
On March 16, 1190, a tragic event unfolded at Clifford’s Tower, York, where a massacre of Jewish residents occurred. During a time of increasing anti-Semitic sentiment, a mob besieged the tower, where the Jews had sought refuge.
The attackers, fueled by religious fervor and economic jealousy, breached the defenses, leading to a tragedy. Many of the besieged, facing imminent death, chose suicide over capture.
This event highlighted the precarious position of Jewish communities in medieval Europe. The massacre was a grim reminder of intolerance and the perils faced by minorities, resonating through history as a call for tolerance.
3. 1244 – Over 200 Cathars Are Burned to Death After the Fall of Montségur
March 16, 1244, saw the tragic end of the Cathar resistance at Montségur in southern France. After a prolonged siege by French royal forces, over 200 Cathars were burned, marking a significant episode in the Albigensian Crusade.
This event was not just a military victory but a symbolic triumph over heresy, as perceived by the Catholic Church. The Cathars, known for their dualistic beliefs, challenged the Church’s authority, leading to their persecution.
Their demise at Montségur underscored the era’s religious intolerance and the lengths to which institutions would go to enforce orthodoxy.
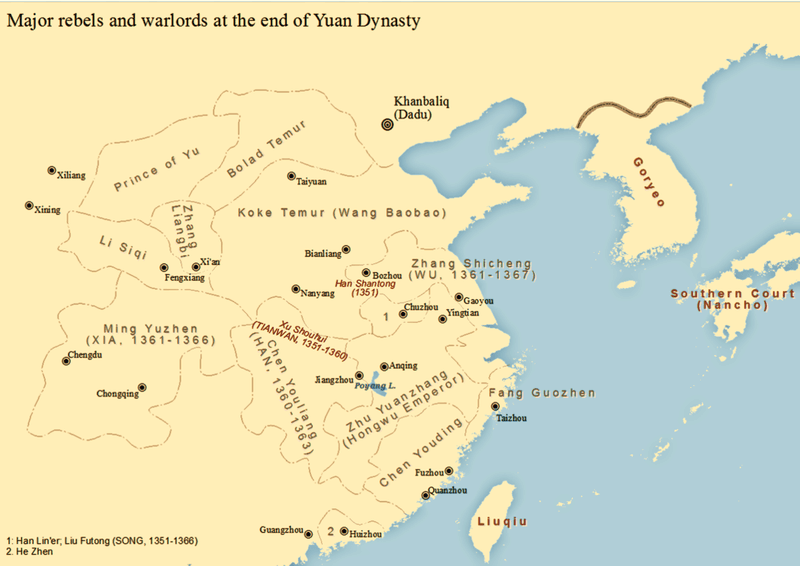
4. 1355 – Amidst the Red Turban Rebellions, Han Lin’er is Proclaimed Emperor of the Restored Song Dynasty
In 1355, amidst the chaos of the Red Turban Rebellions, Han Lin’er was proclaimed emperor of the Restored Song Dynasty. This event, occurring on March 16, was a bold attempt to revive the Song dynasty’s legacy.
The Red Turban Rebellions, driven by dissatisfaction with Mongol Yuan rule, saw numerous factions rise against the regime. Han Lin’er’s proclamation was significant, symbolizing defiance and hope for change.
His reign, however, faced challenges, including internal strife and external threats. Despite its brevity, the declaration was pivotal, reflecting the enduring spirit of resistance and the complex dynamics of power during turbulent times.
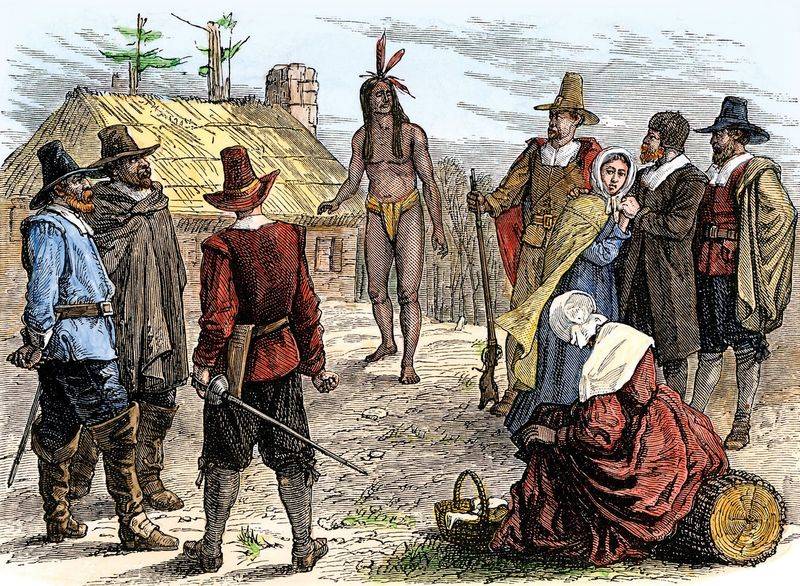
5. 1621 – Abenaki Chief Samoset Greets Plymouth Settlers with “Welcome, Englishmen!”
On March 16, 1621, Abenaki Chief Samoset walked into the Plymouth Colony, greeting the settlers with “Welcome, Englishmen!” This interaction marked one of the first peaceful contacts between Native Americans and English settlers.
Samoset, fluent in English learned from fishermen, offered crucial assistance. His greeting was a gesture of goodwill, setting the tone for subsequent interactions.
This meeting laid the groundwork for relations with the Wampanoag tribe, leading to critical alliances. Samoset’s role exemplified the complex dynamics of diplomacy and survival in the New World, highlighting the potential for cooperation amidst cultural differences.
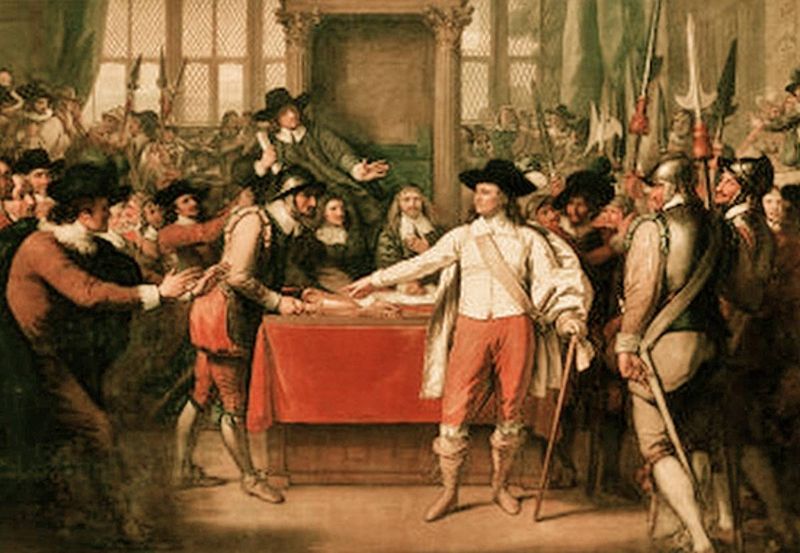
6. 1660 – England’s Long Parliament is Dissolved in Preparation for the Convention Parliament
March 16, 1660, marked the dissolution of England’s Long Parliament, paving the way for the Convention Parliament. This event was pivotal in the restoration of the monarchy under King Charles II.
