The SL-1 disaster is one of the most chilling and little-known nuclear accidents in U.S. history. It didn’t cause mass evacuations or spread radioactive fallout across cities, but it was deadly, dramatic, and left an indelible mark on nuclear safety procedures. Here are the most striking facts and moments from the 1961 SL-1 reactor tragedy that claimed three lives and stunned a nation.
1. SL-1 Stood for “Stationary Low-Power Reactor Number One”
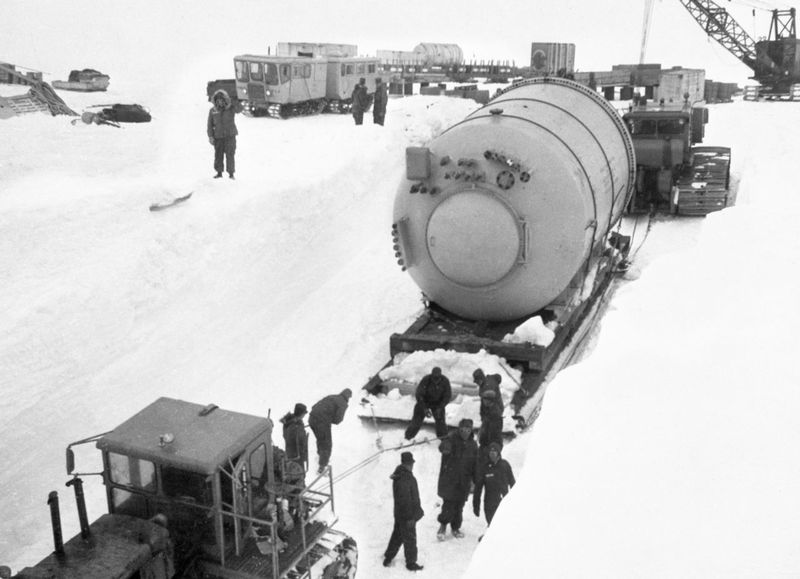
Initially, SL-1 was designed by the U.S. Army to serve remote Arctic military installations with electricity and heat. It stood for “Stationary Low-Power Reactor Number One.” The reactor was compact, enabling it to be transported and installed in inaccessible locations. However, despite its strategic significance, the inherent risks associated with such isolated reactors became evident.
The design, while innovative, emphasized the need for rigorous safety measures, especially in remote areas. The SL-1’s tragic failure highlighted gaps in oversight and safety protocols that were direly needed.
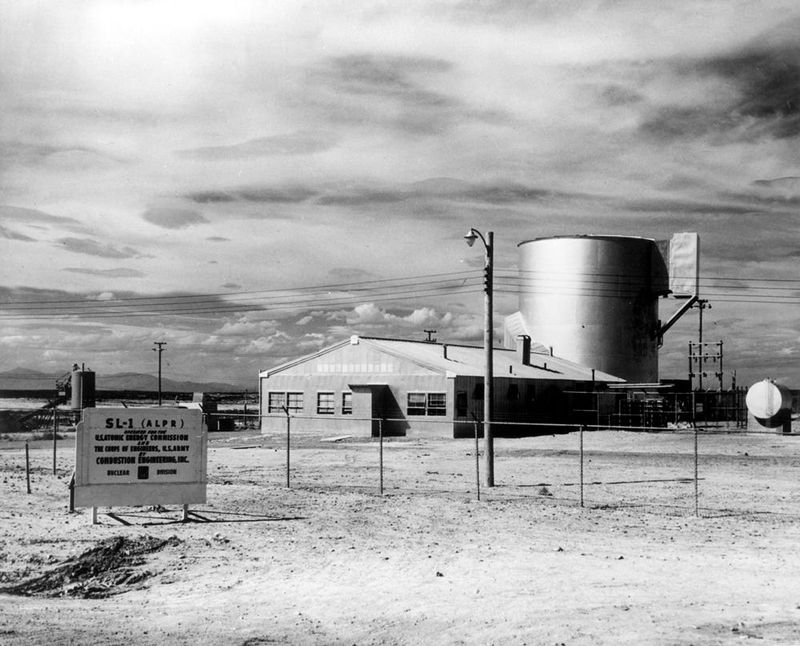
2. Located in the Idaho Desert
The SL-1 reactor was strategically located in the barren expanses of the Idaho desert at the National Reactor Testing Station (NRTS). This placement far from populated areas was an early measure of safety, minimizing the risk to the public in case of an accident.
The remote desert setting offered the perfect backdrop for testing radical nuclear technologies. However, the desolation also posed significant challenges, especially during emergencies when immediate assistance was crucial. The site’s isolation became a double-edged sword, both safeguarding and complicating operations.
