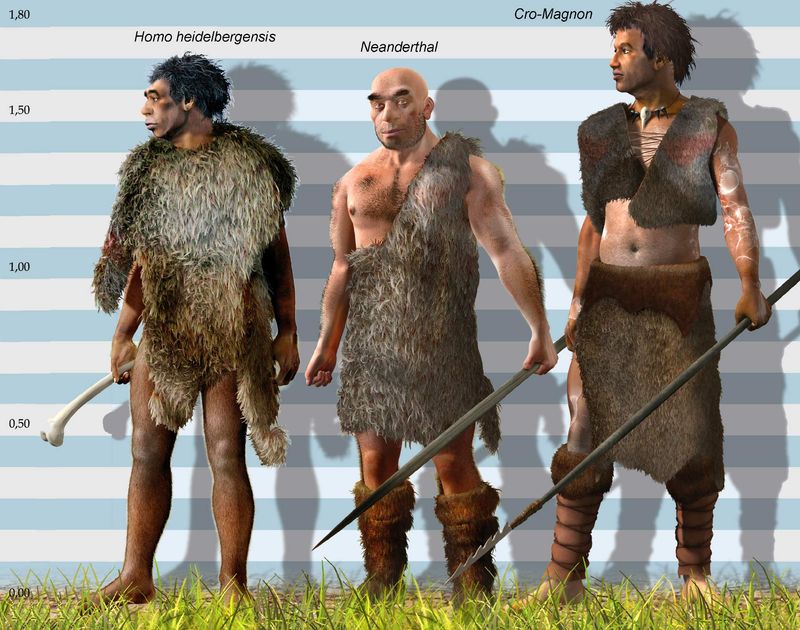
Cro-Magnon people, known as one of the earliest anatomically modern humans in Europe, date back around 40,000 years.
These early humans are fascinating for their innovative contributions to human civilization, from their migration patterns to their artistic expressions and social structures.
1. Early Modern Humans
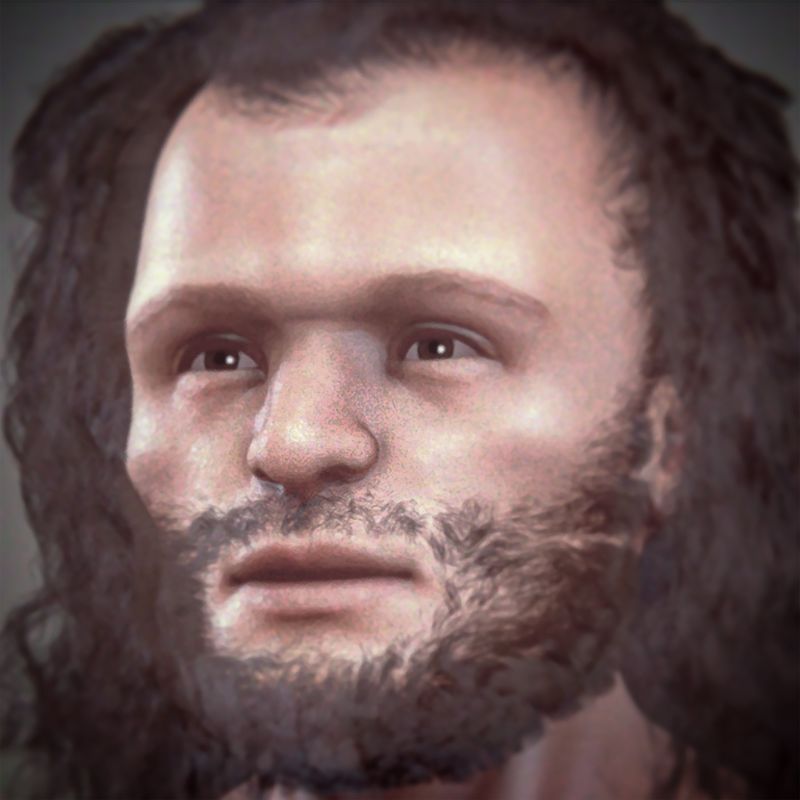
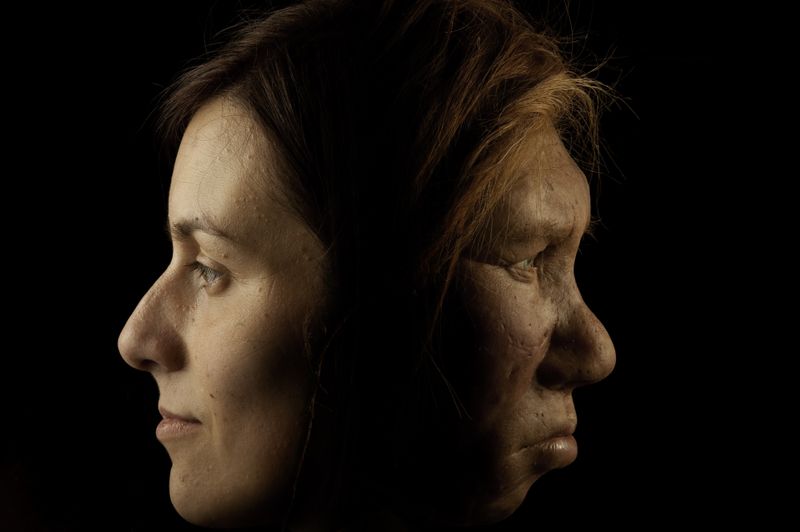
Cro-Magnons, among the first anatomically modern humans in Europe, roamed the continent around 40,000 years ago. Their skeletal remains reveal a robust build and a tall stature, indicative of their capability to endure harsh climates. With pronounced features similar to present-day humans, they marked a significant evolutionary leap. Living during the Upper Paleolithic period, their presence reshaped the interaction between species, notably with Neanderthals. Cro-Magnons’ lifestyle and cultural advancements offer insights into early human development, mirroring the dawn of modern human societies with sophisticated social structures and tools.