The Long Parliament, established in 1640, had seen England through civil war and the execution of Charles I. Its dissolution signified a shift in power and a move toward reconciliation.
The Convention Parliament, convened later, played a crucial role in restoring stability and monarchy. This transition illustrated the fluid nature of political authority and the efforts to balance governance and tradition in a changing landscape.
7. 1696 – The Dutch Bombard Givet During the Nine Years’ War
During the Nine Years’ War, on March 16, 1696, Dutch forces bombarded the town of Givet, a strategic location in France. This military action was part of the broader conflict between France and the Grand Alliance.
The bombardment aimed to weaken French control, showcasing the shifting alliances and military strategies of the period. Givet, situated on the Meuse River, was key for supply lines and troop movements.
The event demonstrated the tactical use of artillery in warfare and highlighted the ongoing struggle for dominance in Europe, reflecting the era’s geopolitical complexities and the quest for territorial advantage.
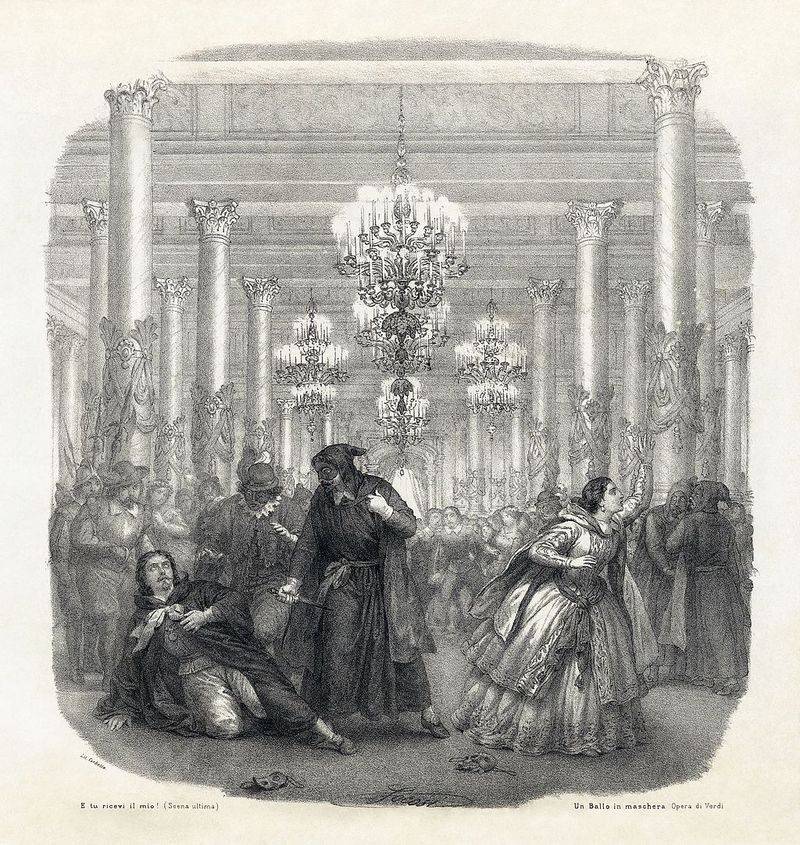
8. 1792 – King Gustav III of Sweden is Shot; He Dies on March 29
On March 16, 1792, King Gustav III of Sweden was shot at a masked ball in Stockholm, an event that would lead to his death on March 29. This assassination attempt stemmed from political unrest and opposition to his autocratic rule.
Gustav’s reign was marked by efforts to consolidate power, leading to tensions with the nobility. The shooting, by an aristocrat discontented with Gustav’s policies, underscored the volatile political climate.
His eventual death precipitated a shift in Swedish governance, highlighting the fragility of monarchical power and the intricate interplay of politics and personal ambition in shaping history.
9. 1802 – The United States Army Corps of Engineers is Established to Operate West Point
On March 16, 1802, the United States Army Corps of Engineers was formally established, tasked with operating West Point. This marked a significant development in American military and engineering history.
West Point, strategically located on the Hudson River, became a training ground for military leaders. The Corps’ creation reflected the growing recognition of engineering’s role in national defense and development.
Its establishment laid the foundation for future infrastructure projects, emphasizing the integration of engineering expertise in military strategy. This event highlighted the evolving needs of a young nation and the importance of technical skills in its growth.
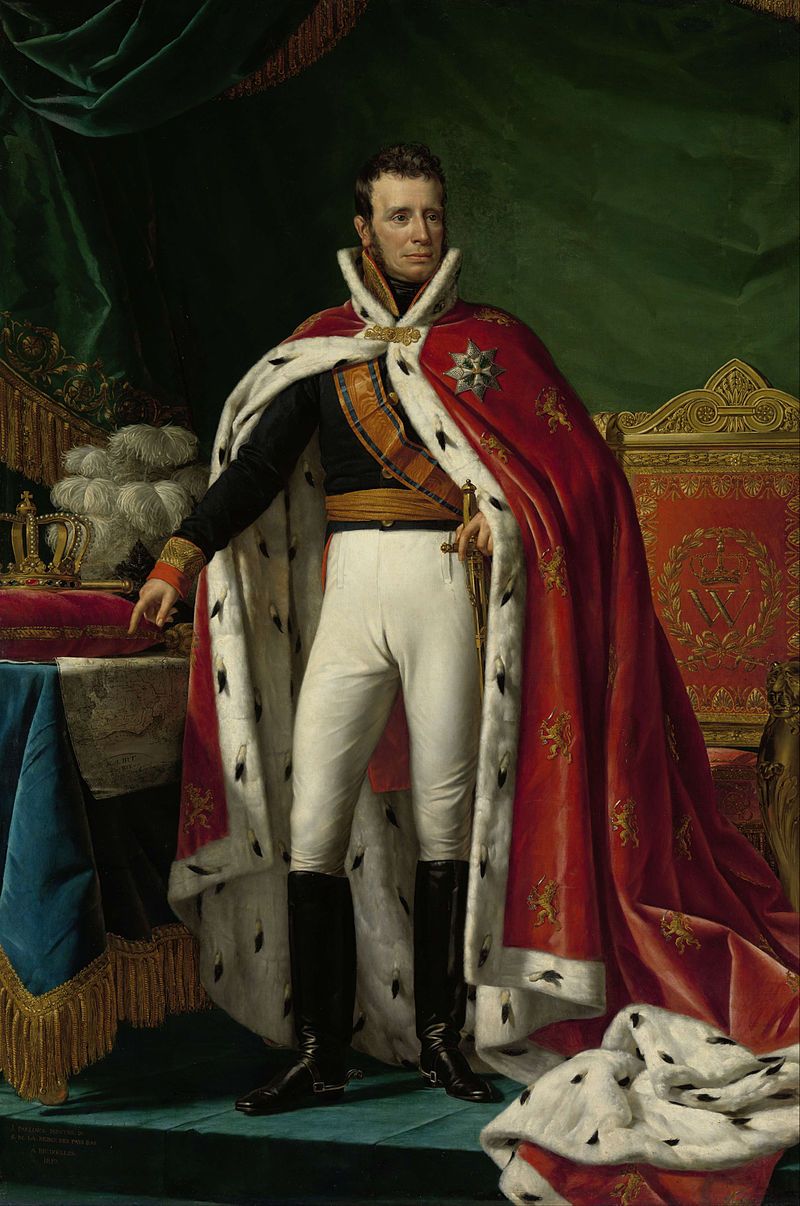
10. 1815 – Prince Willem Proclaims Himself King of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands
On March 16, 1815, Prince Willem of Orange-Nassau proclaimed himself King of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands. This declaration was part of the post-Napoleonic restructuring of Europe.