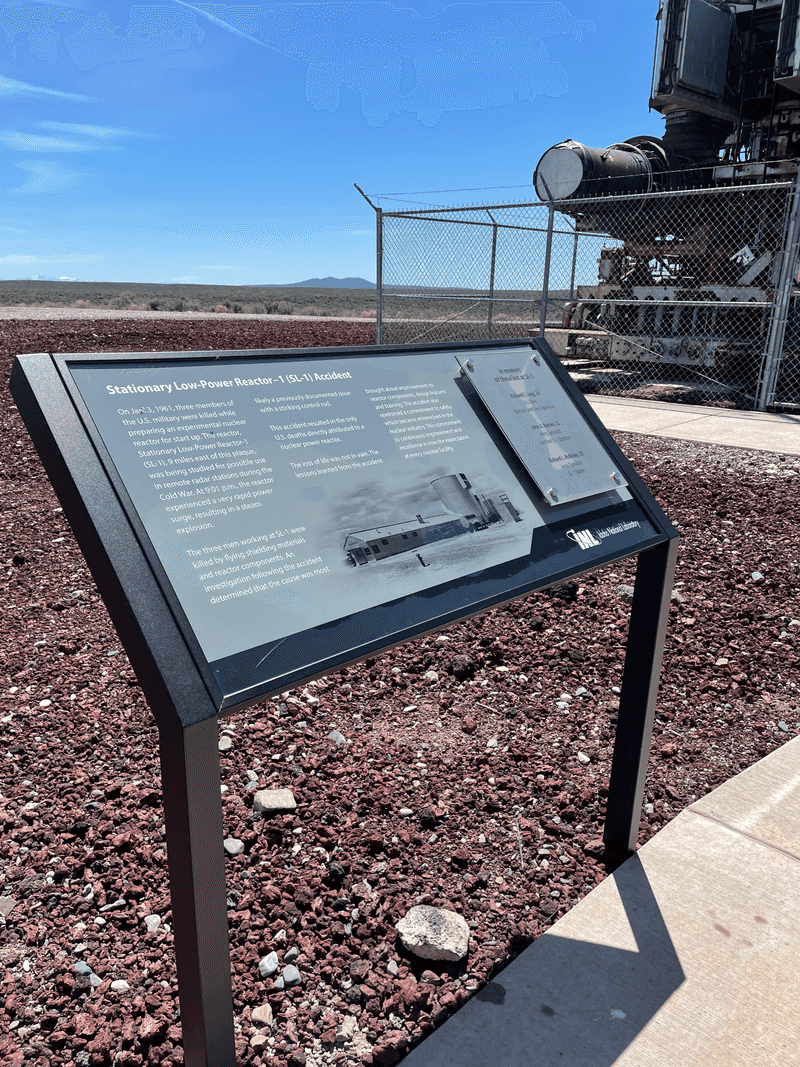
3. The Incident Occurred on January 3, 1961
On January 3, 1961, the SL-1 reactor experienced a catastrophic failure, marking the first and only fatal nuclear reactor accident in the United States. The fateful day dawned like any other, but it soon turned into a nightmare.
The incident unfolded rapidly, catching the nation by surprise and leading to profound changes in nuclear safety protocols. The tragic loss of life underscored the dangers inherent in nuclear energy and prompted urgent reviews of safety measures.
This date remains etched in history as a somber reminder of nuclear power’s potential perils.
