During the chaos of World War II, Adolf Hitler greenlit a plan so bold and bizarre, it sounds like something out of a spy thriller. Known as Operation Greif, the mission involved Nazi soldiers donning American uniforms, driving fake Allied tanks, and infiltrating U.S. lines during the Battle of the Bulge. Here are 12 jaw-dropping facts about this little-known plot to deceive—and destroy—the Allied forces from within.
1. Hitler’s Personal Approval
With audacious ambition, Adolf Hitler authorized Operation Greif, reflecting his belief in psychological warfare over sheer force. The mission’s aim was to confound the Allied forces by deploying Nazi soldiers dressed as Americans. This bizarre and risky endeavor highlighted Hitler’s strategy of surprise and deception as keys to victory. He envisioned a scenario where confusion could shift the war’s balance towards Germany. Such bold plans required both cunning and audacity, something Hitler was never short of. This wasn’t merely a rogue initiative; it was a top-down directive showing the lengths to which Germany would go to achieve its objectives.
2. Special Unit Training
Germany’s creation of Panzer Brigade 150 showcased the meticulous planning behind Operation Greif. This unit comprised English-speaking troops, many with experience living in the U.S. or Britain. Their mission? Assimilate as American soldiers, mimicking their behavior and speech. Such preparation underscored the operation’s emphasis on authenticity and deception. The idea was to seamlessly blend in with the Allies, executing covert tasks unnoticed. This strategic move demonstrated Germany’s innovative approach, blending traditional military tactics with espionage. The unit’s training was extensive, highlighting the operation’s significance in Germany’s broader wartime strategy.
