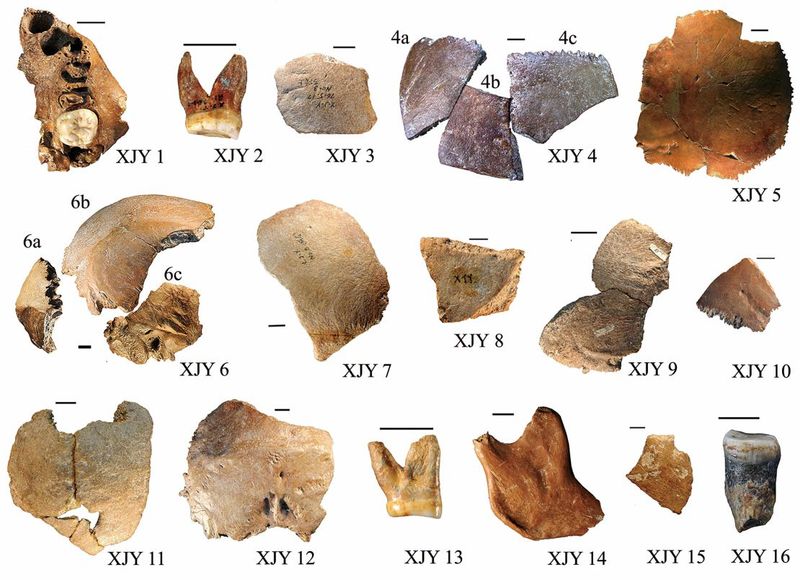
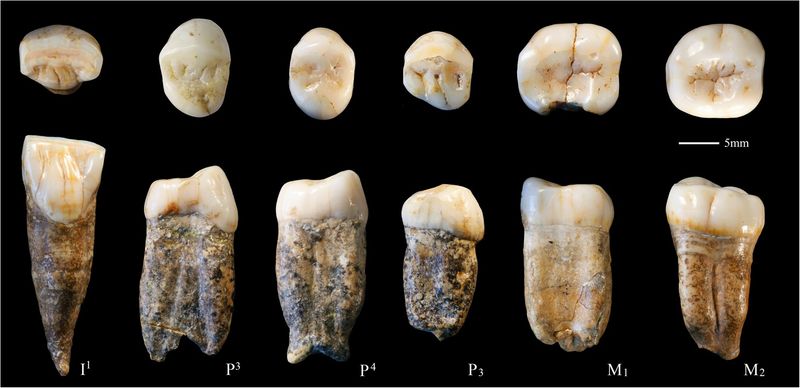
For decades, the story of human origins has been pieced together from fossil evidence scattered across Africa, Europe, and Asia. But recent fossil discoveries in China are raising questions that could reshape our understanding of humanity’s past.
These groundbreaking finds suggest that East Asia may have played a far more significant role in human evolution than previously thought.
What Makes These Fossils So Significant?
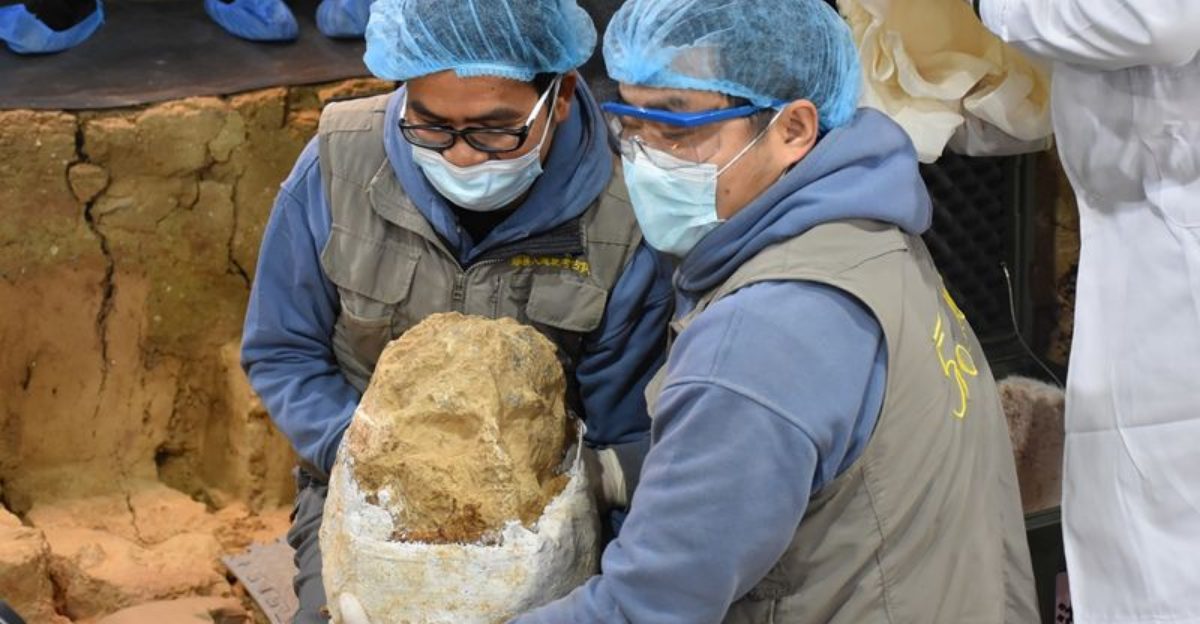