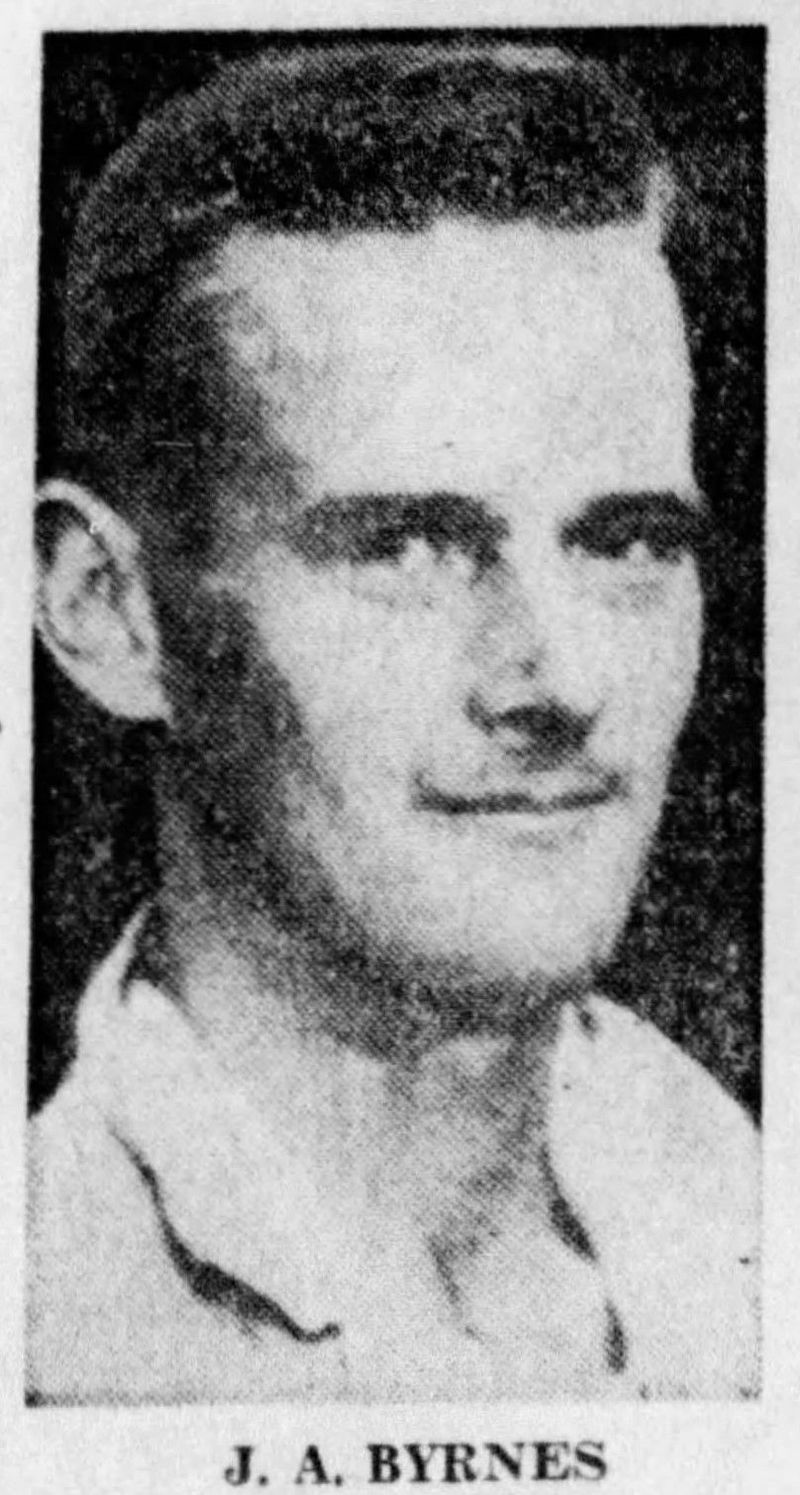
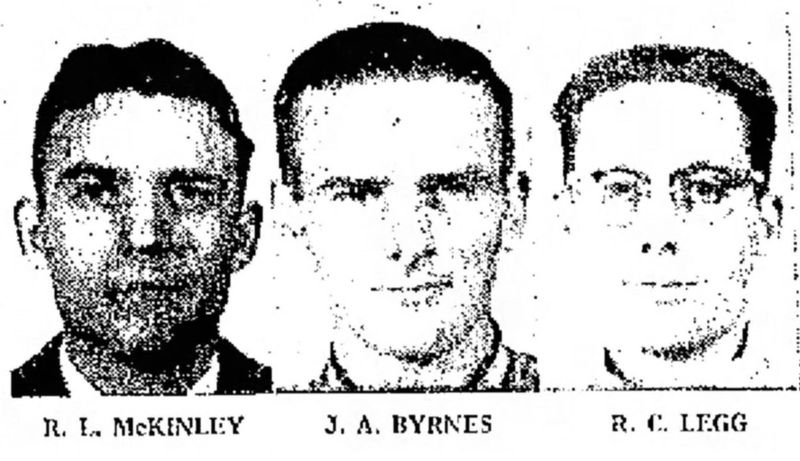
4. Three Men Were on Duty
On that tragic day, three dedicated servicemen were on duty: Army specialists John Byrnes and Richard McKinley, along with Navy Seabee Richard Legg. These men were entrusted with maintaining the reactor’s operations.
Their presence in the reactor building at the time of the incident was a testament to their commitment and duty. The loss of these lives was not just a personal tragedy but a national one, highlighting the human cost of technological advancement.
Their story is a poignant reminder of the risks faced by those who work with nuclear technology.