3. Stolen U.S. Uniforms
The use of stolen U.S. uniforms was a key aspect of Operation Greif’s deception plan. Disguised in authentic American gear, these impostors were able to engage with U.S. troops, even if only briefly, before arousing suspicion. The acquisition and deployment of these uniforms displayed the operation’s intricate planning and execution. Wearing the enemy’s attire blurred lines, creating chaos and mistrust among the Allies. This bold move was a testament to the operation’s cunning design, emphasizing psychological warfare over direct confrontation. The uniforms became symbols of the lengths Germany would go to in its quest for advantage.
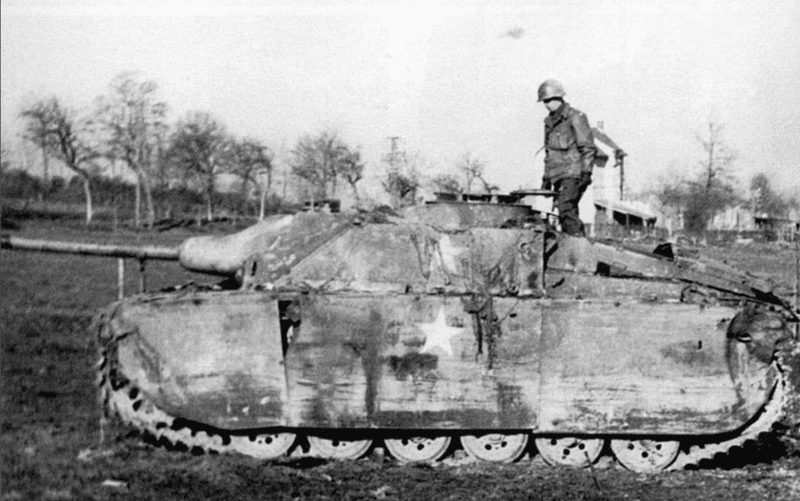
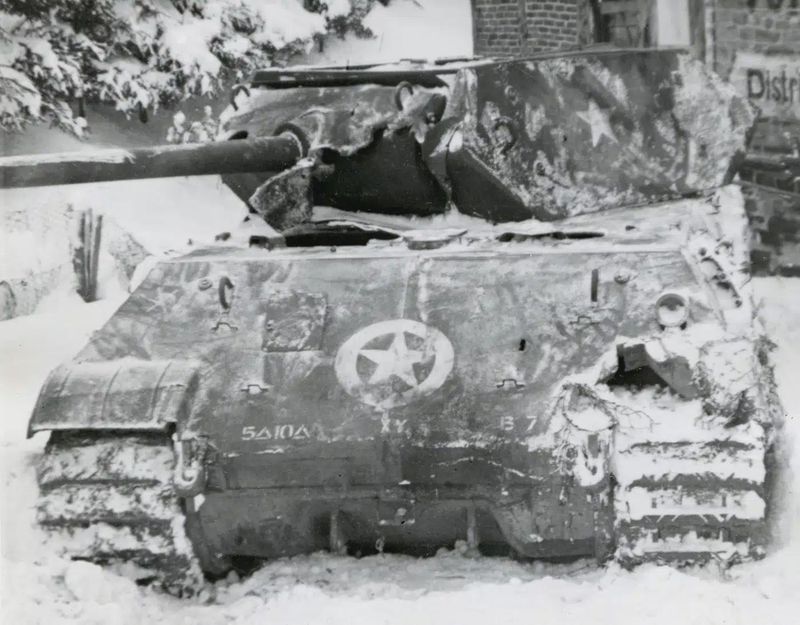
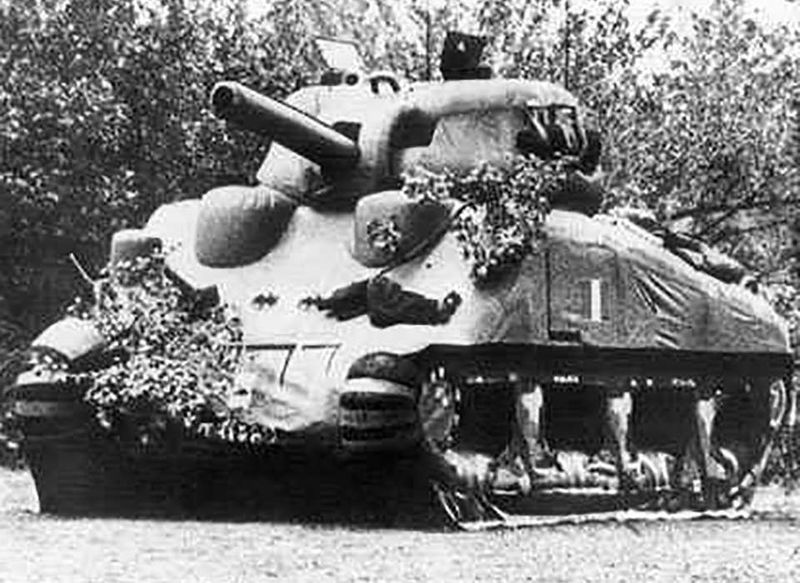
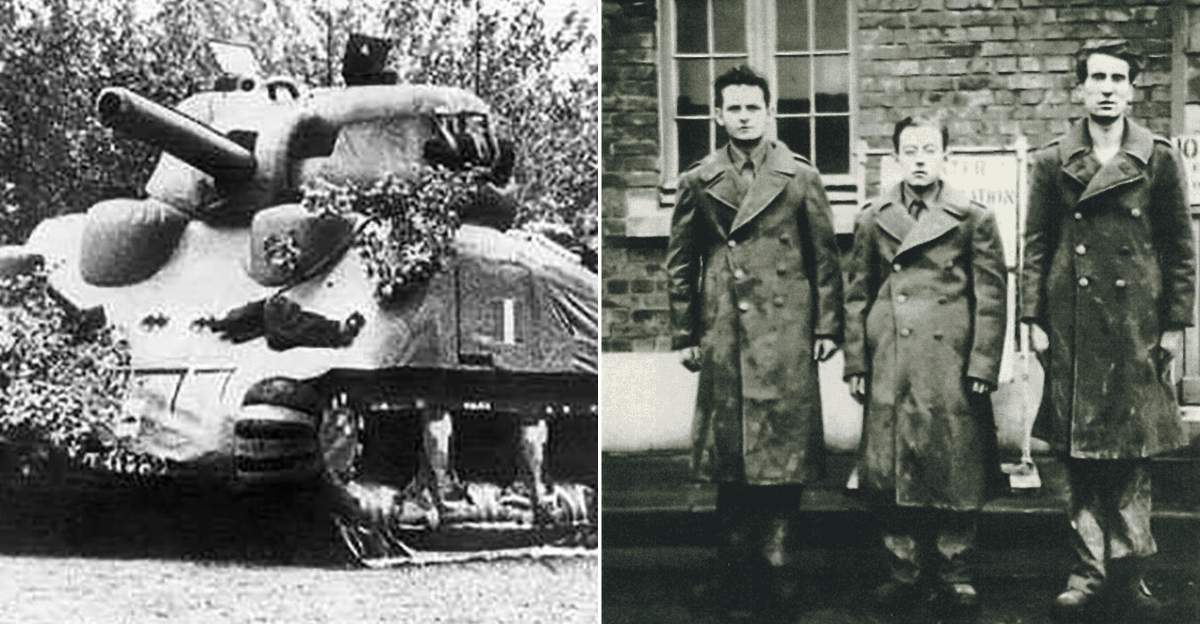
4. Fake American Tanks
In a bid to enhance their deception, the Germans went as far as modifying Panther tanks to resemble U.S. M10 tank destroyers. This extraordinary effort was part of the grand design of Operation Greif, aiming to confuse and mislead Allied forces. The modified tanks symbolized Germany’s commitment to this clever ruse, hoping to delay detection long enough to penetrate enemy lines. Though the replicas weren’t perfect, their existence demonstrated the operation’s audacious creativity. This tactic was not just about blending in but also about crafting an illusion of power and coordination, pushing the boundaries of traditional warfare tactics.