Willem’s ascension marked the unification of the northern and southern Netherlands, a move aimed at stabilizing the region. The new kingdom faced challenges, including internal divisions and external pressures.
His reign sought to balance these dynamics, promoting modernization and national identity. This proclamation was a crucial step in shaping the Netherlands’ future, illustrating the complexities of nation-building in a rapidly changing European landscape.
11. 1872 – Wanderers F.C. Win the First FA Cup, Beating Royal Engineers A.F.C. 1–0
March 16, 1872, saw Wanderers F.C. clinch victory in the first-ever FA Cup, defeating Royal Engineers A.F.C. 1–0. This historic match took place at the Kennington Oval, marking the dawn of organized football competitions.
The FA Cup, conceived to standardize the game, brought together clubs to compete for the prestigious trophy. Wanderers’ triumph was a testament to the growing popularity of football as a sport.
This event laid the groundwork for modern football, fostering the spirit of competition and camaraderie. It highlighted the sport’s potential to unite diverse communities and inspire collective enthusiasm.
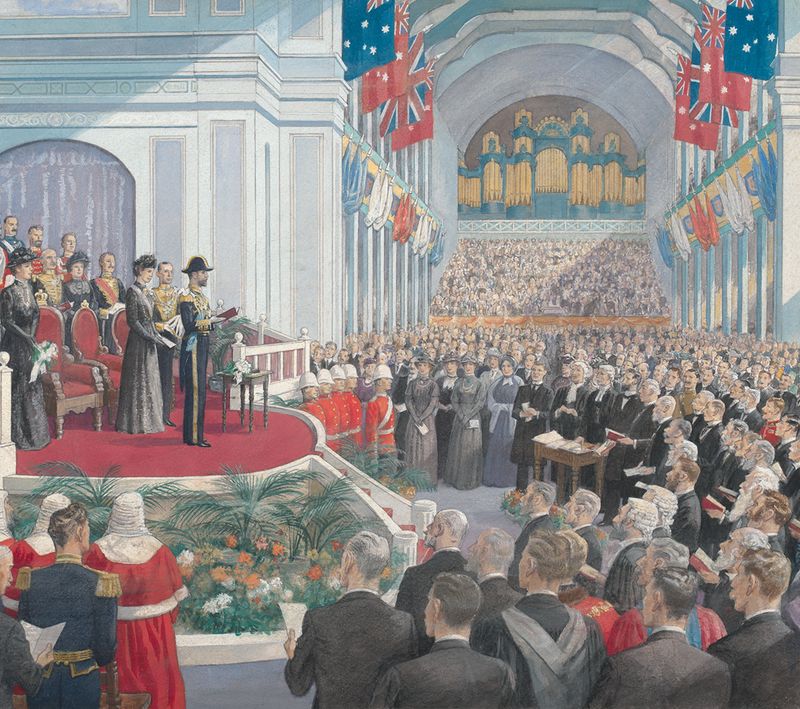
12. 1898 – Representatives of Five Australian Colonies Adopt a Constitution, Forming the Basis of the Commonwealth of Australia
On March 16, 1898, representatives from five Australian colonies adopted a constitution, forming the foundation of the Commonwealth of Australia. This pivotal moment marked a significant step toward nationhood.
The constitution, inspired by democratic ideals, sought to unify the colonies while respecting regional autonomy. The process involved negotiations and compromises, reflecting the diverse aspirations of the colonies.
This development laid the legal and political groundwork for Australia’s federation in 1901. It underscored the importance of dialogue and cooperation in nation-building, highlighting Australia’s journey toward unity and identity on the global stage.
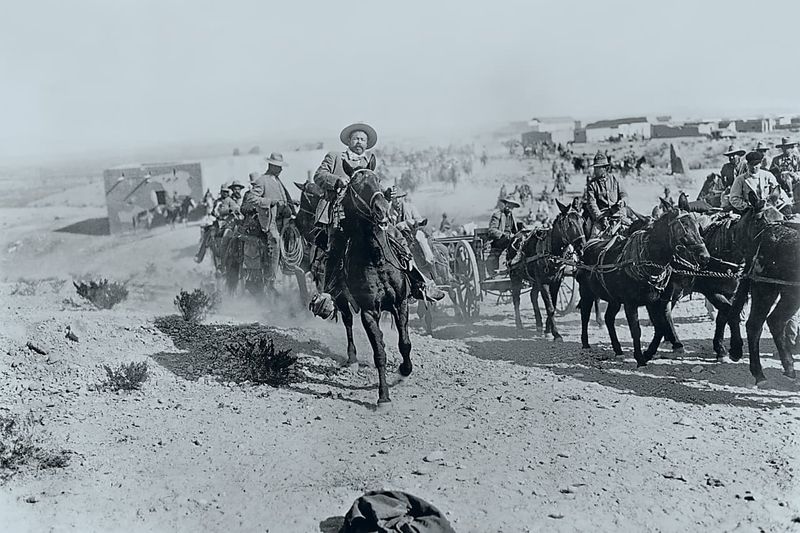
13. 1916 – U.S. Cavalry Under John J. Pershing Crosses the U.S.–Mexico Border to Hunt Pancho Villa
On March 16, 1916, the U.S. Cavalry, led by General John J. Pershing, crossed the U.S.–Mexico border in pursuit of Pancho Villa. This military expedition was a response to Villa’s raid on Columbus, New Mexico.
Pershing’s campaign aimed to capture Villa, showcasing the complexities of U.S.–Mexico relations. The incursion highlighted tensions and cross-border challenges, reflecting the era’s geopolitical dynamics.
Despite its limited success, the expedition emphasized the interplay between domestic security and international diplomacy. It underscored the difficulties of military pursuits in unfamiliar territory and the intricate nature of international relations.