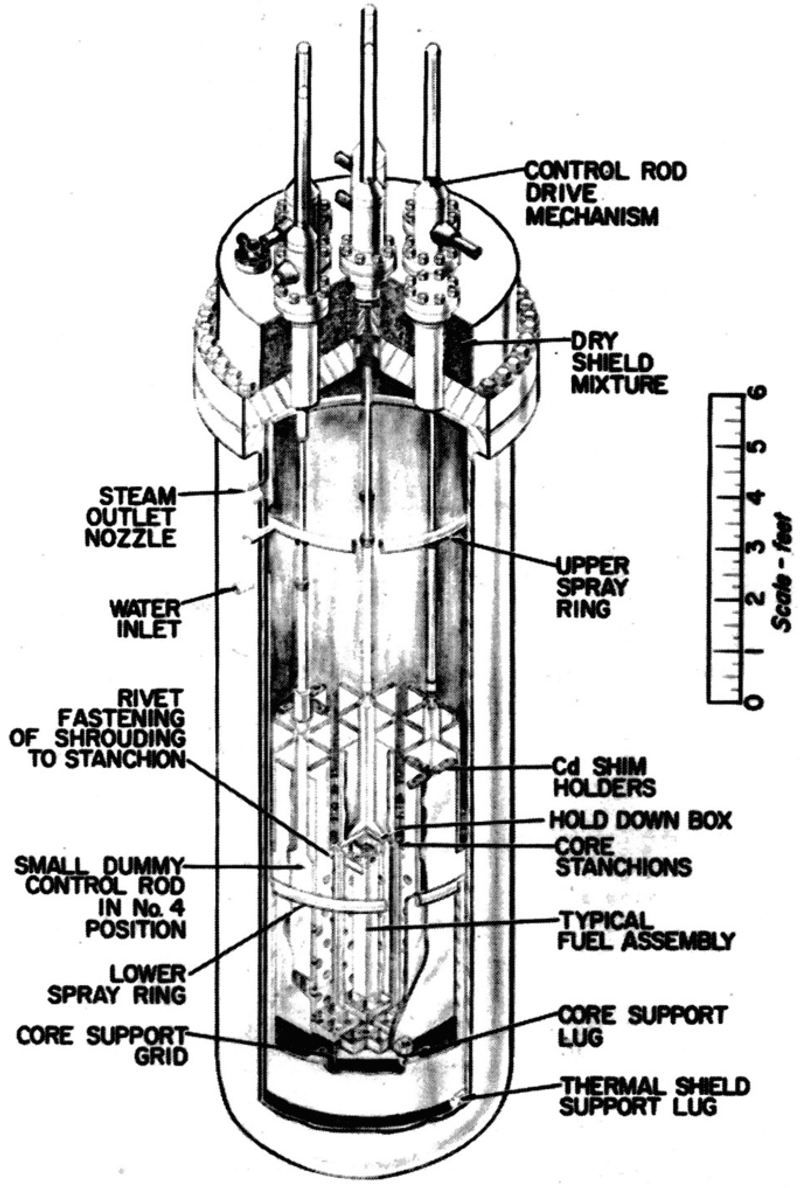
5. A Single Control Rod Caused the Explosion
During routine maintenance, a single control rod was accidentally withdrawn too far, triggering a prompt critical reaction in the SL-1 reactor. This seemingly minor error had catastrophic consequences.
The reactor’s design failed to prevent such an occurrence, revealing significant flaws in safety protocols. The explosive reaction was swift and devastating, leading to an immediate crisis.
This incident underscored the critical importance of meticulous engineering and fail-safes in nuclear design, ensuring that similar tragedies would not occur in the future.
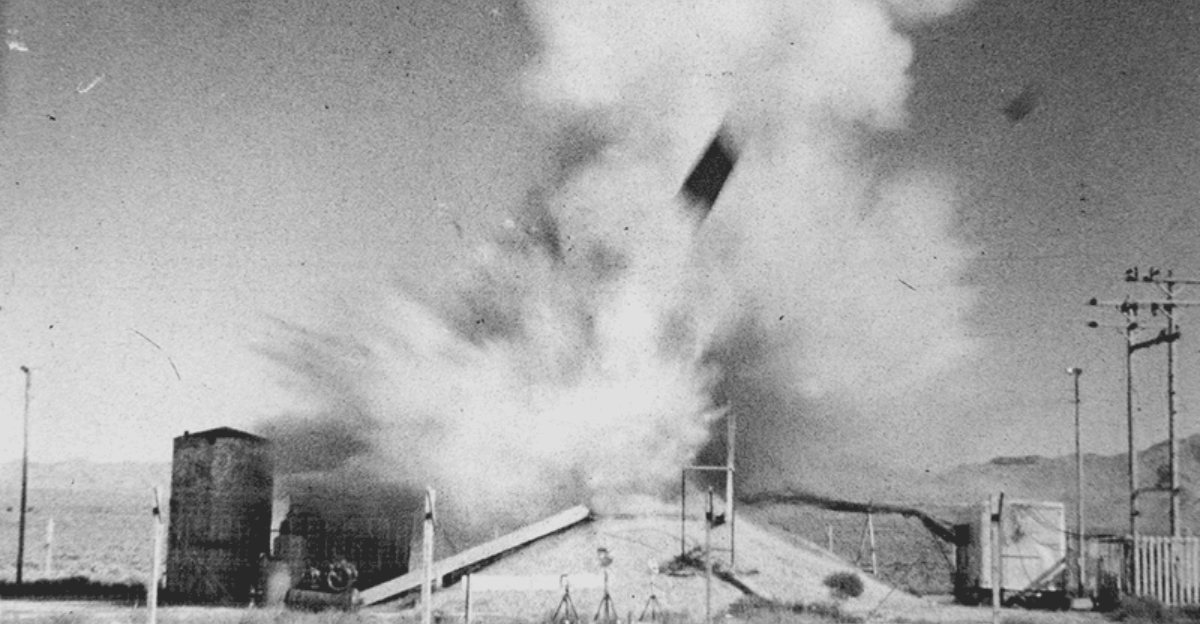
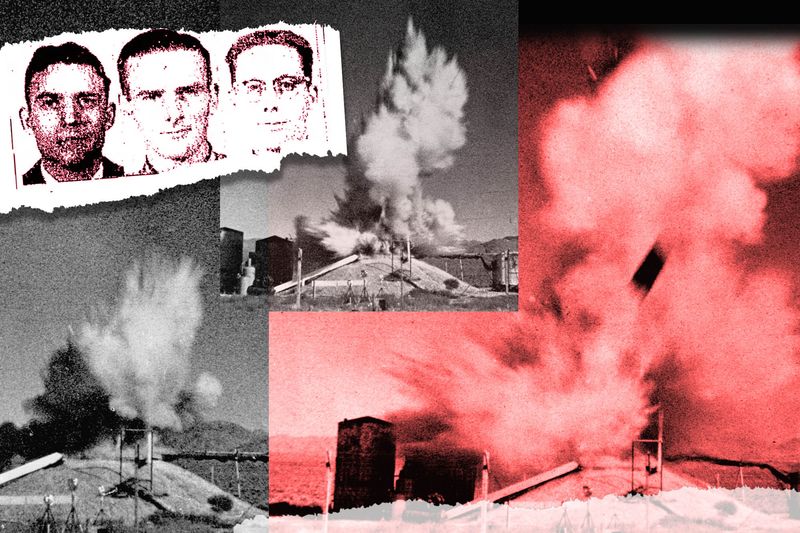
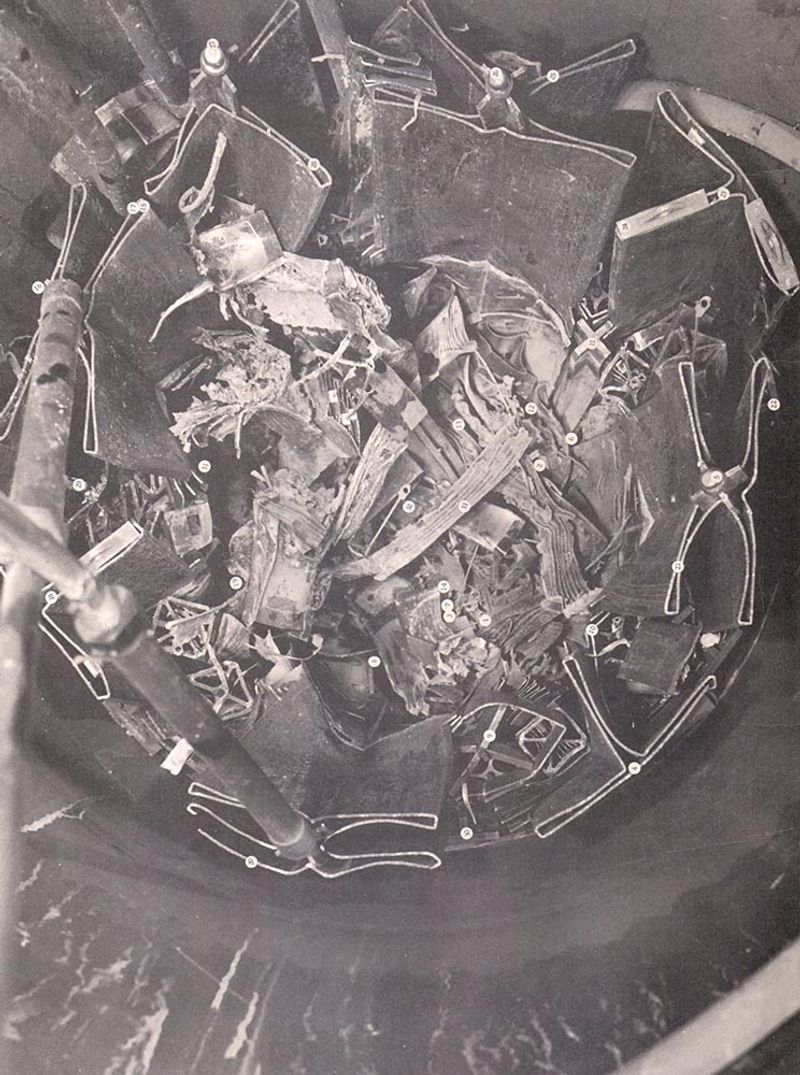
6. The Reactor Exploded in a Flash
In an instant, the SL-1 reactor experienced a violent steam explosion, propelling the 26,000-pound reactor vessel lid into the air. The force was so immense that it hurled Richard Legg’s body onto the ceiling.
This catastrophic explosion was both a physical and symbolic eruption, shaking the foundations of nuclear safety assumptions. The speed and ferocity of the event left no room for intervention.
The explosion’s aftermath demanded urgent action and highlighted the reactor’s vulnerabilities, driving changes in future reactor designs.
7. All Three Men Died—One Instantly
The explosion’s immediate impact was fatal for Richard Legg, who died instantly. Tragically, John Byrnes and Richard McKinley succumbed to their injuries and radiation exposure within hours.
This loss of life was a profound tragedy, resonating beyond the confines of the reactor building. The incident served as a grave reminder of the human stakes involved in nuclear operations.
