Japan’s ancient human fossils offer a fascinating glimpse into the history of human evolution. These remnants, discovered across various locations in the country, have provided crucial insights into the lives and cultures of early humans.
By examining these fossils, researchers have been able to piece together the story of migration, adaptation, and survival.
This blog post will explore nine significant discoveries, each shedding light on different aspects of our past and illustrating how these findings contribute to our understanding of human history.
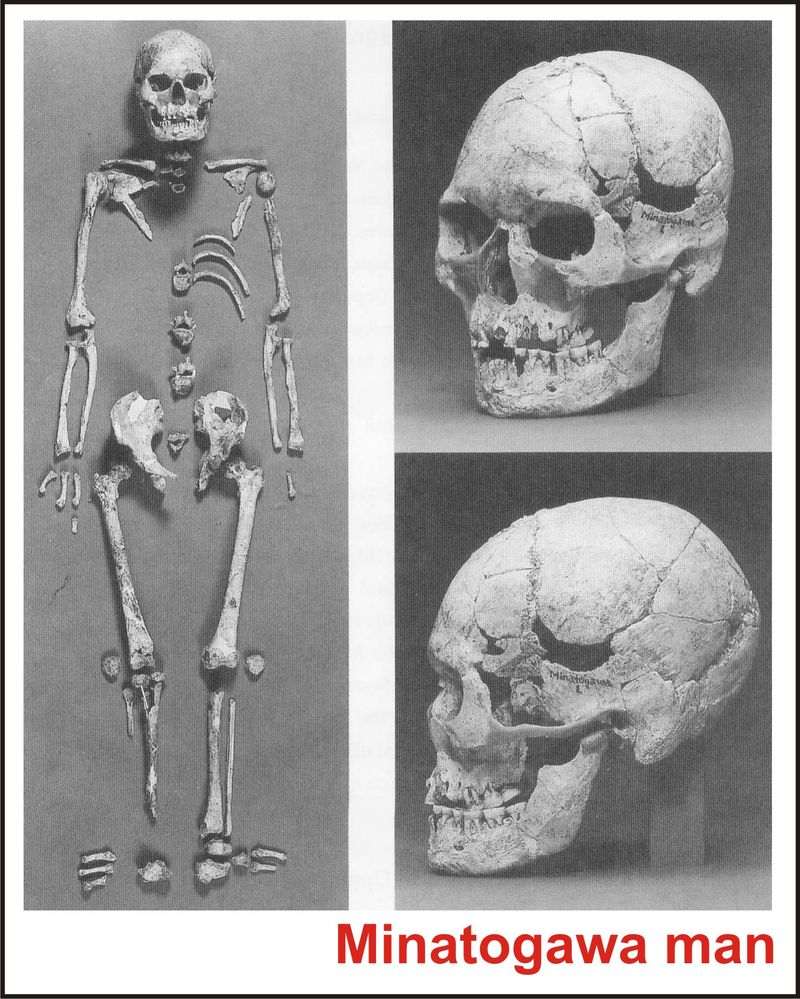
1. The Minatogawa Man
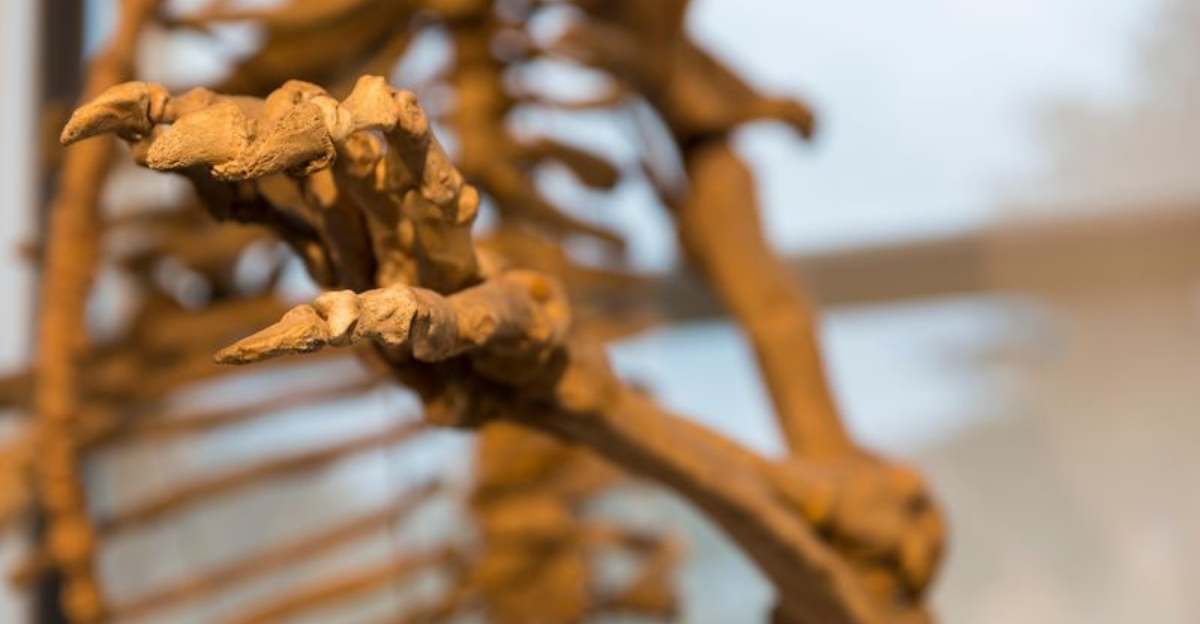
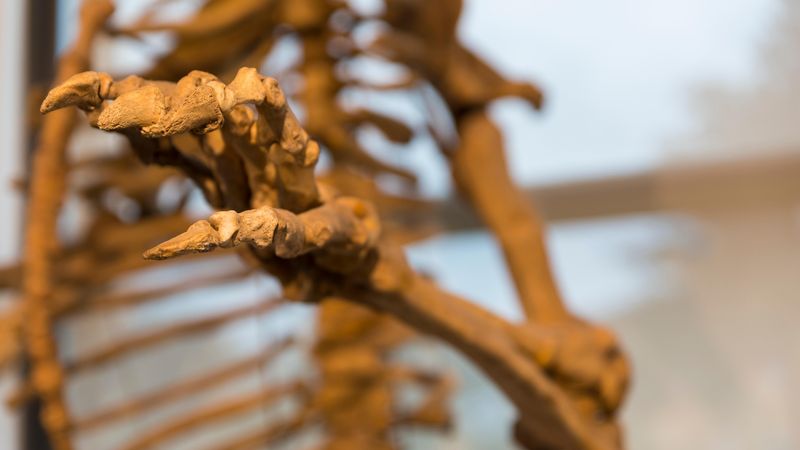
The Minatogawa Man, discovered in Okinawa, dates back approximately 18,000 years. This fossil provides evidence of early human presence in Japan, showcasing unique skeletal features. Researchers have studied these bones to understand the diet, lifestyle, and physical characteristics of these ancient people.
The Minatogawa Man’s skeletal structure has revealed adaptations to the environment, offering clues about the challenges faced by early humans. These findings are vital for understanding human migration patterns.
Such discoveries not only illuminate the past but also help unravel the complex history of human evolution in the Japanese archipelago.