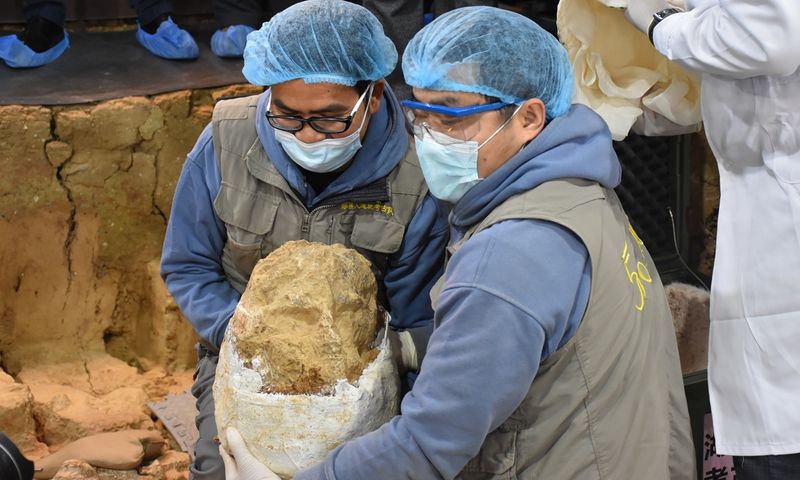
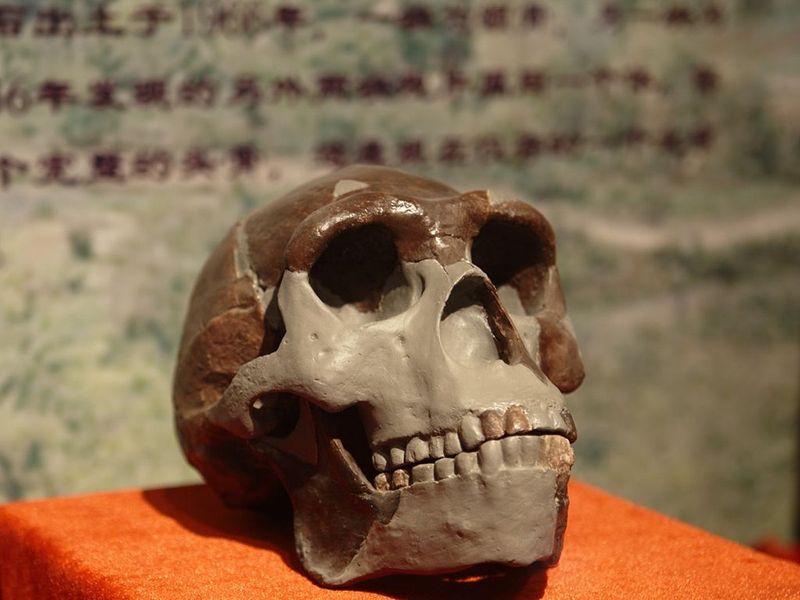
In recent years, Chinese scientists have unearthed a treasure trove of ancient fossils, including skull fragments, jawbones, and teeth, dating back hundreds of thousands of years.
These fossils belong to ancient human species, including Homo erectus and the enigmatic Denisovans, who roamed the region long before modern humans arrived.
One of the most exciting discoveries involves a mysterious lineage of hominins whose traits do not entirely match those of any known species.