Their sacrifice was not in vain, as it catalyzed significant advancements in reactor safety protocols and awareness.
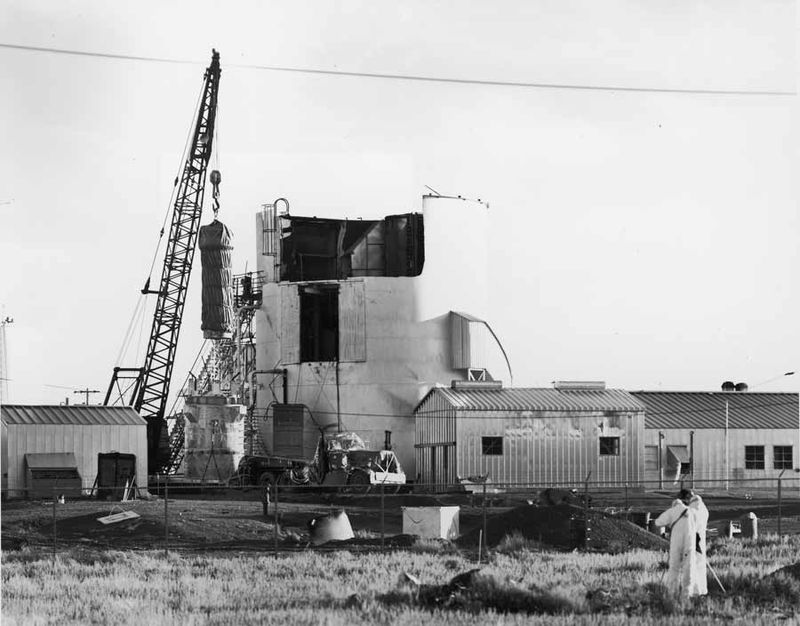
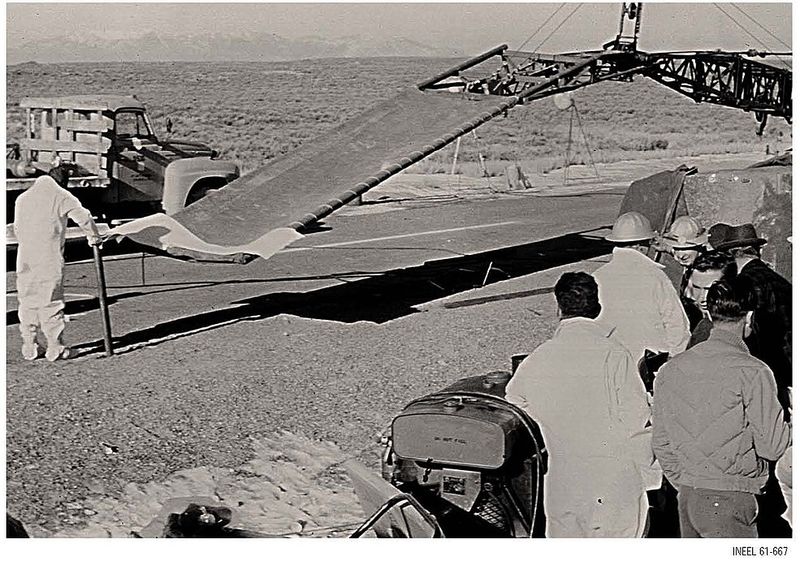
8. Recovery Took Weeks
The SL-1 reactor’s intense radiation levels necessitated an arduous recovery process that took nearly a week. Teams had to rely on remote-operated equipment and shielded gear to safely retrieve the bodies.
This painstaking process highlighted the complexities and dangers of handling nuclear disasters. Even with advanced technology, the task was fraught with risk, underscoring the need for improved emergency preparedness.
The prolonged recovery effort emphasized the challenges of managing nuclear incidents, shaping future response strategies.
9. Extremely High Radiation Levels
The reactor’s interior was so radioactive that even protective suits offered limited safety. During recovery, some rescuers received measurable doses, despite stringent precautions.
This alarming fact underscored the perilous nature of the SL-1 incident, shedding light on the invisible dangers of nuclear energy. The high radiation levels presented a formidable barrier to rescue and recovery efforts.
This aspect of the disaster drove home the urgency of enhancing protective measures and safety protocols in nuclear facilities.