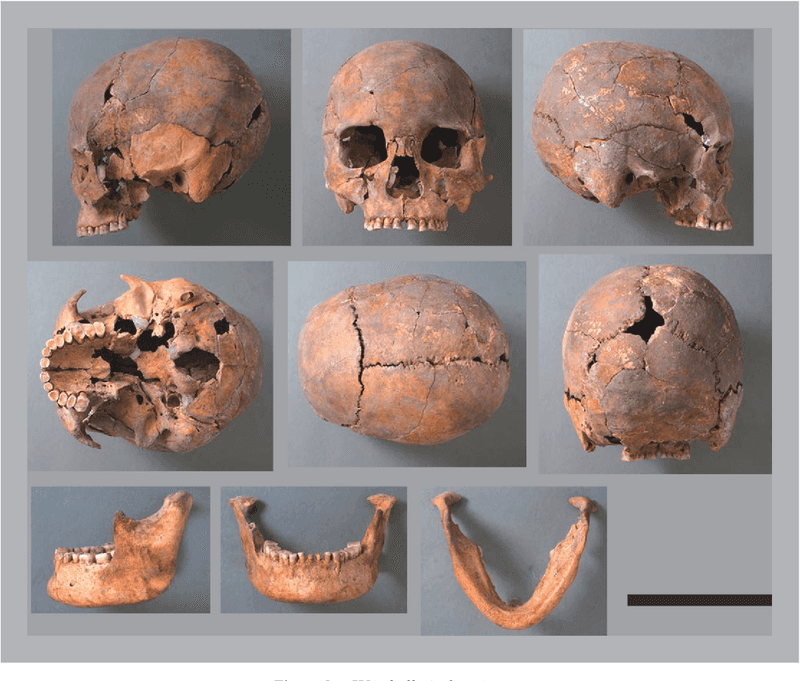
2. Jomon Period Skulls
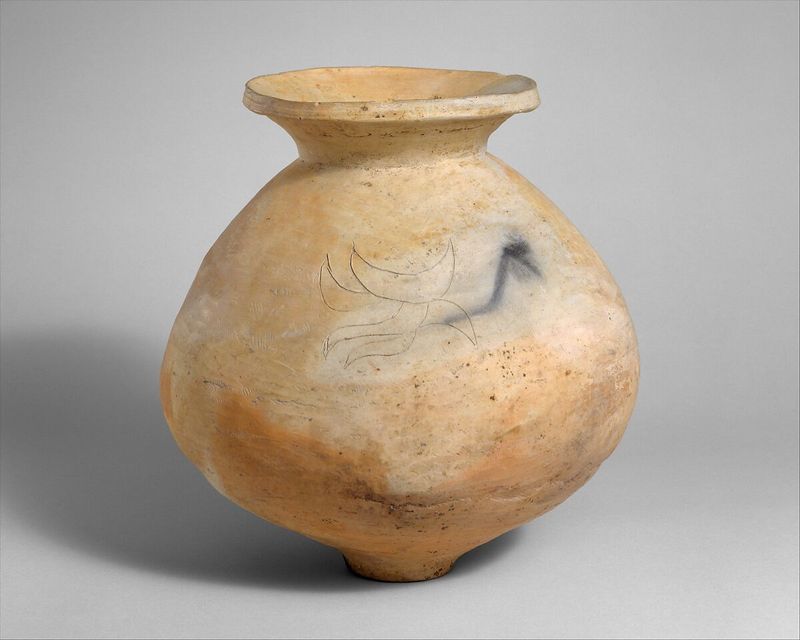
The Jomon period, known for its pottery, also bears significant fossil discoveries. Skulls from this era reveal distinct cranial features, hinting at diverse ancestral lines.
These ancient remains help paint a picture of life over 10,000 years ago, illustrating the advanced culture that thrived in Japan. The Jomon people’s skulls have been a subject of extensive study, providing clues about their diet, health, and social structures.
Understanding these aspects offers a glimpse into how these early inhabitants adapted to their environment and developed complex societies.
3. Yayoi Period Remains
The Yayoi period marks a significant transition in ancient Japan, characterized by shifts in agriculture and lifestyle. Fossils from this time show a blend of features from various Asian populations.
These remains reflect the migration and interaction of different groups, contributing to the cultural tapestry of ancient Japan. By analyzing these bones, researchers gain insights into the social and technological advancements during this era.
The Yayoi period’s human remnants are crucial for understanding the evolution of complex societies in Japan, highlighting the influence of continental cultures.