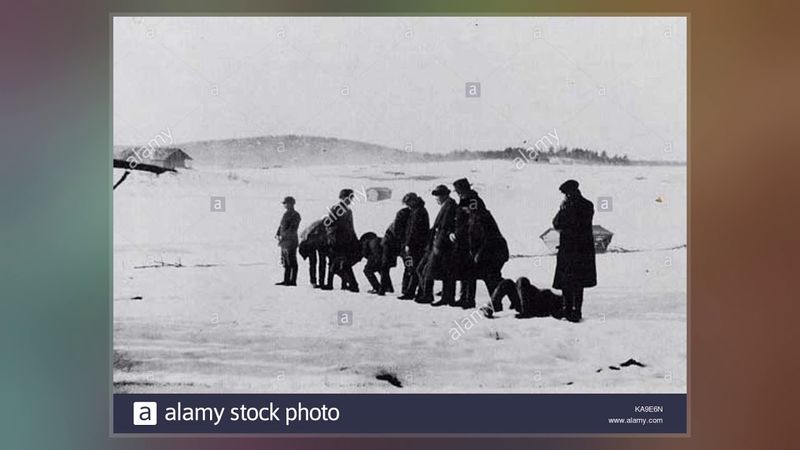
14. 1918 – Finnish Civil War: The Battle of Länkipohja Ends in the Execution of 70–100 Capitulated Reds
March 16, 1918, marked the end of the Battle of Länkipohja during the Finnish Civil War, resulting in the execution of 70–100 capitulated Reds. This conflict was a key episode in the struggle between the Reds and Whites.
The battle’s outcome reflected the deep divisions within Finnish society, fueled by political ideologies and socio-economic disparities. The executions were a stark reminder of the war’s brutality.
This event underscored the challenges of national unity and the cost of civil strife. It highlighted the complex interplay of ideology and power, shaping Finland’s path toward stability and reconciliation.
15. 1924 – In Accordance with the Treaty of Rome, Fiume is Annexed by Italy
On March 16, 1924, the city of Fiume was officially annexed by Italy, a move aligned with the Treaty of Rome. This event marked the resolution of a long-standing territorial dispute between Italy and Yugoslavia.
Fiume’s annexation was significant for its strategic location on the Adriatic Sea, symbolizing nationalistic ambitions. This event highlighted the complexities of post-World War I territorial adjustments.
The annexation underscored the era’s geopolitical tensions and the challenges of nation-building. It reflected the interplay of diplomacy and nationalism, influencing regional stability and international relations in the interwar period.
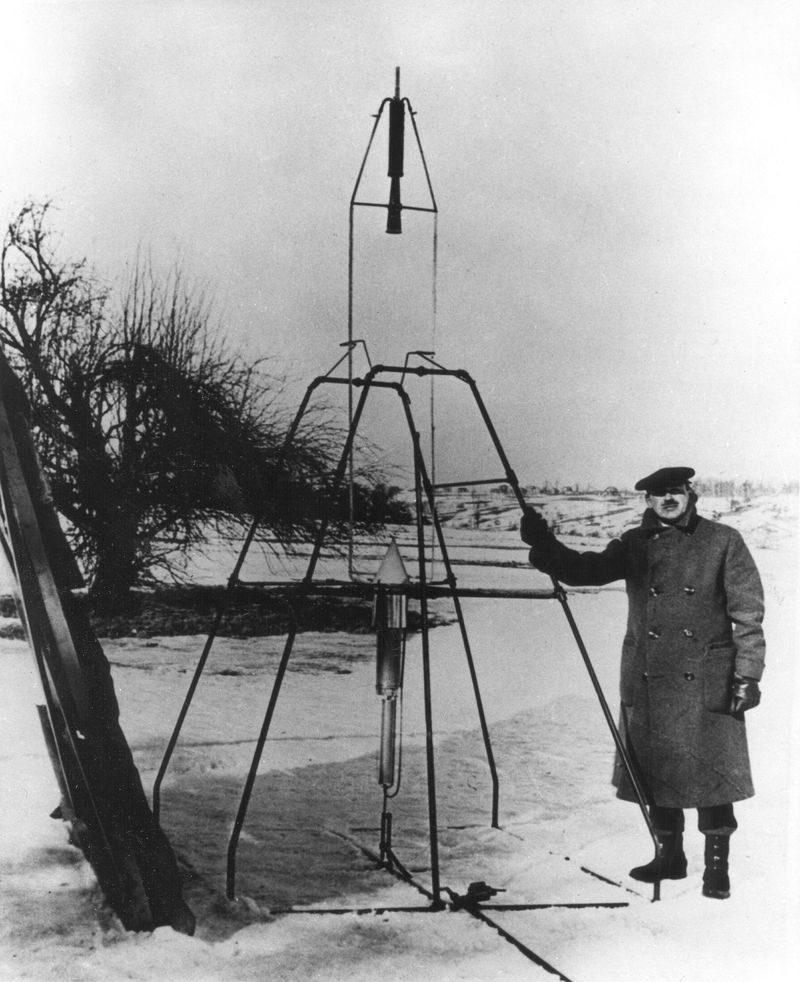
16. 1926 – Robert Goddard Launches the First Liquid-Fueled Rocket in Massachusetts
On March 16, 1926, Robert Goddard launched the first liquid-fueled rocket in Auburn, Massachusetts. This groundbreaking achievement marked the dawn of modern rocketry.
Goddard’s innovation utilized liquid fuel, a significant departure from solid propellants. The rocket’s successful flight, though short, demonstrated the potential for space exploration.
This event laid the foundation for future advancements in aerospace technology, highlighting the role of innovation and perseverance.
Goddard’s work inspired generations of scientists and engineers, underscoring the importance of visionary thinking in pushing the boundaries of human achievement.