2. Origin and Migration
Cro-Magnons originated in Africa and embarked on a remarkable journey to Europe, a migration that spanned thousands of years. Their path was fraught with challenges, traversing diverse terrains and climates. This migration marked their encounter with Neanderthals, leading to either their replacement or interbreeding. Their ability to adapt and integrate into new environments was pivotal, showcasing their resilience. This trek was not merely a physical journey but a transformative phase that shaped their cultural and genetic legacy in Europe. Understanding their migration offers insights into humanity’s adaptability and interconnected history.
3. Advanced Tools and Weapons
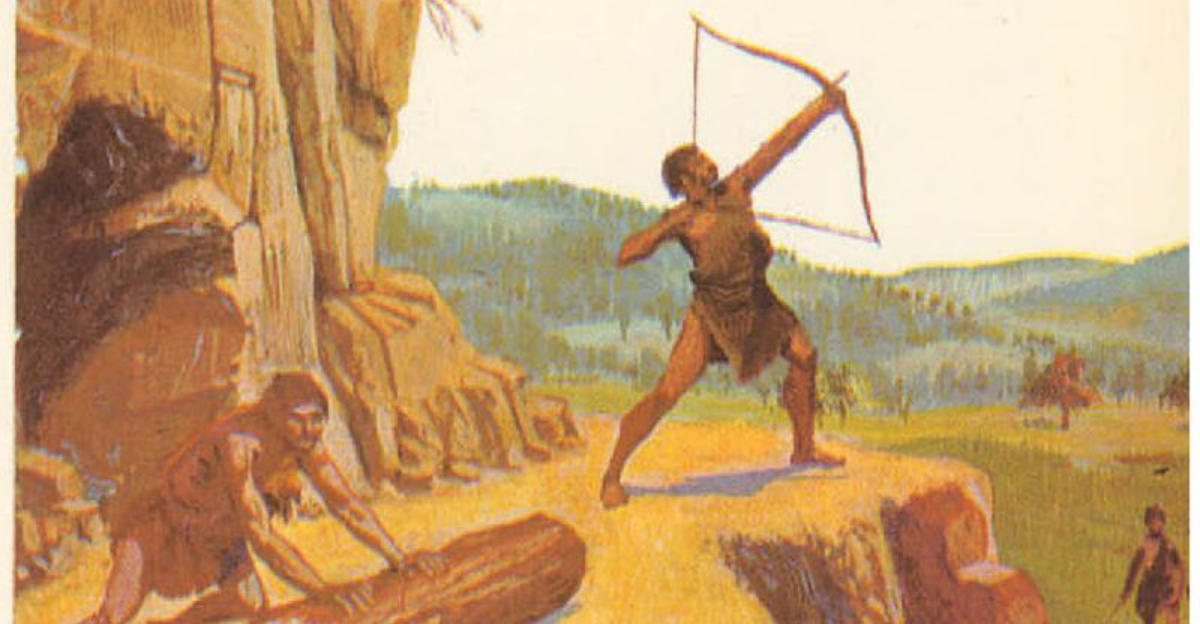