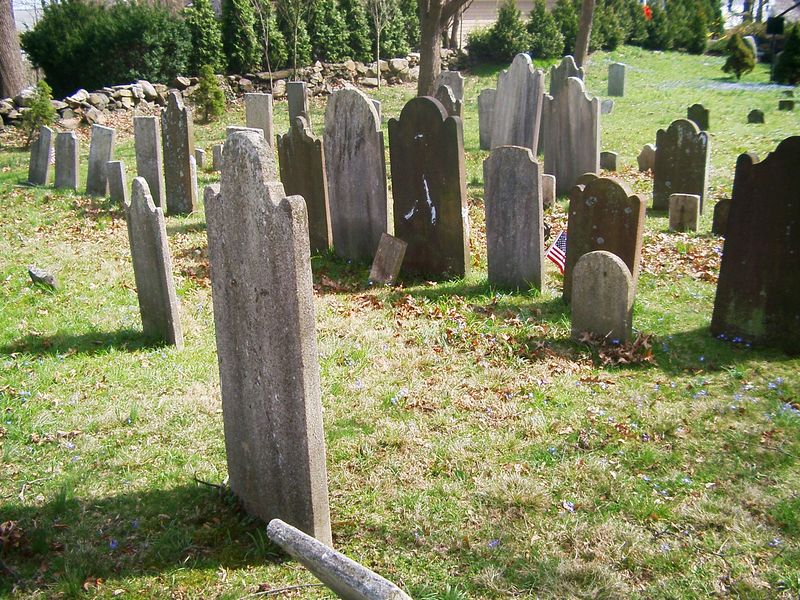
10. Victims Were Buried in Lead-Lined Caskets
To safely contain lingering radiation, the victims of the SL-1 disaster were interred in lead-lined caskets, subsequently sealed within concrete vaults. This extraordinary measure was necessary to prevent further contamination.
The decision reflected the gravity of the situation, highlighting both a deep respect for the deceased and an unwavering commitment to public safety. This practice of using specially designed caskets underscored the lasting impact of the incident.
It served as a poignant reminder of the invisible but persistent dangers posed by nuclear accidents.
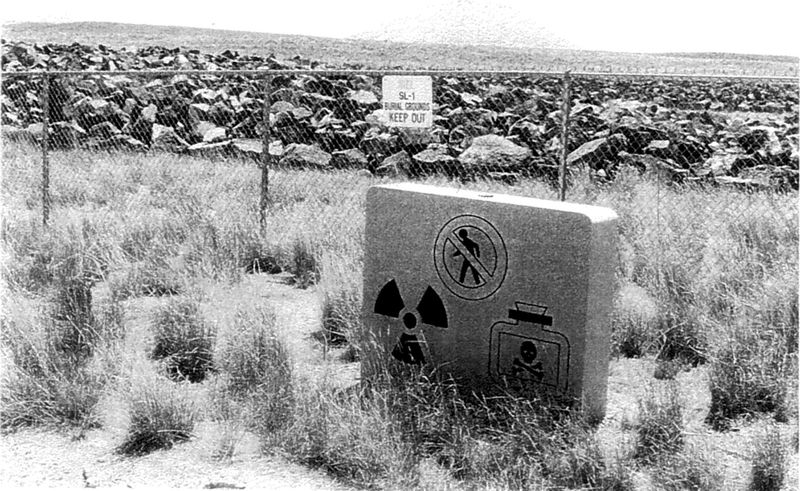
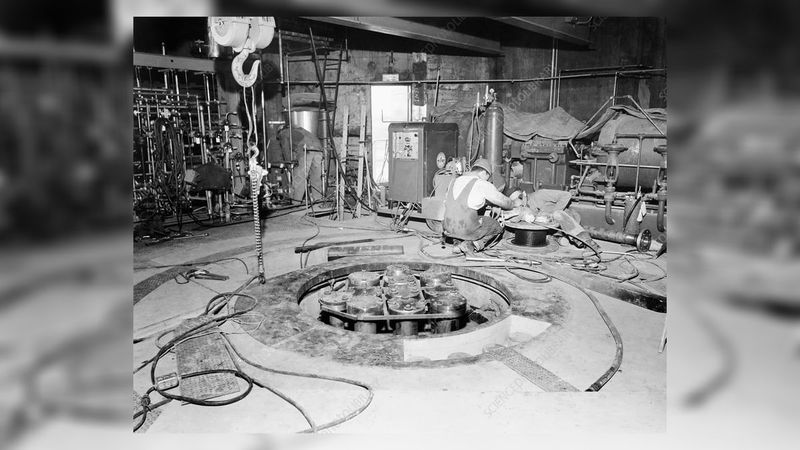
11. The Reactor Was Dismantled and Buried
Following the investigation, the SL-1 reactor was permanently shut down, dismantled, and buried near the site. This decisive action ensured the containment of any residual radiation and prevented future hazards.
The dismantling process was an engineering challenge, requiring meticulous planning and execution. It symbolized both the end of the SL-1 reactor’s operational life and a commitment to safety.
Burying the reactor served as a haunting reminder of the incident’s severity and the lessons learned in its wake.
12. Caused Major Design Overhauls
The SL-1 incident prompted a comprehensive reassessment of reactor safety design, particularly focusing on control rod systems and maintenance protocols. The disaster revealed critical vulnerabilities that needed urgent attention.
In response, the nuclear industry adopted more robust safety measures and technologies, minimizing the risk of similar accidents. These changes marked a turning point in nuclear engineering, prioritizing fail-safes and redundancies.
The lessons learned from SL-1 had far-reaching implications, reshaping the future of nuclear technology and safety.