5. Mission to Sabotage
The core goal of Operation Greif was to unleash chaos behind U.S. lines. Tasked with severing communication lines, misdirecting military traffic, and sabotaging critical infrastructure, these Nazi infiltrators aimed to destabilize and demoralize the Allied forces. Their objectives went beyond mere disruption; they were designed to fracture the cohesion of the enemy, creating opportunities for German advances. This operation highlighted the strategic shift towards psychological and unconventional warfare. The mission embodied a complex blend of tactics, where traditional combat was augmented by efforts to sow confusion and panic, altering the battlefield’s psychological landscape.
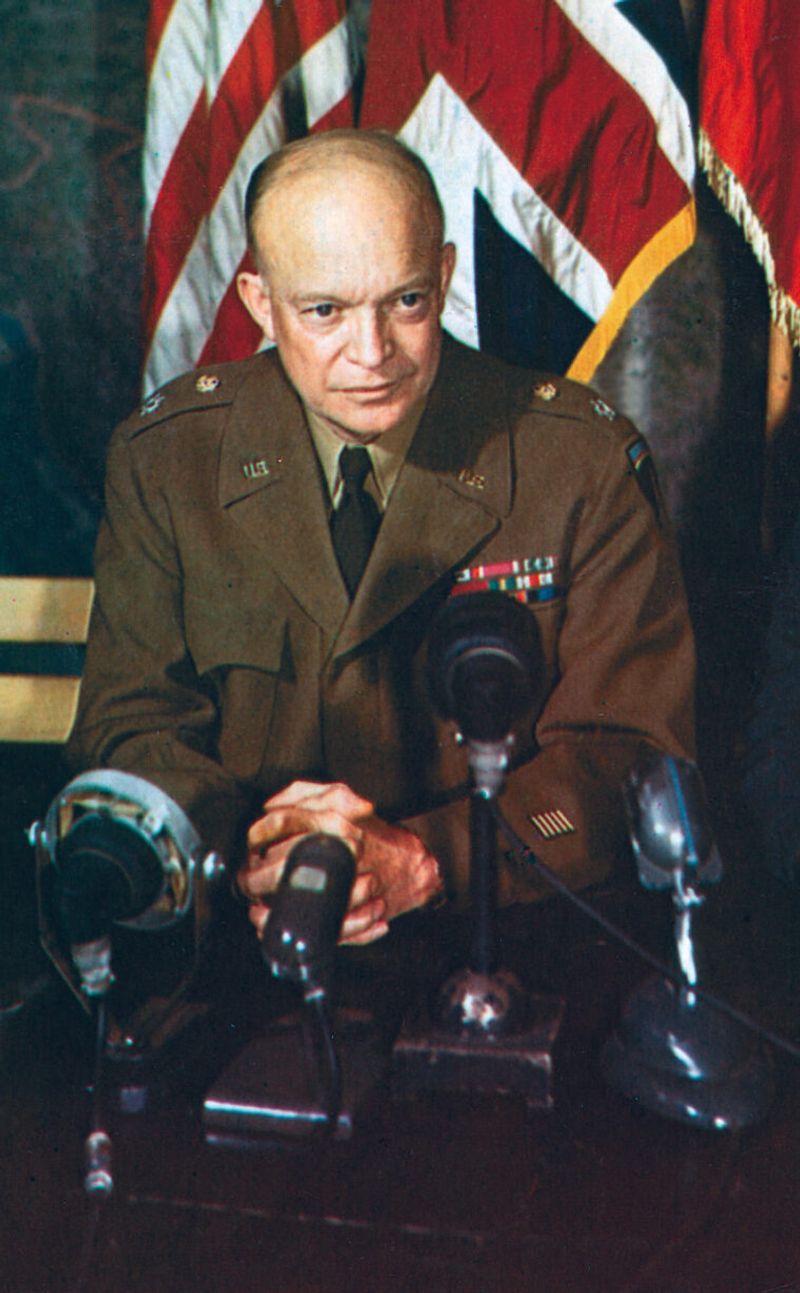
6. Assassination Rumors
Operation Greif’s audacity extended to rumors of an assassination plot against General Eisenhower. Though never realized, such whispers struck fear and paranoia among the Allies. The heightened security around Eisenhower reflected the seriousness with which these threats were taken, affecting military operations and command decisions. This facet of the operation demonstrated the Nazis’ willingness to employ extreme measures to achieve their goals, even targeting top military leaders. The rumors, whether substantiated or not, served to unsettle the enemy, showcasing the psychological warfare elements embedded within Operation Greif, influencing both tactics and morale.