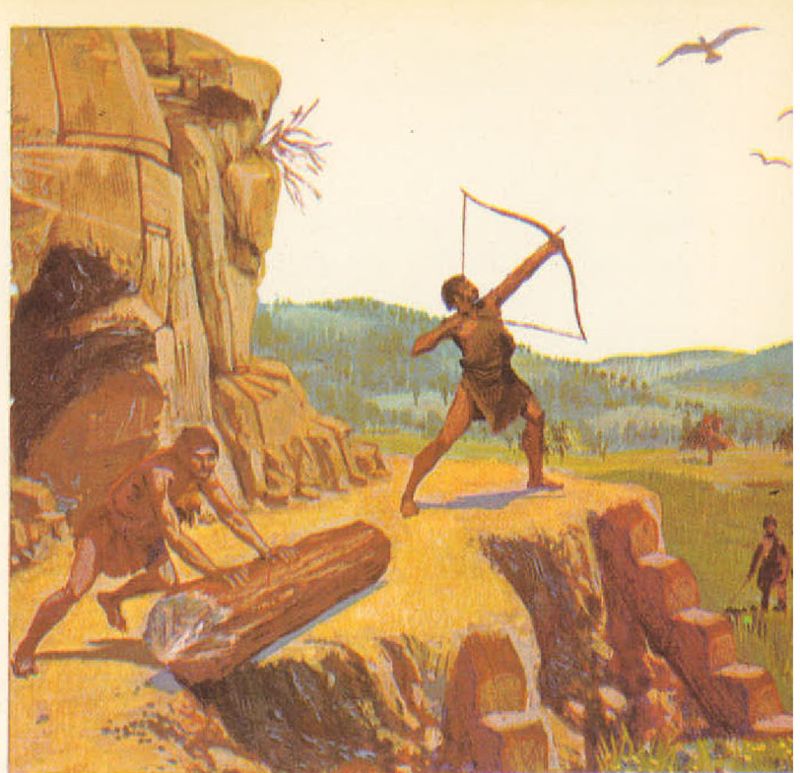
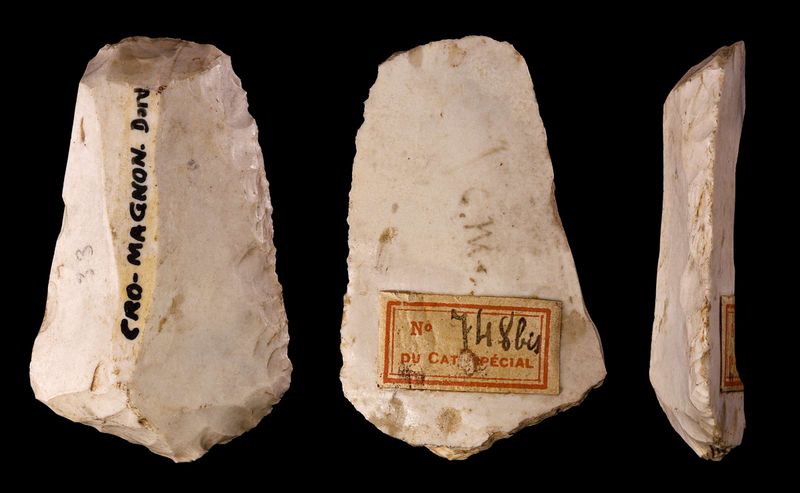
The Cro-Magnons were pioneers in crafting advanced tools and weapons, a testament to their ingenuity. They utilized materials like stone, bone, and antler to fashion items such as spears, harpoons, and sewing needles. These tools were not only functional but also aesthetically designed, reflecting their creators’ artistic sensibilities. The precision in crafting these items demonstrates their advanced cognitive abilities. Such advancements enabled Cro-Magnons to hunt effectively, make clothing, and build shelters, ensuring their survival in diverse environments. Their legacy in tool-making laid the foundation for subsequent technological innovations.