13. Initial Reports Were Vague
In the aftermath of the SL-1 disaster, initial reports to the public described it merely as a “steam accident.” The full details only emerged gradually as investigations progressed.
This initial vagueness fueled speculation and uncertainty, reflecting both the sensitive nature of the incident and the challenges of communicating nuclear risks. The delay in transparency highlighted the need for clearer reporting.
As more information surfaced, public awareness and understanding of nuclear safety deepened, driving calls for reform.
14. It Sparked Cold War Fears
During the Cold War, nuclear incidents like SL-1 amplified fears about reactor safety and potential sabotage. This heightened tension reflected global anxieties over nuclear technology in a politically charged environment.
The SL-1 disaster became a focal point for discussions on nuclear security, both within the U.S. and internationally. The incident underscored vulnerabilities that could be exploited during conflicts.
It highlighted the dual challenges of advancing nuclear technology while ensuring robust security measures against potential threats.
15. Speculation About Intentional Sabotage
Rumors circulated that the rod withdrawal might have been intentional, possibly a suicide act. However, no conclusive evidence ever supported this theory.
The speculation added an element of mystery to the already complex disaster, prompting thorough investigations into the motives and circumstances surrounding the incident.
While no definitive answers were found, the theories highlighted the psychological and human factors in nuclear operations, driving further scrutiny into personnel safety and mental health.
16. The First Nuclear Fatalities in the U.S.
The SL-1 disaster marked the first instance of fatalities directly caused by a nuclear reactor malfunction in the United States. This grim milestone underscored the potential human cost of nuclear energy.
The incident served as a wake-up call for the industry, emphasizing the need for enhanced safety standards and protocols. It was a somber reminder of the responsibilities inherent in harnessing nuclear power.
The lessons from SL-1 influenced future policies, ensuring that the memory of those lost would drive continuous safety improvements.
17. One Body Was Too Radioactive for Embalming
Richard Legg’s remains were so contaminated by radiation that traditional embalming methods were impossible. This presented a unique and tragic complication in the aftermath of the disaster.
Special protocols were required to manage his remains safely, highlighting the extreme conditions faced by those involved in the recovery. This aspect of the incident shed light on the far-reaching implications of nuclear accidents.
The incident demanded a reevaluation of safety procedures, influencing how future nuclear disasters would be managed.
18. The Event Remains Classified in Detail
Many aspects of the SL-1 incident remain shrouded in secrecy, with documents still partially redacted or restricted. This continued classification reflects the sensitive nature of nuclear technology and security concerns.
The partial disclosure has fueled interest and speculation about the full story, prompting ongoing debates about transparency and the public’s right to know.
The classified status underscores the complexity of balancing security with openness in the nuclear industry, a challenge that persists today.
19. It’s Still Taught in Nuclear Safety Courses
The SL-1 accident serves as a pivotal case study in nuclear safety training programs around the world. Its lessons continue to inform engineers and reactor technicians, underscoring the importance of rigorous safety standards.
By analyzing the incident’s causes and effects, students gain insights into the complexities of nuclear operations and the continuous need for vigilance.
The event’s educational value lies in its ability to convey real-world consequences and drive home the critical nature of safety in nuclear facilities.
20. A Quiet Memorial Exists at the Site
Near the original location of the SL-1 reactor, a modest memorial stands, honoring the three men who lost their lives. This quiet tribute offers a place for reflection and remembrance, though the site remains off-limits to the public.
The memorial’s simplicity belies the profound impact of the disaster, serving as a poignant reminder of the human cost of technological advancement.
While largely unknown to the general public, this site holds significant meaning for those connected to the nuclear industry and its history.
21. One of the Least Known Yet Most Fatal U.S. Incidents
Despite its severity, the SL-1 tragedy is seldom mentioned alongside more infamous incidents like Chernobyl or Three Mile Island. Its relative obscurity contrasts with its deadly impact and contribution to nuclear safety reforms.
The incident’s limited public recognition belies its significance in shaping industry standards and protocols. It remains a crucial chapter in the history of nuclear energy.
Acknowledging SL-1’s legacy ensures that its lessons continue to influence safety measures, preventing future tragedies.
22. Prompted Improved Reactor Design for Military Use
The SL-1 disaster spurred advancements in nuclear reactor design, particularly for military applications. Future designs shifted from manually controlled rod systems to automated, fail-safe technologies.
These innovations aimed to enhance safety and efficiency, reducing the likelihood of human error and ensuring more secure operations in military settings. The incident highlighted the need for robust, reliable systems.
The changes marked a significant evolution in nuclear technology, driven by the lessons learned from SL-1, aiming for safer, more efficient applications.
23. It Changed the Public Perception of Nuclear Power
The SL-1 incident, though not widely publicized at the time, cast early doubts about the safety of nuclear energy, especially in military contexts. It contributed to growing public apprehension about the risks associated with nuclear technology.
This shift in perception influenced both policy and public discourse, leading to increased scrutiny and demand for transparency in the nuclear industry.
The incident highlighted the delicate balance between technological advancement and public safety, a debate that continues to this day.