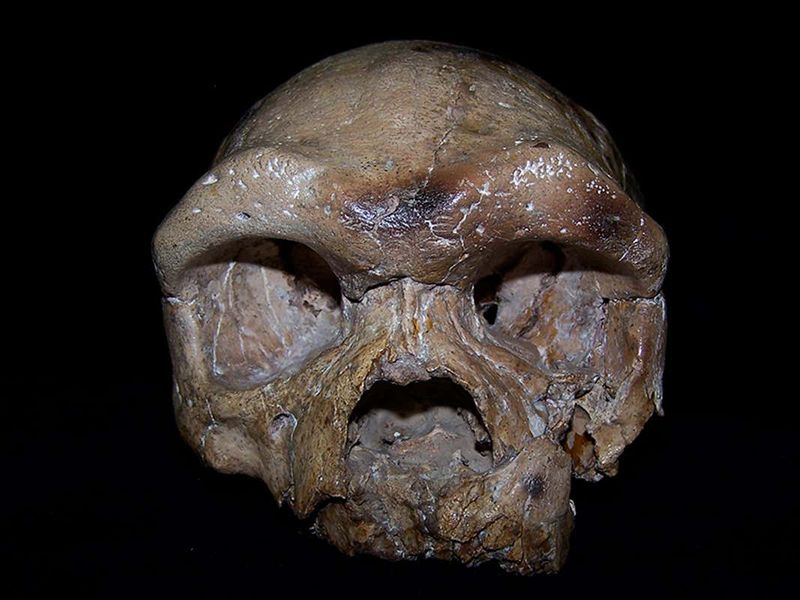
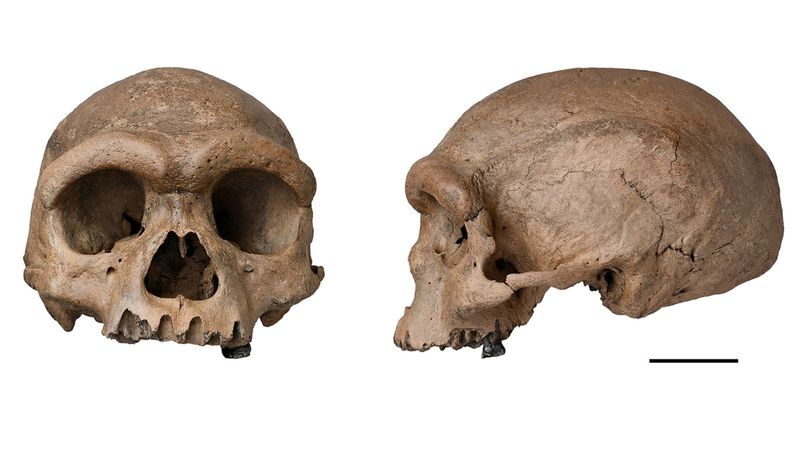
Dubbed “Dragon Man” (Homo longi), this fossilized skull, discovered in northeastern China, boasts a mix of archaic and modern features.
Its sheer size and unique characteristics suggest it could represent a new branch of the human family tree, potentially living alongside early modern humans.
How These Fossils Challenge Long-Standing Theories
For decades, the “Out of Africa” model has been the dominant theory of human evolution. It posits that modern humans evolved in Africa and then migrated to other continents, replacing earlier hominins.
While this theory remains widely accepted, the Chinese fossil discoveries add complexity to the narrative.
The fossils hint that East Asia may have been a melting pot of ancient human species, where interbreeding and genetic exchange occurred over tens of thousands of years.
For instance, traces of Denisovan DNA in modern populations, especially in Southeast Asia and Oceania, suggest that these ancient humans had a lasting impact on our genetic heritage.
Moreover, these discoveries could indicate that human evolution was less linear and more of a web, with multiple human species coexisting, migrating, and interacting across vast regions.
Advanced Tools and Climate Adaptation
Another fascinating aspect of these Chinese fossils is the evidence of advanced tool use and environmental adaptation. Archaeological findings at some sites reveal that these early humans were not just surviving—they were thriving.
They developed stone tools, utilized fire, and adapted to diverse climates, from frigid northern China to the subtropical south. This adaptability may have played a crucial role in their long-term survival and influence.
The Role of Technology in Understanding the Past
The revelations emerging from Chinese fossils wouldn’t be possible without cutting-edge technology.
Advances in DNA analysis, radiometric dating, and CT scanning have allowed scientists to reconstruct the lives of these ancient humans with incredible precision.
For example, genetic studies of fossils have revealed surprising interbreeding events between Denisovans and early modern humans, some of which took place in East Asia.
These insights not only shed light on the origins of modern humans but also reveal how environmental changes and migrations influenced our ancestors’ development.
Implications for the Story of Humanity
The discoveries in China underscore the importance of expanding our view of human evolution beyond traditional hotspots like Africa and Europe.
East Asia, with its vast and diverse fossil record, has proven to be a vital region for uncovering new chapters of our shared history.
These findings also remind us that human evolution was far from straightforward. It was a complex process influenced by migration, adaptation, and the interplay of multiple species over millennia.
By incorporating these Chinese discoveries into the broader narrative, scientists are beginning to see a more intricate and interconnected picture of how humanity came to be.
A Story Still Unfolding
While these discoveries are reshaping our understanding of human origins, many questions remain unanswered. Who exactly were the Denisovans, and what role did they play in shaping modern humans?
How did these ancient species interact, and what can they teach us about our own resilience and adaptability?
As scientists continue to unearth and analyze fossils across China, the story of humanity grows richer and more complex. Each discovery adds another layer to the puzzle, bringing us closer to understanding our place in the vast tapestry of life on Earth.
In the words of one researcher, “These fossils remind us that the story of humanity is not just about where we came from, but how interconnected our journey has always been.”