4. Artistic and Cultural Development
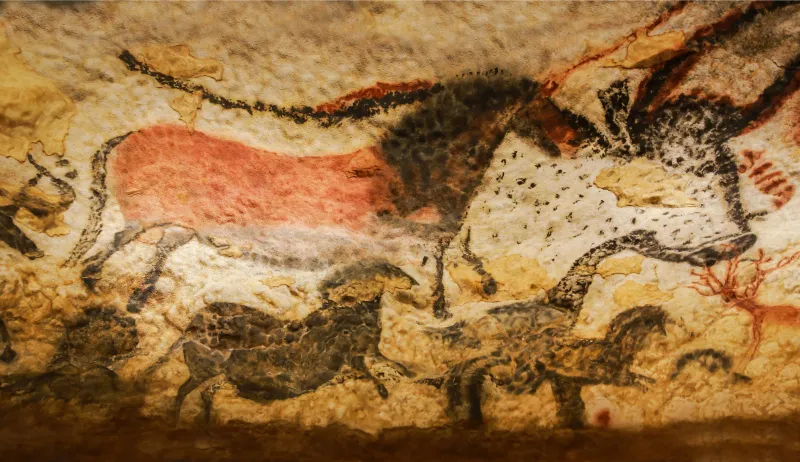
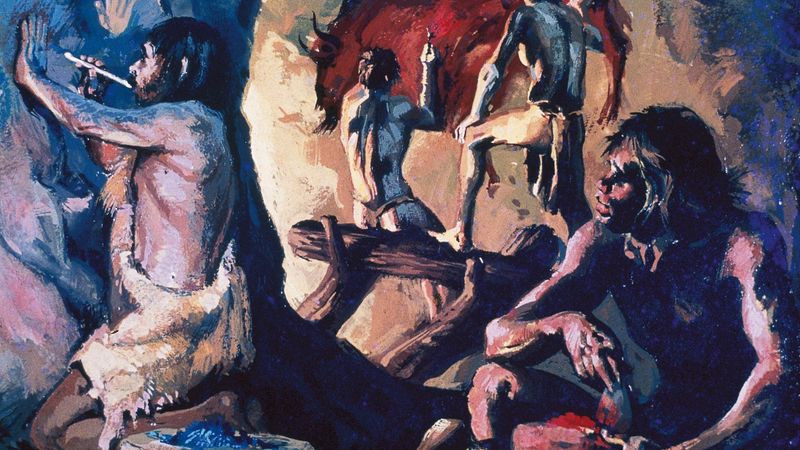
Cro-Magnons left an indelible mark on history with their artistic and cultural achievements. Their most famous works include the Lascaux Cave paintings in France, showcasing vivid depictions of animals and human figures. These artworks reveal their appreciation for beauty and understanding of their environment. Beyond paintings, they carved sculptures and crafted intricate jewelry, indicating a complex cultural identity. These artistic expressions were not merely decorative; they served as communication tools, conveying stories and beliefs. The cultural richness of Cro-Magnons highlighted their role as early arbiters of human creativity and expression.
5. Skilled Hunters and Gatherers
The Cro-Magnons excelled as hunters and gatherers, a skill crucial for their survival. Their diet included large game like mammoths, reindeer, and bison, supplemented by plants and fish. Their hunting techniques were sophisticated, involving coordinated group efforts and strategic planning. These skills ensured a steady food supply and contributed to their robust health. Gathering provided essential nutrients, and their knowledge of flora was comprehensive. Cro-Magnons’ ability to adapt their diet to available resources was a testament to their ingenuity and understanding of their environment.
6. Social and Family Structures
Cro-Magnons lived in small, organized groups, indicative of their social complexity. These groups were likely structured around strong family bonds, with a clear division of labor. Men and women had distinct but complementary roles, maximizing efficiency and survival. Children were integral to society, learning essential skills for future roles. Such social structures fostered cooperation and innovation, key to their thriving existence. Their ability to form complex relationships and communities paved the way for the development of modern social systems, highlighting the enduring adaptability of human societies.
7. Use of Fire and Shelters
Fire played a crucial role in Cro-Magnon life, providing warmth, protection, and a means to cook food. They constructed shelters using materials like bones and animal hides, showcasing their resourcefulness. These shelters were strategically built to withstand harsh weather, reflecting their survival acumen. Fire not only offered practical benefits but also held social significance, being a focal point for gatherings. The combination of fire and shelter marked a significant technological advancement, crucial for surviving in the Ice Age. Their innovations in living conditions were precursors to modern architectural and social practices.
8. Linguistic Abilities
While no direct evidence exists of Cro-Magnon language, their complex society implies sophisticated communication methods. The social structures and cultural richness suggest spoken language was likely a part of their daily interactions. Language would have facilitated cooperation in hunting, sharing knowledge, and cultural continuity. It also likely played a role in storytelling and passing down traditions. Understanding Cro-Magnon linguistic capabilities helps in appreciating the evolution of communication. Their potential language skills highlight the cognitive advancement of early humans, laying groundwork for future linguistic development in human societies.
9. Survival During the Ice Age
Adapting to the harsh conditions of the Ice Age was a testament to Cro-Magnons’ resilience. They developed advanced clothing from animal hides, providing essential warmth. Their shelters were strategically designed to offer protection against extreme weather, ensuring their survival. Hunting techniques evolved to meet the challenges posed by the icy terrain. These adaptations were crucial in maintaining their way of life during a period of climatic uncertainty. The Cro-Magnons’ ability to thrive in such conditions underscores their innovative spirit, marking them as pioneers of human adaptation and evolution.
10. Legacy and Connection to Modern Humans
Cro-Magnons are recognized as direct ancestors of modern Europeans, playing a crucial role in human evolution. Their genetic legacy is evident in contemporary populations, linking past and present. Their advancements in tools, art, and social organization laid foundations for future civilizations. The knowledge and cultural heritage passed down through generations continue to influence modern societies. The connection between Cro-Magnons and today’s humans highlights a shared evolutionary journey. Understanding their legacy provides valuable insights into human history, illustrating the continuity and progression of human development over millennia.