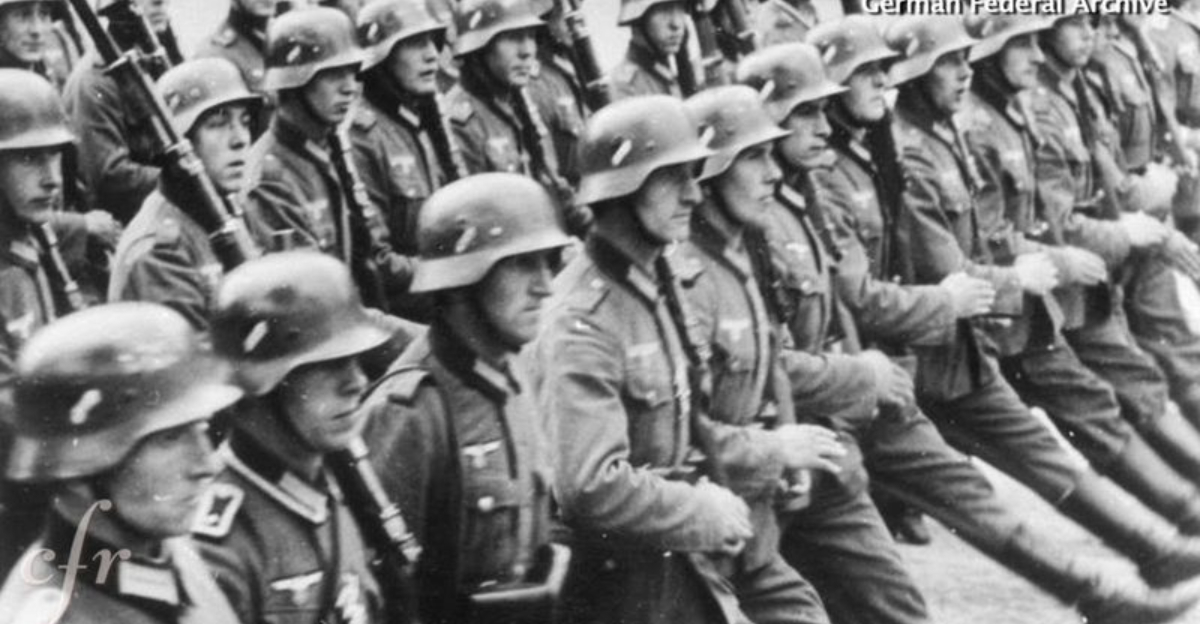
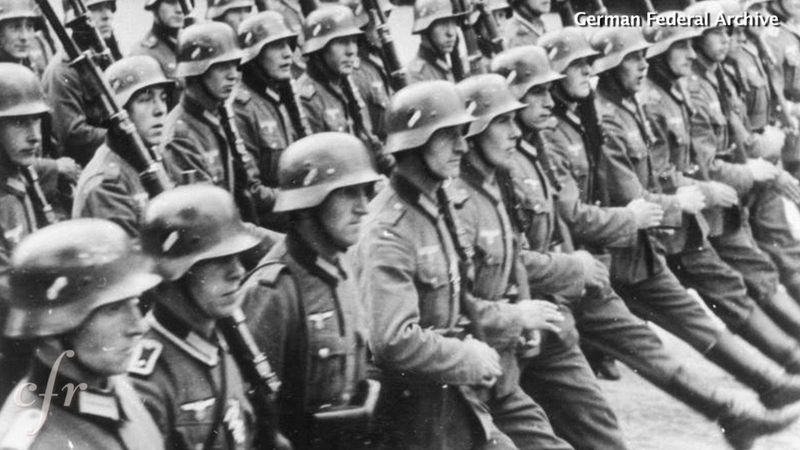
17. 1935 – Adolf Hitler Orders Germany to Rearm in Violation of the Treaty of Versailles
On March 16, 1935, Adolf Hitler defied the Treaty of Versailles by ordering Germany to rearm. This bold move marked a significant escalation in the lead-up to World War II.
The rearmament reflected Hitler’s ambitions to restore German military power and national pride. This decision was met with international condemnation, yet it bolstered Hitler’s domestic support.
The event underscored the limitations of post-World War I peace efforts and highlighted the challenges of enforcing international agreements.
It foreshadowed the aggressive policies that would lead to further conflict, illustrating the fragile nature of peace in a volatile world.
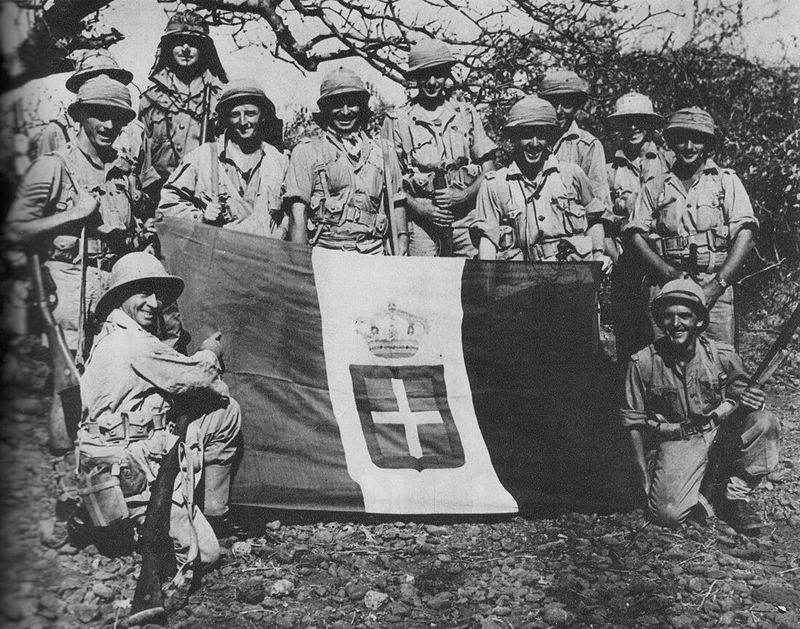
18. 1941 – British Forces Re-Establish Control of British Somaliland in Operation Appearance
March 16, 1941, saw British forces successfully re-establish control over British Somaliland during World War II’s Operation Appearance. This operation was part of the broader East African Campaign.
The recapture of Somaliland was a strategic victory against Italian forces, highlighting the shifting tides of war. British efforts to regain territory emphasized the significance of colonial holdings in the global conflict.
This operation demonstrated the complexities of warfare in the region and underscored the importance of strategic planning and coordination. It reflected the broader geopolitical implications of territorial control during the war.
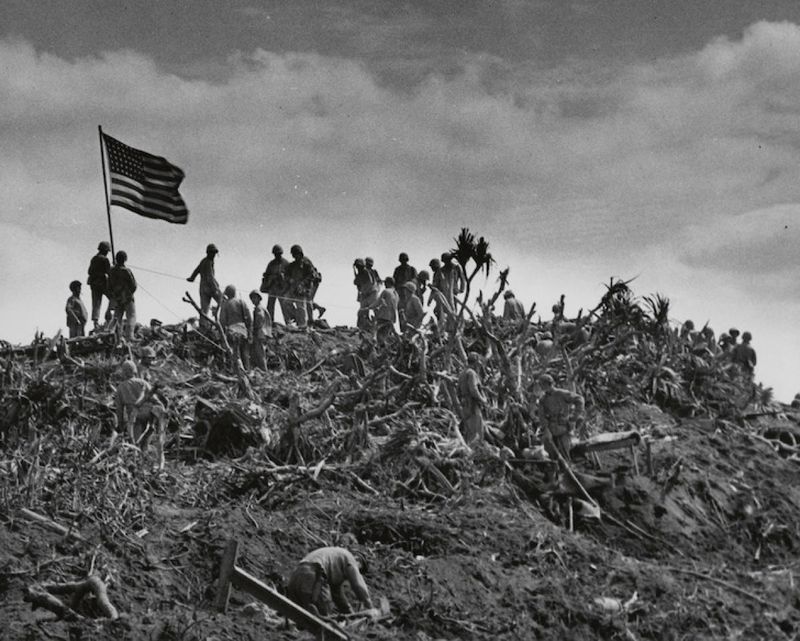
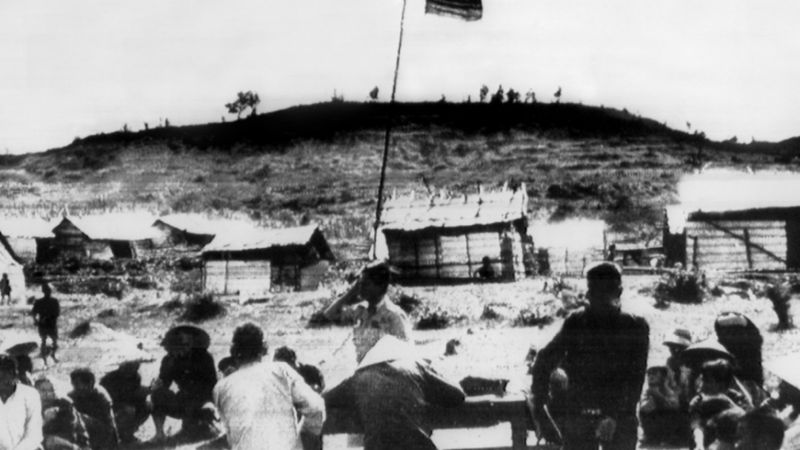
19. 1945 – World War II: The Battle of Iwo Jima Ends, Though Japanese Resistance Persists
On March 16, 1945, the Battle of Iwo Jima officially ended, though Japanese resistance persisted. This fierce battle was a pivotal moment in the Pacific Theater of World War II.