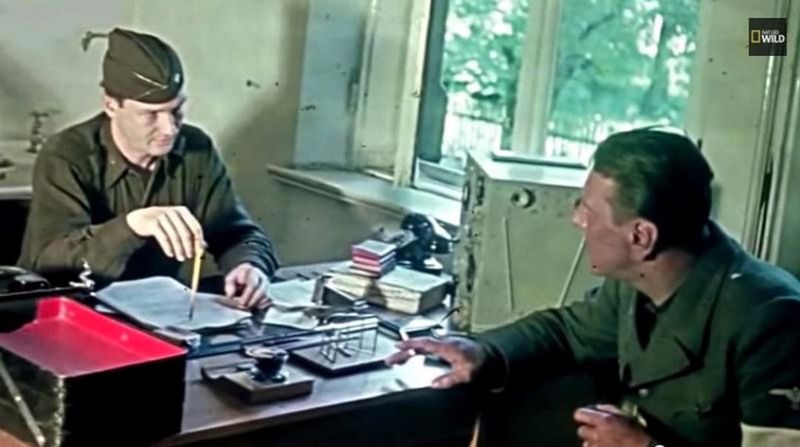
7. Password Challenges
To counter the threat of infiltration, American soldiers devised clever password challenges. These tests included trivia on state capitals or baseball, designed to trip up German impostors. Such measures became vital in unveiling disguised soldiers who couldn’t keep up with American cultural nuances. This tactic highlighted the adaptive strategies of the Allies, turning ordinary knowledge into a tool of war. The password challenges not only safeguarded military lines but also fostered a sense of vigilance among troops. This ingenious method exemplified the broader theme of intelligence and adaptability, critical in countering the complex threats posed by Operation Greif.
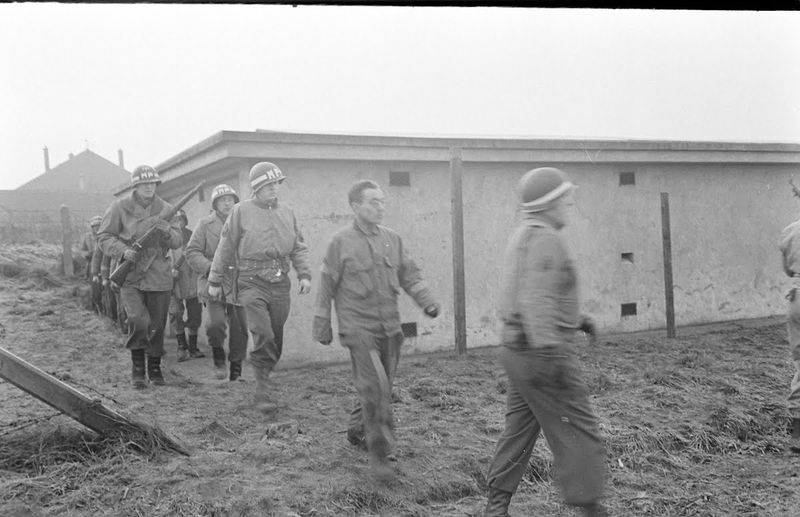
8. Executed Spies
Caught in enemy uniforms, 23 Nazi infiltrators faced execution under the rules of war. This harsh consequence underscored the grave risks involved in Operation Greif. The execution of these spies highlighted the uncompromising stance on wartime justice, where deception on such a scale warranted severe punishment. This grim outcome served as a reminder of the operation’s high stakes and the fine line between cunning and peril. The captured soldiers became symbols of both the audacity and the failure of the mission, marking a sobering chapter in the history of wartime espionage and the brutal realities of conflict.