4. The Edo Period Burial Site
Uncovering human remains from the Edo period offers a unique window into more recent history. These sites reveal burial practices and provide insights into Japanese societal norms and cultural influences at the time.
The well-preserved remains allow researchers to study the health, diet, and lifestyle of people from this period. Such findings illustrate the evolution of burial customs over time.
By examining these burial sites, historians and archaeologists gain a deeper understanding of cultural transitions in Japan’s historical timeline.
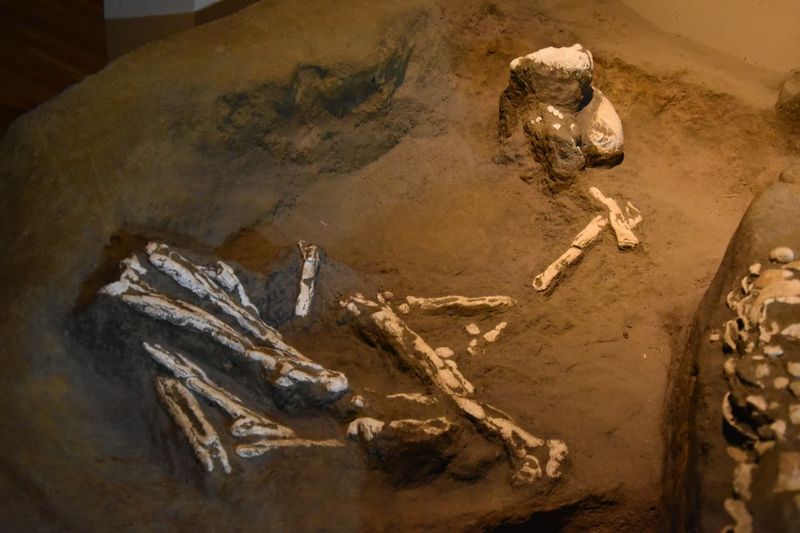
5. Hakodate’s Ancient Cemetery
In Hakodate, an ancient cemetery reveals well-preserved skeletons that provide a glimpse into past societies. These findings have been instrumental in understanding regional variations in burial customs.
The artifacts found alongside the human remains tell stories of daily life, trade, and cultural influences. By studying these elements, researchers can piece together the lifestyle and interactions of those who once lived there.
Such discoveries contribute to a broader understanding of Japan’s diverse historical landscape and the evolution of its cultural practices.