The capture of Iwo Jima provided the Allies with a strategic base for operations against Japan. Despite declaring victory, the ongoing resistance highlighted the battle’s intensity and the Japanese resolve.
This event underscored the high cost of warfare and the determination of both sides. It served as a testament to the bravery and sacrifice of those involved, reflecting the broader struggles of the war.
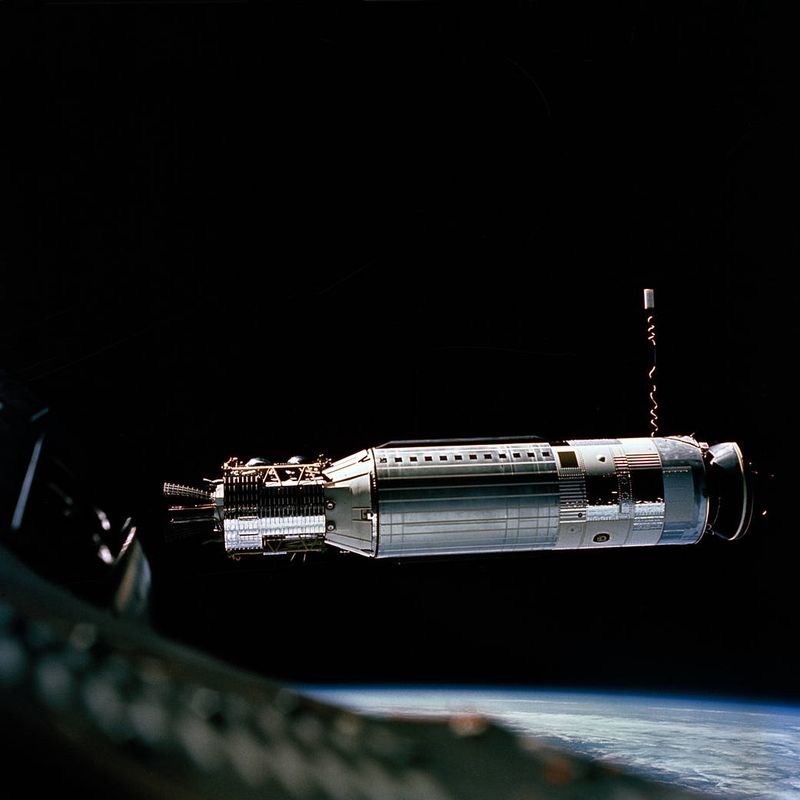
20. 1966 – Gemini 8 Performs the First Docking of Two Spacecraft in Orbit
On March 16, 1966, Gemini 8 achieved the first successful docking of two spacecraft in orbit, a landmark achievement in space exploration. This mission was a critical step in the Space Race.
Astronauts Neil Armstrong and David Scott demonstrated precision and teamwork in overcoming technical challenges. The docking maneuver was pivotal for future lunar missions, showcasing human ingenuity.
This event propelled advancements in space technology, emphasizing international competition and collaboration. It highlighted the potential of human spaceflight, inspiring a generation to reach for the stars and setting the stage for future explorations.
21. 1968 – Vietnam War: The My Lai Massacre Kills Between 347 and 500 Vietnamese Villagers
On March 16, 1968, the My Lai Massacre occurred during the Vietnam War, resulting in the deaths of between 347 and 500 Vietnamese villagers.
This tragic event exposed the brutal realities of war. U.S. troops, in a controversial operation, attacked the village, sparking global outrage. The massacre highlighted the ethical and moral dilemmas faced by military personnel in conflict zones.
This event fueled anti-war sentiment and called for accountability, impacting public perception of the war. It underscored the need for vigilance in military operations, advocating for human rights and the importance of military discipline.
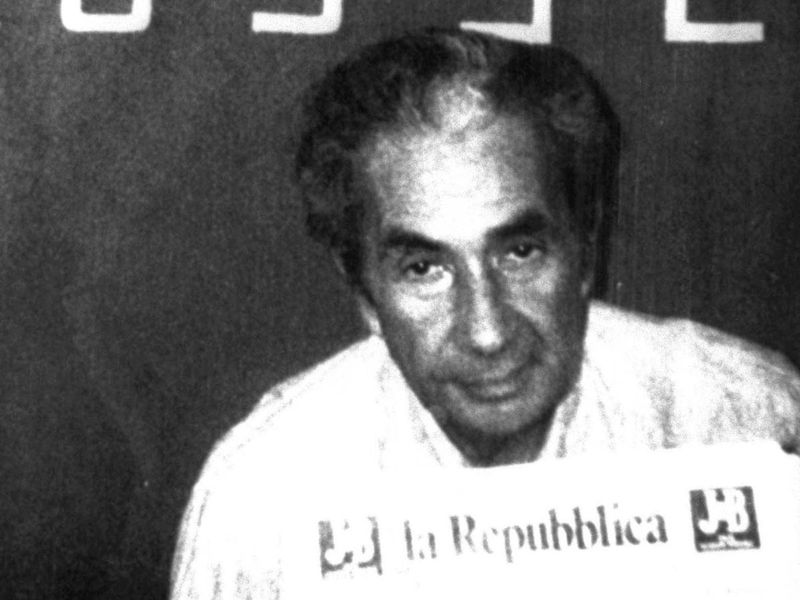
22. 1978 – Former Italian Prime Minister Aldo Moro is Kidnapped; Later Murdered by His Captors
On March 16, 1978, former Italian Prime Minister Aldo Moro was kidnapped by the Red Brigades, a radical left-wing group. This event shocked Italy and had profound political repercussions.
Moro, a prominent political figure, was held captive for 55 days before being murdered. His kidnapping exposed the vulnerabilities within Italy’s political landscape and heightened fears of domestic terrorism.
This tragedy underscored the challenges of maintaining political stability amidst extremist threats. It highlighted the need for robust security measures and dialogue to address ideological divides, impacting Italy’s approach to counter-terrorism and governance.