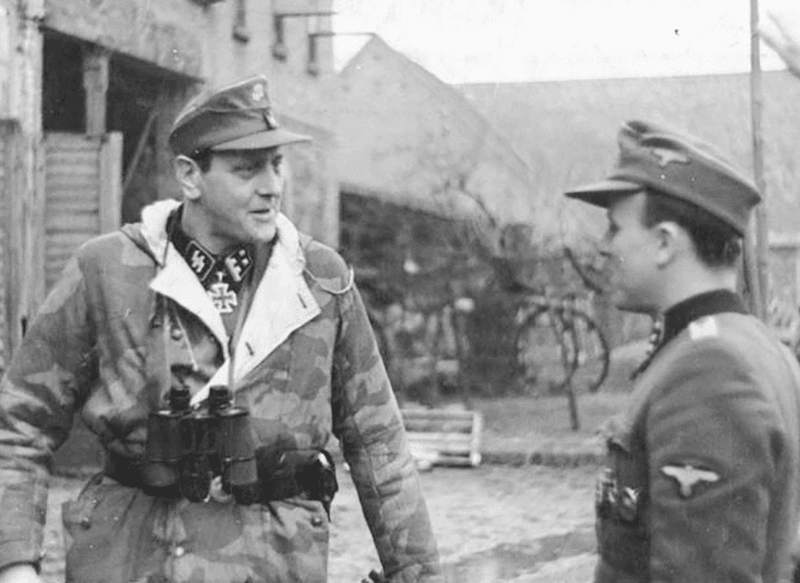
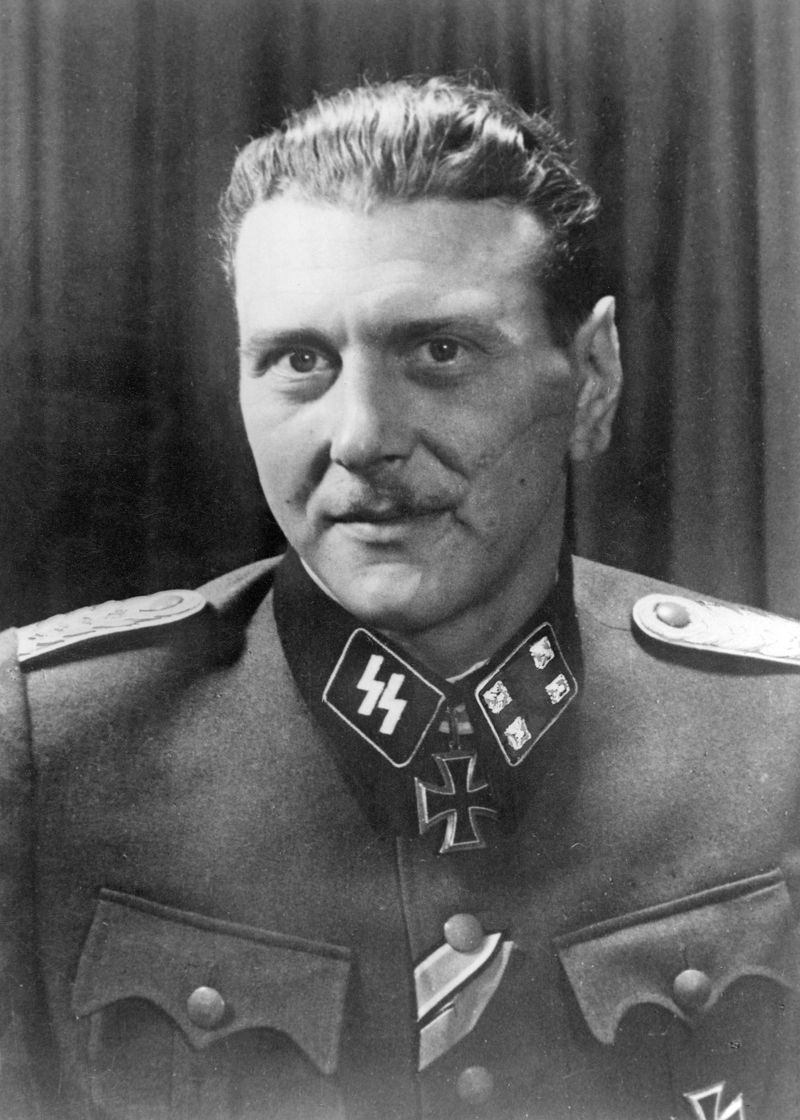
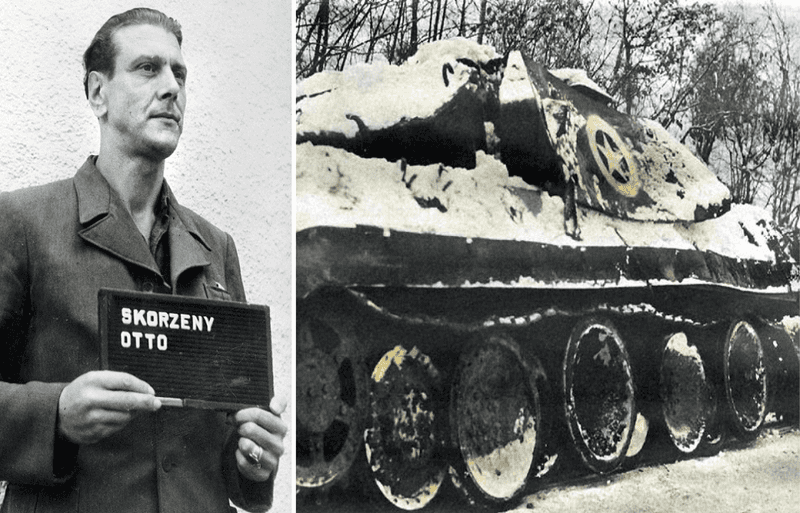
9. Otto Skorzeny’s Leadership
Nicknamed “the most dangerous man in Europe,” Otto Skorzeny was the mastermind behind Operation Greif. Known for his flair in covert operations, Skorzeny had previously rescued Mussolini in a daring raid. His involvement in Operation Greif was a testament to his reputation and skill in psychological and unconventional warfare. Under his leadership, the mission took shape, blending audacity with strategy. Skorzeny’s role underscored the operation’s emphasis on innovative tactics and bold moves. He became a key figure in this daring venture, exemplifying the type of leadership that thrived on risk and ingenuity during wartime.
10. American Paranoia
Amidst the fear of Nazi infiltrators, American troops grew suspicious, often arresting their own over trivial suspicions. This paranoia highlighted the psychological impact of Operation Greif, where the mere presence of disguised enemies created widespread distrust. Soldiers found themselves second-guessing their allies, illustrating the chaos that the operation sought to inflict. Such incidents reflected the operation’s indirect success in sowing confusion, even if its primary objectives were unmet. The atmosphere of suspicion unearthed the vulnerability within the ranks, showing how strategic deception could disrupt unity and command. This psychological warfare became a notable facet of the operation’s legacy.
11. Operation’s Failure
Despite the high stakes and intricate planning, Operation Greif ultimately floundered. Challenges in coordination, language barriers, and alert Allies thwarted many sabotage efforts. The failure underscored the complexities of executing such an ambitious plan, where even the smallest disconnect could unravel the mission. The operation’s shortcomings provided valuable lessons in the limitations of deception as a wartime strategy. While the initial concept was daring, the practical execution exposed weaknesses. The story of Operation Greif thus became a poignant reminder of the fine line between innovative tactics and the realities of war’s unpredictability.
12. Skorzeny’s War Crimes Trial
Post-war, Otto Skorzeny faced trial for violating the laws of war. Acquitted partly due to the Allies employing similar tactics, his trial highlighted the complex moral landscape of wartime actions. Skorzeny’s escape and subsequent involvement in Cold War espionage added layers to his controversial legacy. This chapter in his life illustrated the blurred lines in wartime ethics and justice, where acts of war shifted between heroism and criminality. His story remains a fascinating exploration of leadership, morality, and the enduring impact of WWII strategies on post-war geopolitics, illustrating how wartime actions can resonate far beyond the battlefield.