6. Ryukyu Islands’ Fossil Discoveries
The Ryukyu Islands have yielded fascinating fossil discoveries, shedding light on early seafaring and isolated communities. These fossils suggest a unique adaptation to island life.
The remains indicate a distinct lineage, offering clues about the genetic diversity and migration patterns in the region. This isolation allowed for unique cultural and biological developments.
Studying these ancient fossils helps unravel the complex history of human settlement in the islands and their interactions with neighboring regions.
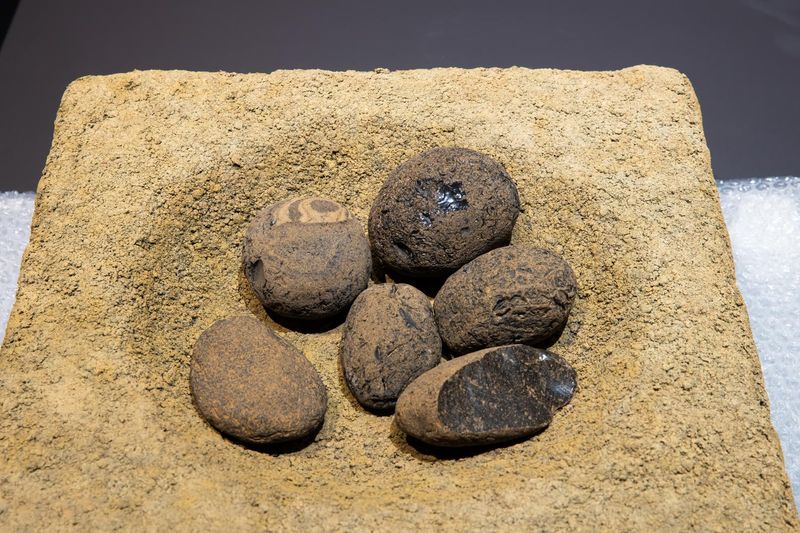
7. The Takaido Shell Midden
The Takaido shell midden is a treasure trove of information about early coastal communities in Japan. Human remains found here provide insights into the diet and lifestyle of these ancient people.
The abundance of shells and tools offers clues about the economic activities and environmental adaptations of the time. By analyzing these remains, archaeologists can understand the relationship between humans and their coastal environment.
These discoveries highlight the importance of marine resources in shaping early human societies in Japan.
8. Fukui Cave Fossils
Fukui Cave is a significant archaeological site where fossilized human remains have been discovered alongside stone tools. These findings shed light on the ancient habitation of the area.
The cave’s fossils provide evidence of early human ingenuity and adaptation to challenging environments. Researchers study these remains to understand the social and technological achievements of the time.
Such discoveries offer a window into the resilience and innovation of early humans, enriching our understanding of prehistoric life in Japan.
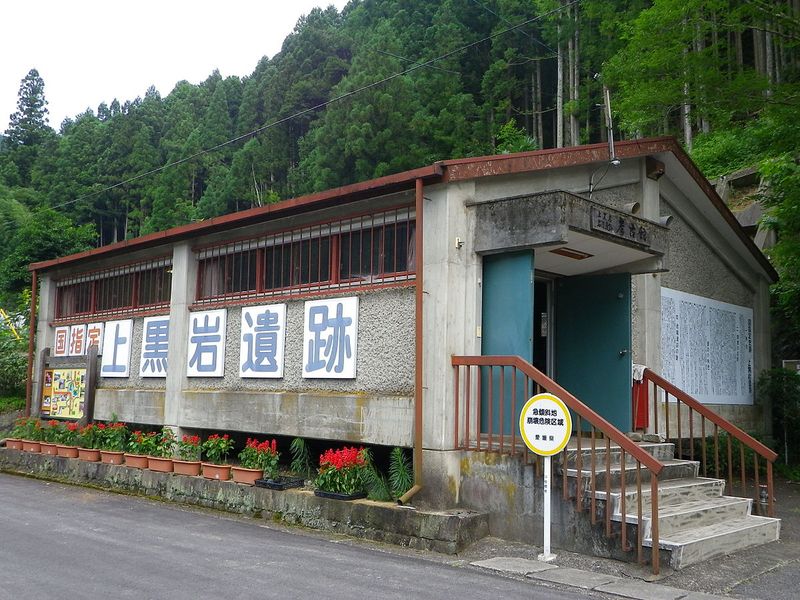
9. Kamikuroiwa Rock Shelter
The Kamikuroiwa Rock Shelter is an archaeological gem, revealing human remains and cultural artifacts. These findings offer insights into the prehistoric communities that once thrived there.
The artifacts and bones unearthed provide a glimpse into the daily lives, rituals, and survival strategies of these early inhabitants. By studying them, researchers can trace the evolution of human culture in the region.
This site enriches our understanding of the dynamic history of human settlement and cultural development in Japan.