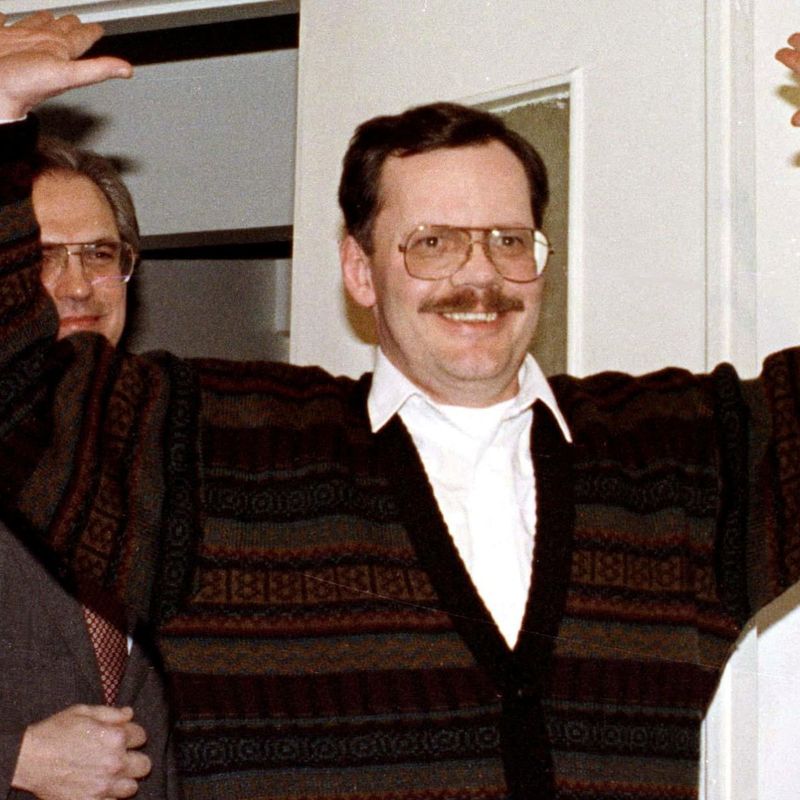
23. 1985 – AP Journalist Terry Anderson is Taken Hostage in Beirut, Held Until 1991
On March 16, 1985, AP journalist Terry Anderson was taken hostage in Beirut, marking the beginning of a six-year ordeal. Anderson’s capture was part of a series of kidnappings during the Lebanese Civil War.
His detention highlighted the dangers faced by journalists in conflict zones, raising awareness of press freedom and safety. Anderson’s release in 1991 was a significant moment, symbolizing hope amid ongoing conflict.
This event underscored the role of media in war, advocating for the protection of journalists. It emphasized the need for international efforts to secure the safety of those reporting from volatile environments.
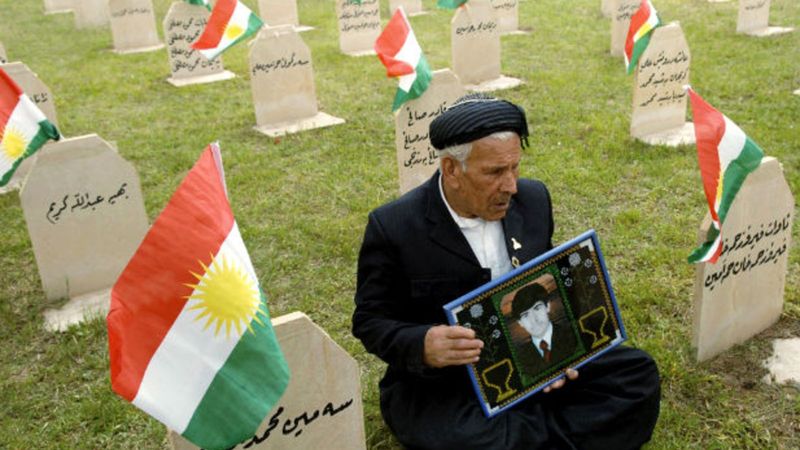
24. 1988 – Halabja Chemical Attack Kills 5,000 Kurds on the Orders of Saddam Hussein
On March 16, 1988, the Halabja chemical attack, ordered by Saddam Hussein, resulted in the deaths of 5,000 Kurds. This atrocity occurred during the Iran-Iraq War, targeting civilians with chemical weapons.
The attack was a stark violation of international laws, highlighting the brutality of the conflict. It drew global condemnation and raised awareness of the need for chemical weapons control.
This event underscored the human cost of war and the devastating impact of chemical warfare. It called for accountability and reinforced the importance of international treaties to prevent such atrocities in the future.
25. 1995 – Mississippi Formally Ratifies the Thirteenth Amendment, Becoming the Last U.S. State to Abolish Slavery
On March 16, 1995, Mississippi formally ratified the Thirteenth Amendment, becoming the last U.S. state to abolish slavery. This long-overdue action was symbolic, reaffirming the state’s commitment to civil rights.
The ratification highlighted the historical legacy of slavery and the ongoing journey toward equality. It reflected the importance of acknowledging past injustices and promoting social justice.
This event underscored the need for continuous efforts in championing civil rights, advocating for education and awareness. It illustrated the power of legislative action in shaping a more inclusive society, emphasizing reconciliation and progress.
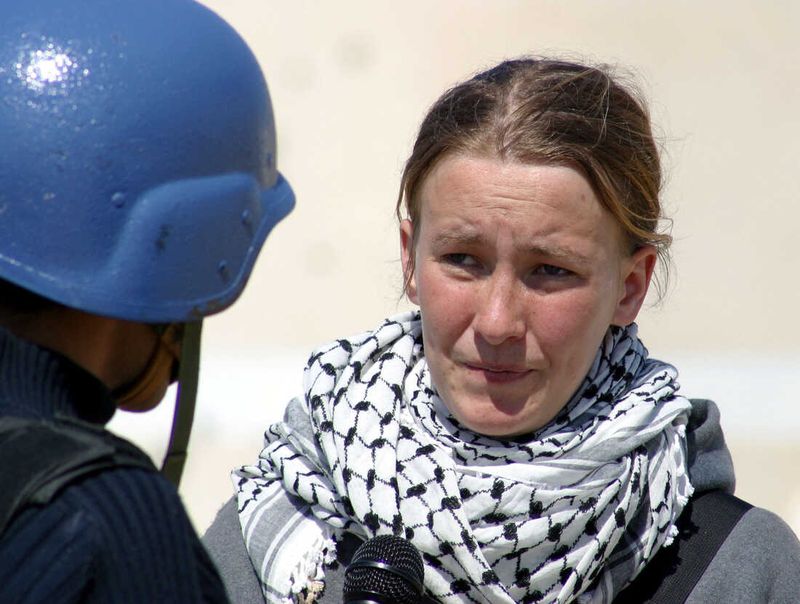
26. 2003 – American Activist Rachel Corrie is Killed by an Israeli Bulldozer While Protesting Home Demolitions
On March 16, 2003, American activist Rachel Corrie was killed by an Israeli bulldozer while protesting home demolitions in the Gaza Strip. Her death drew international attention to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Corrie’s activism highlighted the role of individuals in advocating for human rights and justice. Her tragic end underscored the dangers faced by those standing against oppression.
This event emphasized the need for peaceful resolution and dialogue in conflict areas. It called for accountability and international cooperation to address humanitarian issues, advocating for the protection of civilians and activists alike.
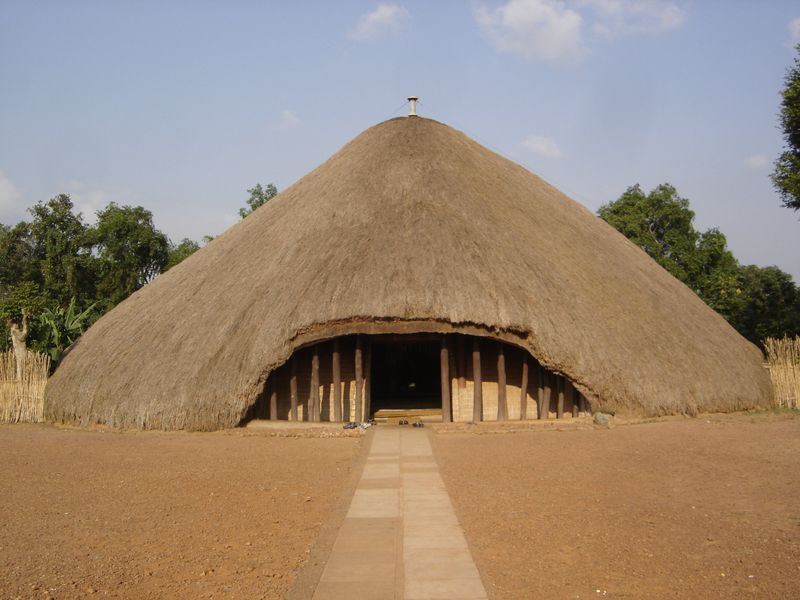
27. 2010 – The Kasubi Tombs, Uganda’s Only Cultural World Heritage Site, are Destroyed by Fire
On March 16, 2010, the Kasubi Tombs in Uganda were destroyed by fire, devastating the nation’s only cultural World Heritage Site. This loss was a blow to Uganda’s cultural heritage and history.
The tombs, a symbol of the Buganda kingdom, represented architectural and spiritual significance. Their destruction highlighted the vulnerability of cultural sites to disasters, emphasizing the need for preservation efforts.
This event underscored the importance of safeguarding heritage for future generations. It called for increased awareness and international collaboration in preserving cultural landmarks, ensuring their continuity amidst modern challenges.
28. 2014 – Crimea Votes in a Controversial Referendum to Join Russia
On March 16, 2014, Crimea voted in a controversial referendum to join Russia, a decision that sparked international tensions. The vote, held amidst political unrest in Ukraine, drew widespread condemnation.
The annexation of Crimea by Russia was viewed as a violation of international law, raising concerns about sovereignty and territorial integrity. This event highlighted the complexities of regional politics and national identities.
The referendum underscored the impact of geopolitical maneuvers on international relations. It emphasized the need for diplomacy and dialogue in addressing territorial disputes, reflecting the broader challenges of global governance.
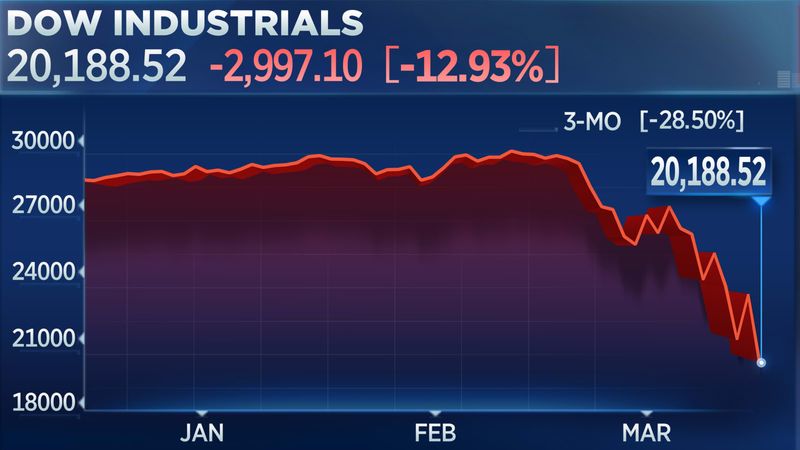
29. 2020 – Dow Jones Industrial Average Falls by 2,997 Points, the Largest Single-Day Drop in History
On March 16, 2020, the Dow Jones Industrial Average plummeted by 2,997 points, marking the largest single-day drop in history. This dramatic fall was triggered by fears surrounding the COVID-19 pandemic.
The market’s response reflected widespread uncertainty and anxiety, impacting global economies. The drop underscored the interconnected nature of global finance and the vulnerabilities of economic systems.
This event highlighted the importance of financial resilience and strategic planning in times of crisis. It called for coordinated efforts to stabilize markets and support recovery, emphasizing the need for adaptive economic policies.
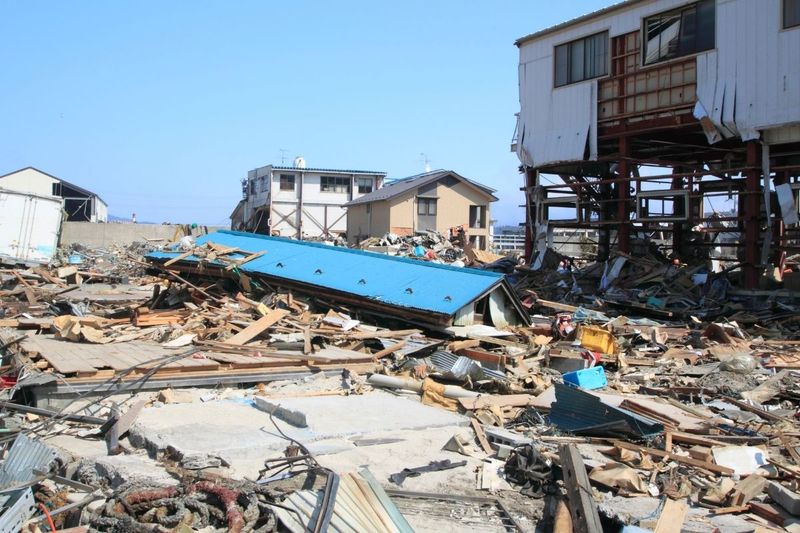
30. 2022 – A 7.4-Magnitude Earthquake Strikes off Fukushima, Japan, Killing 4 and Injuring 225
On March 16, 2022, a 7.4-magnitude earthquake struck off the coast of Fukushima, Japan, causing significant damage and loss. The quake resulted in four fatalities and injured 225 people, illustrating the region’s vulnerability to seismic activity.
This event was a reminder of Japan’s ongoing challenges with natural disasters, emphasizing the need for preparedness and resilient infrastructure. The earthquake’s impact underscored the importance of emergency response systems.
It highlighted the necessity of continuous efforts in disaster mitigation and recovery planning, advocating for international cooperation in addressing the effects of climate change and natural hazards.